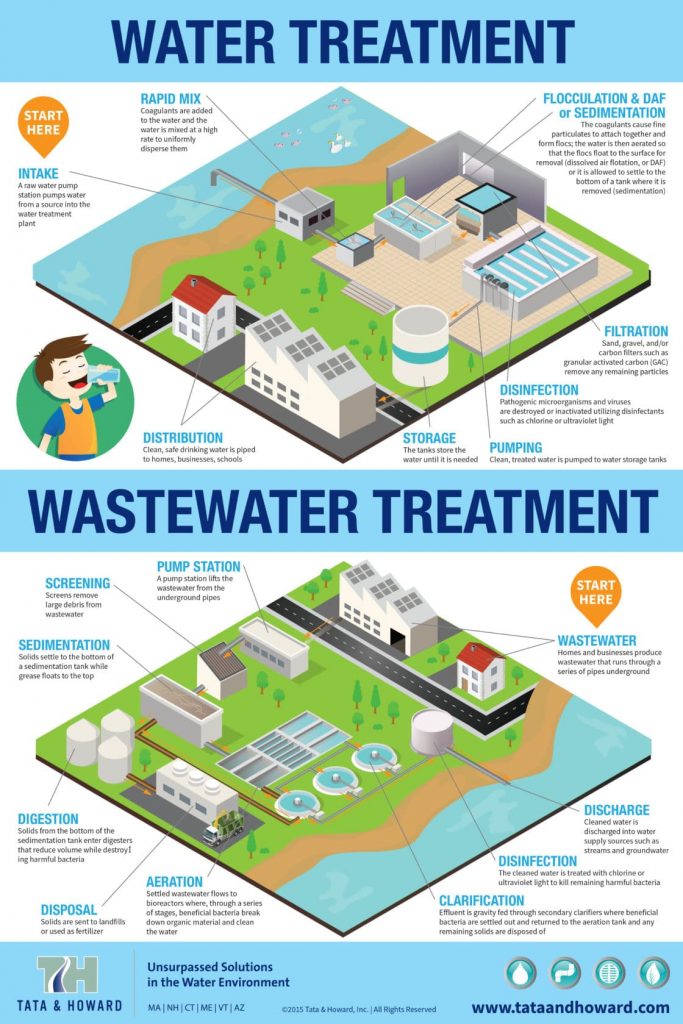
A common problem facing municipal water systems today is the need to maintain safe water supplies in the midst of increasing demand, limited supply, crumbling infrastructure, decreasing budgets, dwindling governmental funding, and more stringent regulations. Never before have municipal suppliers been faced with such a daunting task, and utilities are scrambling to find ways to make ends meet. And while there are technologies today that are more efficient than the decades-old systems still in use at many facilities, most utilities simply do not have the resources to upgrade in light of limited local, state, and federal funding and budgetary constraints.
Fortunately, there are many steps that municipal water systems can take to increase efficiency without having to upgrade entire facilities and piping systems. Implementing a few comparatively inexpensive initiatives can save utilities significant, much-needed funds that can be used for future upgrades required for regulatory compliance.
Business Practice Evaluations

Very often, operational procedures of municipal water systems are overshadowed by the need to provide safe, clean drinking water to the public, and understandably so — the dedication that water utilities show to their customers is commendable. However, the fact remains that operational procedures typically have the potential for drastic improvement, resulting in reduced operational expenses and smoother utility management.
One way to address operational inefficiencies is with a Business Practice Evaluation (BPE), which assesses the health of a utility’s work practices by implementing a framework for a structured approach to managing, operating, and maintaining in a more business-like manner. In other words, approaching a municipal water supply as a for-profit business rather than as a public supplier results in better operational and managerial procedures, and an improved bottom line.

The overall goal of the assessment process is more efficient and effective work practices, and the assessment includes documentation of current business practices, identification of opportunities for improvement, conducting interviews including a diagonal slice of the organization, and observation of work practices in the field.
This assessment provides a birds-eye view of the utility along with objective recommendations to improve system performance. As no two utilities are alike, the structured approach is fully customized and includes all functions of the utility — from administration and technical to operations and maintenance. The result is an organized, systematic plan and timeline to optimize the overall utility by implementing specific steps including developing rating criteria to determine level of performance of work practices; conducting kick-off, consensus, and findings workshops; reviewing utility documents and documentation of work practices; conducting interviews with employees; and observing field operations of current work practices.
Organizations that have conducted a BPE significantly improve the operational efficiency of their utility, and the evaluation typically pays for itself in well under a year.
Non-Revenue Water and Water Audits
 Besides improving operational efficiency, utilities of today need to find ways to reduce non-revenue water. Non-revenue water is water that has been pumped but is lost before it ever reaches the customer, either through real — or physical — losses such as leaks, or through apparent losses such as theft or meter inaccuracy. Globally, water utilities lose 34% of their supply to non-revenue water, and in the United States, that number is about 20%, with 75% of that loss being easily recoverable. Because non-revenue water is both detrimental to the financial health of a utility as well as our nation’s limited water resources, the AWWA recommends that utilities conduct annual water audits using M36: Water Audits and Loss Control methodology to accurately account for real and apparent losses.
Besides improving operational efficiency, utilities of today need to find ways to reduce non-revenue water. Non-revenue water is water that has been pumped but is lost before it ever reaches the customer, either through real — or physical — losses such as leaks, or through apparent losses such as theft or meter inaccuracy. Globally, water utilities lose 34% of their supply to non-revenue water, and in the United States, that number is about 20%, with 75% of that loss being easily recoverable. Because non-revenue water is both detrimental to the financial health of a utility as well as our nation’s limited water resources, the AWWA recommends that utilities conduct annual water audits using M36: Water Audits and Loss Control methodology to accurately account for real and apparent losses.
Tata & Howard Vice President Steve Rupar, P.E., served as co-chair of the South Central Connecticut Regional Water Authority (RWA) Non-Revenue Water Goal Team, which completed the first water audit of the RWA system based on the AWWA M36 third edition methodology in 2010. Recently, Mr. Rupar was part of the AWWA Water Loss Control Committee and in charge of writing two new chapters on apparent loss control for the 4th edition update to AWWA M36.
A water audit can help water systems identify the causes and true costs of water loss, and develop strategies to reduce water loss and recapture lost revenue. In the northeast, drinking water infrastructure is typically several decades old, sometimes over a century, and deteriorating distribution systems can be a significant source of water loss through leakage. In addition, policies and procedures that lead to inaccurate accounting of water use along with customer metering inaccuracies also contribute to NRW. Of the estimated $200 billion that the United States will need to spend over the next 20 years to upgrade water distribution systems, almost half of that is needed for water loss control.
 Water audits are often the most cost-effective and efficient solution to increasing demand. And like BPEs, the cost of a water audit is typically recovered in under a year. Effective water loss control programs significantly reduce the need for costly facility upgrades, and the recovered water can be sold to consumers, generating desperately needed revenue while meeting water demands. Another benefit of a water loss control program is the reduction of entry points for disease-causing pathogens, resulting in increased public health.
Water audits are often the most cost-effective and efficient solution to increasing demand. And like BPEs, the cost of a water audit is typically recovered in under a year. Effective water loss control programs significantly reduce the need for costly facility upgrades, and the recovered water can be sold to consumers, generating desperately needed revenue while meeting water demands. Another benefit of a water loss control program is the reduction of entry points for disease-causing pathogens, resulting in increased public health.
In Conclusion
Municipal water systems of today face a number of significant challenges including water quantity and quality concerns, aging infrastructure, population growth, increased regulatory requirements, climate change, and depleted resources. In order for water systems to remain profitable, and therefore functional, they must implement efficiencies that will increase revenue and decrease water loss, all with the least capital expenditure possible. Both BPEs and water audits are inexpensive ways to improve efficiency and to realize a return on investment in less than one year, saving limited funds for future upgrades and expansions.