About the System
The water distribution system in the City of Newton, MA (City) serves approximately 90,000 people and includes 319 miles of water main ranging from 2-inches up to 30-inches. There is a southern pressure zone, a northern pressure zone, and three additional high service areas. All water is supplied by Massachusetts Water Resources Authority (MWRA) and the system utilizes two tanks, the Waban Hill Reservoir and the Oak Hill Tank.

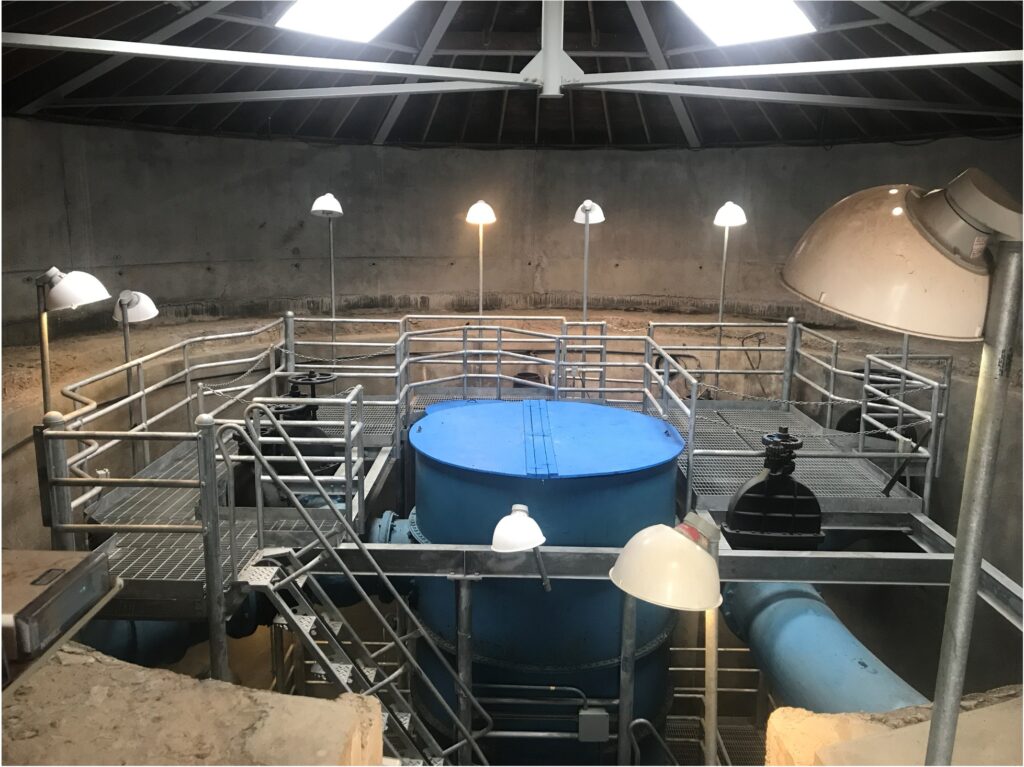
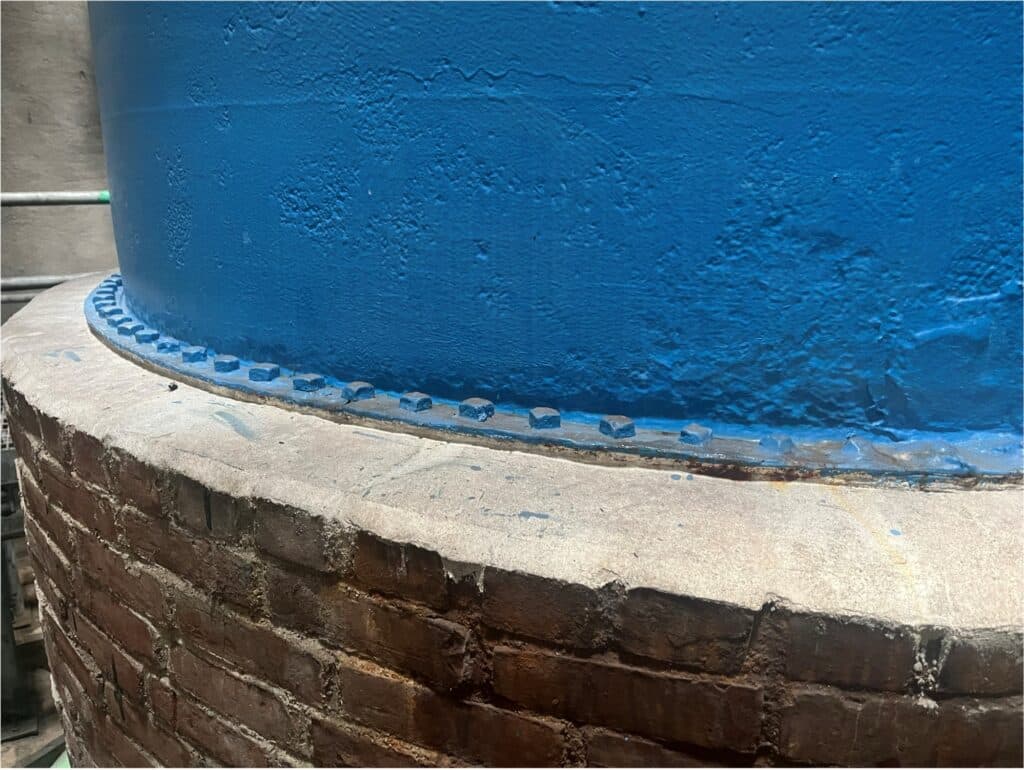
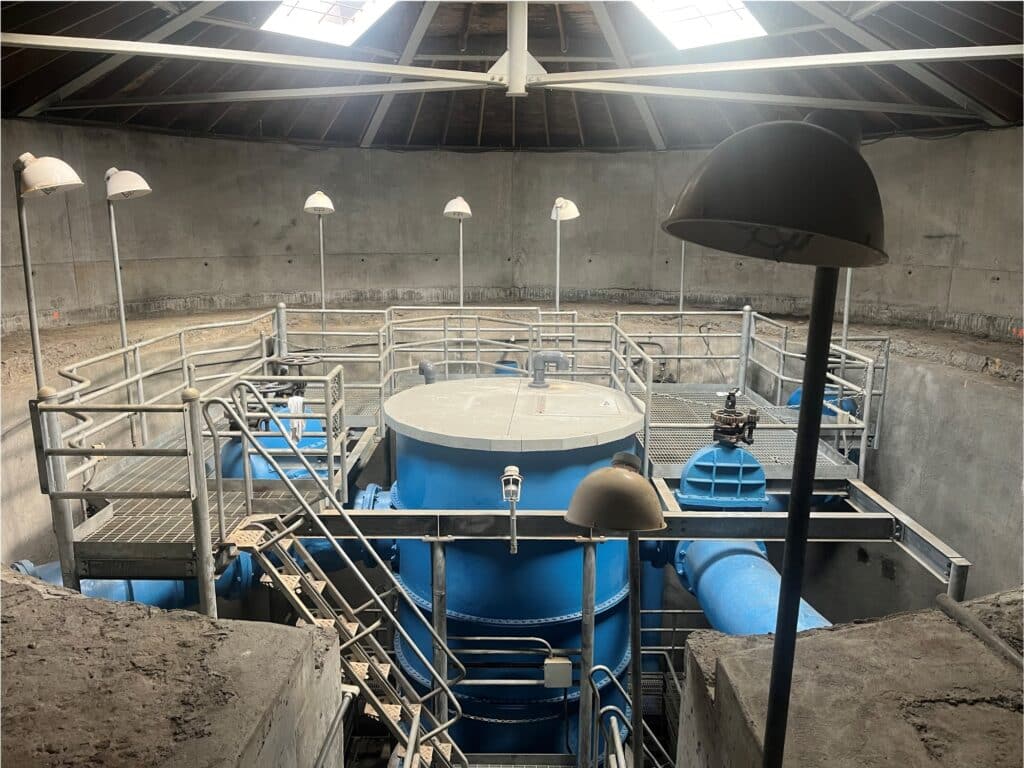
The Waban Hill Reservoir (Reservoir) is located in the Chestnut Hill area of Newton and serves the southern pressure zone. The Commonwealth Avenue Pump Station, operated by the MWRA, serves Newton’s southern pressure zone and fills the Reservoir. The Reservoir has a capacity of approximately 10 million gallons (MG) with four chambers that were built in stages: Chamber 1 was constructed in 1891, Chamber 2 in 1901, and Chambers 3 and 4 in 1917. Each chamber is approximately 2.5 MG. At the center of the reservoir is a gate chamber building that houses the influent and effluent valves and piping to each of the chambers as well as the 90-inch diameter central core standpipe.
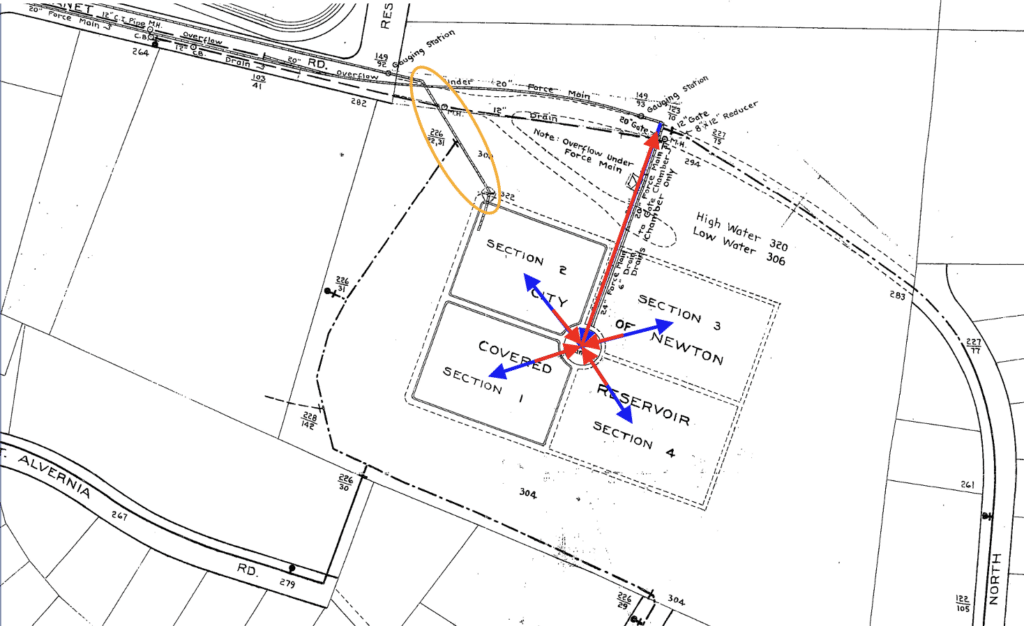
As shown in Figure 1, there is a 24-inch diameter common inlet/outlet line that fills the interior standpipe and then overflows equally into all four chambers. When drawing, the 24-inch diameter check valve opens and draws through the effluent lines and out the common inlet/outlet. An additional 24-inch diameter inlet/outlet pipe is located in the corner of Chamber 2 that operates Chamber 2 only if needed. During construction, Chamber 2 was used to feed the system through the secondary inlet/outlet pipe while work was completed on the effluent valves for all chambers. During construction, the effluent pipe from Chamber 2 to the core was plugged so that work could be performed on the piping and valve while keeping Chamber 2 in service.
All chambers have a drain line and valve that manifold into a 24-inch diameter drain line that runs under the existing common inlet/outlet pipe. The bottom of the interior standpipe as well as the standpipe overflow both drain into the 24-inch drain line.
Design
The original scope of the repair project included rehabilitating the 90-inch diameter standpipe, replacing four 24-inch effluent valves, and replacing the asphalt shingle roof.
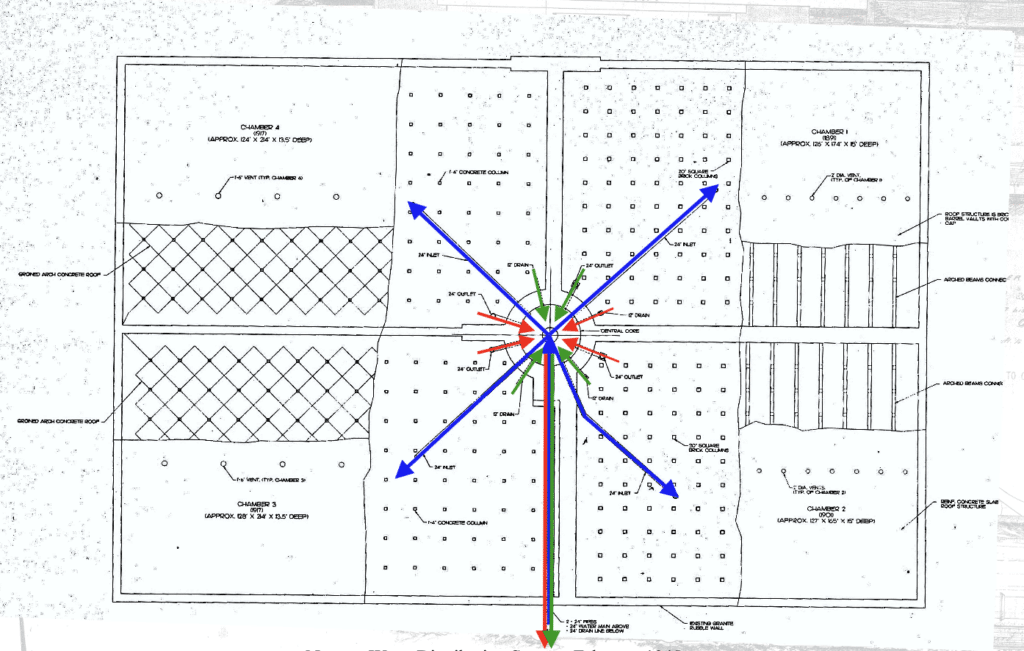
Prior to construction, it was important to review the impacts of removing Chambers 1, 3, and 4 from service on the distribution system. The existing hydraulic model for the City was used to evaluate pressures and available fire flow throughout the system with just Chamber 2 online. The inlet/outlet pipe for Chamber 2 runs down Commonwealth Avenue to the Pump Station (blue line in Figure 2) while the main inlet/outlet pipe from the Central Core runs down Ward Street to the Pump Station (red line in Figure 2). Changing the location of where water enters the system from the Reservoir in turn impacted the hydraulics at certain areas of the system, specifically at higher elevations north of the Reservoir. A recently installed 12-inch diameter interconnection between the two feed lines was opened, reducing the overall headloss in the system.
The design required a contingency plan, addressing potential challenges such as losing the entire Reservoir due to a water main break on the inlet/outlet pipe to Chamber 2. Through close coordination with T&H, the City, and MWRA, an emergency response plan was created that added enhanced scenarios. T&H evaluated the model for the best location of a mobile pumping unit and location of pressure relief valves. The City installed additional hydrants so the City could use MWRA’s mobile pumping unit if needed to pump from the northern pressure zone to the southern pressure zone, which required coordinating availability of equipment with MWRA.
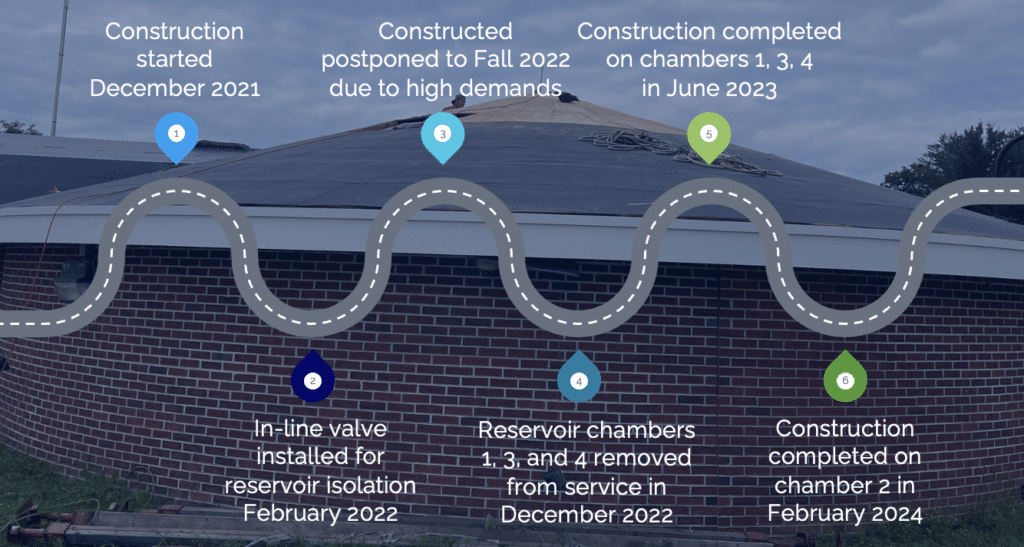 Following a review of the challenges, the design scope was revised. Final design and bidding on the project included standpipe rehabilitation, effluent valve and piping replacement, drain valve replacement, check valve replacement, and asphalt shingle roof replacement as well as the standpipe cover and man-way, interior lighting improvements, and instrumentation.
Following a review of the challenges, the design scope was revised. Final design and bidding on the project included standpipe rehabilitation, effluent valve and piping replacement, drain valve replacement, check valve replacement, and asphalt shingle roof replacement as well as the standpipe cover and man-way, interior lighting improvements, and instrumentation.
Construction Challenges
There were many construction challenges to overcome as part of the design. Record drawings indicated an isolation valve was located on the common inlet/outlet pipe; however, the valve was unable to be found. A new valve was installed as a change order for the project.
The construction contractor was limited to light loads due to the uncertainty of the structural integrity of the roof to support specific loads, meaning no cranes or heavy equipment could be used, and spanning a crane from the access road to the gate chamber was cost prohibitive.
The existing valves were embedded in concrete and the flanges were severely deteriorated. Because of the age of the pipe, angles and bolt patterns were not easily matched with modern piping. Therefore, stainless steel piping was used to fabricate the needed angles to connect the new valves to the common inlet/outlet pipe.
The standpipe was showing signs of severe deterioration. Under recommendations from MassTank, specialty repairs were required to prolong the life of the standpipe. Steel plates were installed at the joints within the standpipe, both interior and exterior surfaces were sand blasted, a 200 mil epoxy coating was installed on the interior surfaces, and a 10 mil coating was applied to all exterior surfaces.
Initial filling of the reservoir caused Chamber 2 to fill faster than Chambers 1, 3, and 4 which caused the Commonwealth Ave. Pump Station to shut down. Therefore, the MWRA mobile pumping unit was relocated to the Waban Hill Reservoir and water was pumped from the hatch in Chamber 2 through the hatch in Chamber 1 which was connected to Chamber 3 and 4 through the central core.
Conclusion
Construction was completed in February 2024 and the project was highly successful with minimal service interruption due to a close working partnership with Tata & Howard, the City of Newton (client), and MWRA.





 A PFAS Journey to Determine Effective Management and Treatment Options
A PFAS Journey to Determine Effective Management and Treatment Options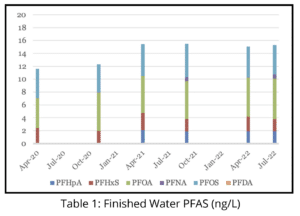 Currently, the Town has been managing the sources to improve water quality and stay under the current MCL of 20 ng/L for PFAS6. A mass balance is utilized to estimate finished water PFAS concentrations based on updated sample results and changes in the operation of the sources. Tata & Howard created the base tool which can be used to see how changes to PFAS levels or flow rates can affect the finished water concentration.
Currently, the Town has been managing the sources to improve water quality and stay under the current MCL of 20 ng/L for PFAS6. A mass balance is utilized to estimate finished water PFAS concentrations based on updated sample results and changes in the operation of the sources. Tata & Howard created the base tool which can be used to see how changes to PFAS levels or flow rates can affect the finished water concentration.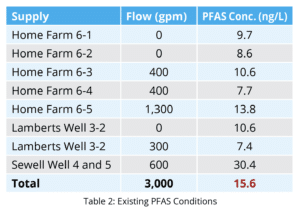

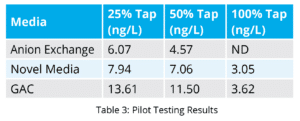 Table 3 shows the result from the different taps at the end of the pilot.
Table 3 shows the result from the different taps at the end of the pilot.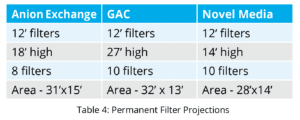 Table 4 is a summary as to what the permanent filter system may look like. The filters are similar in size but the number of recommended filters differs for each resin. The overall building footprint is similar as well. The anion exchange did perform slightly better than the novel media, however, the overall PFAS removal results over the duration of the pilot was similar. Because of this, construction costs, long term media replacement costs, and operational considerations were included as part of the media selection process.
Table 4 is a summary as to what the permanent filter system may look like. The filters are similar in size but the number of recommended filters differs for each resin. The overall building footprint is similar as well. The anion exchange did perform slightly better than the novel media, however, the overall PFAS removal results over the duration of the pilot was similar. Because of this, construction costs, long term media replacement costs, and operational considerations were included as part of the media selection process.







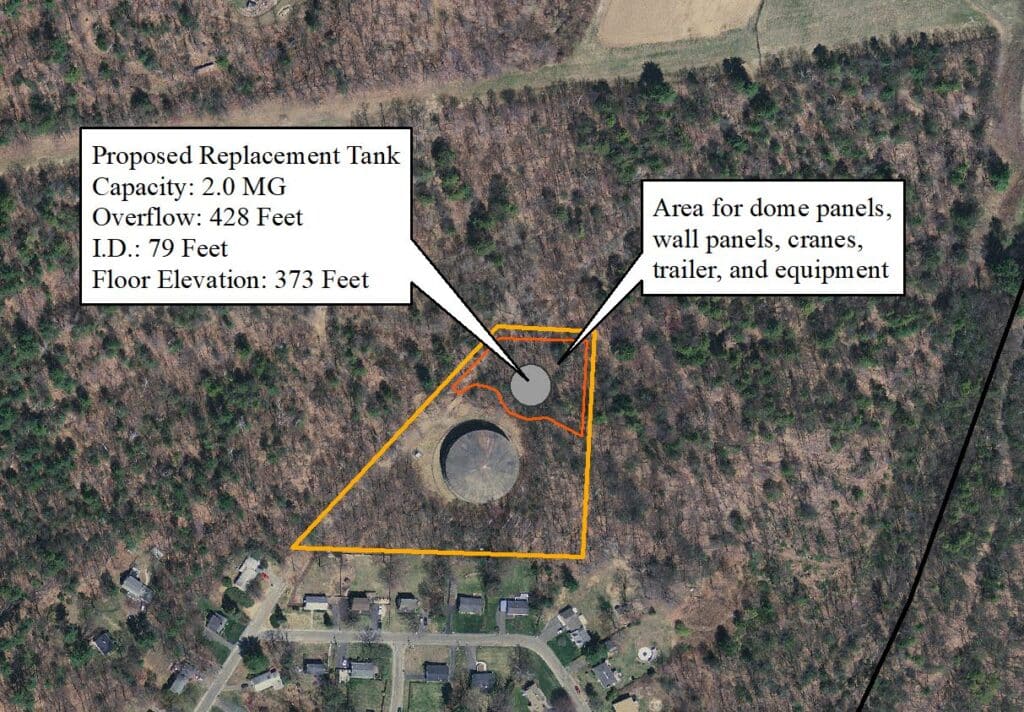 Hydraulic impact was also studied. Pressure decreased 2-4 PSI depending on which sources were running, and the available fire flow decreased up to 600 gpm, but was limited to the area around the tank which is mostly residential. Resultant flows were sufficient for the residential area.
Hydraulic impact was also studied. Pressure decreased 2-4 PSI depending on which sources were running, and the available fire flow decreased up to 600 gpm, but was limited to the area around the tank which is mostly residential. Resultant flows were sufficient for the residential area.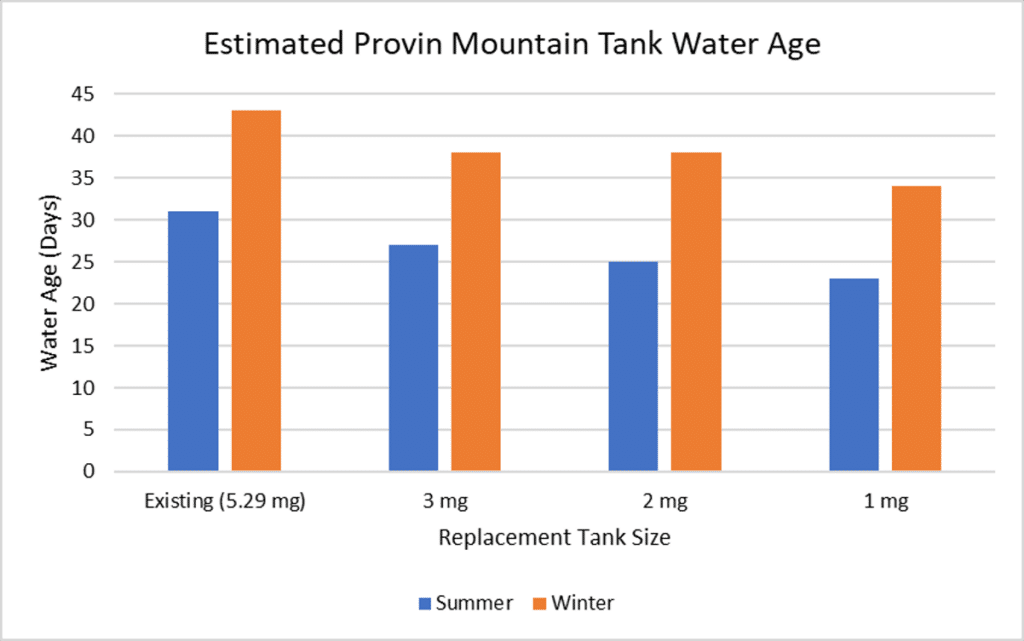 While storage and hydraulics showed that the tank was not needed, it was determined that there would be significant lack of fire protection in much of the system if the Sackett Tank was offline for repairs or other issues in addition to elimination of the Provin Mountain Tank. Due to the lack of fire protection under this scenario, it was ultimately recommended to replace the tank.
While storage and hydraulics showed that the tank was not needed, it was determined that there would be significant lack of fire protection in much of the system if the Sackett Tank was offline for repairs or other issues in addition to elimination of the Provin Mountain Tank. Due to the lack of fire protection under this scenario, it was ultimately recommended to replace the tank. Tata & Howard contracted with the Town of Amherst for design, permitting, and bidding of the 1.5 million gallon per day (MGD) Centennial Water Treatment Plant, to treat surface water from the Pelham Reservoir System. The existing Centennial WTP, located in the Town of Pelham but supplying the Amherst Public Water System, has a history of issues with turbidity, color, and disinfection byproducts in the form of total trihalomethanes (TTHM) and haloacetic acids (HAA5) because of high levels of organics in the Pelham Reservoir System. Due to the age and condition of the existing WTP, the filters which were the primary treatment process at the existing WTP were no longer effective at removing organics, leading to a decrease in finished water quality and total WTP capacity. The existing Centennial WTP has been offline since 2018 due to water quality, as well as infrastructure concerns related to a lightning strike which impacted pumping equipment and communications at the Centennial Water Treatment Plant’s raw water pump station.
Tata & Howard contracted with the Town of Amherst for design, permitting, and bidding of the 1.5 million gallon per day (MGD) Centennial Water Treatment Plant, to treat surface water from the Pelham Reservoir System. The existing Centennial WTP, located in the Town of Pelham but supplying the Amherst Public Water System, has a history of issues with turbidity, color, and disinfection byproducts in the form of total trihalomethanes (TTHM) and haloacetic acids (HAA5) because of high levels of organics in the Pelham Reservoir System. Due to the age and condition of the existing WTP, the filters which were the primary treatment process at the existing WTP were no longer effective at removing organics, leading to a decrease in finished water quality and total WTP capacity. The existing Centennial WTP has been offline since 2018 due to water quality, as well as infrastructure concerns related to a lightning strike which impacted pumping equipment and communications at the Centennial Water Treatment Plant’s raw water pump station.










