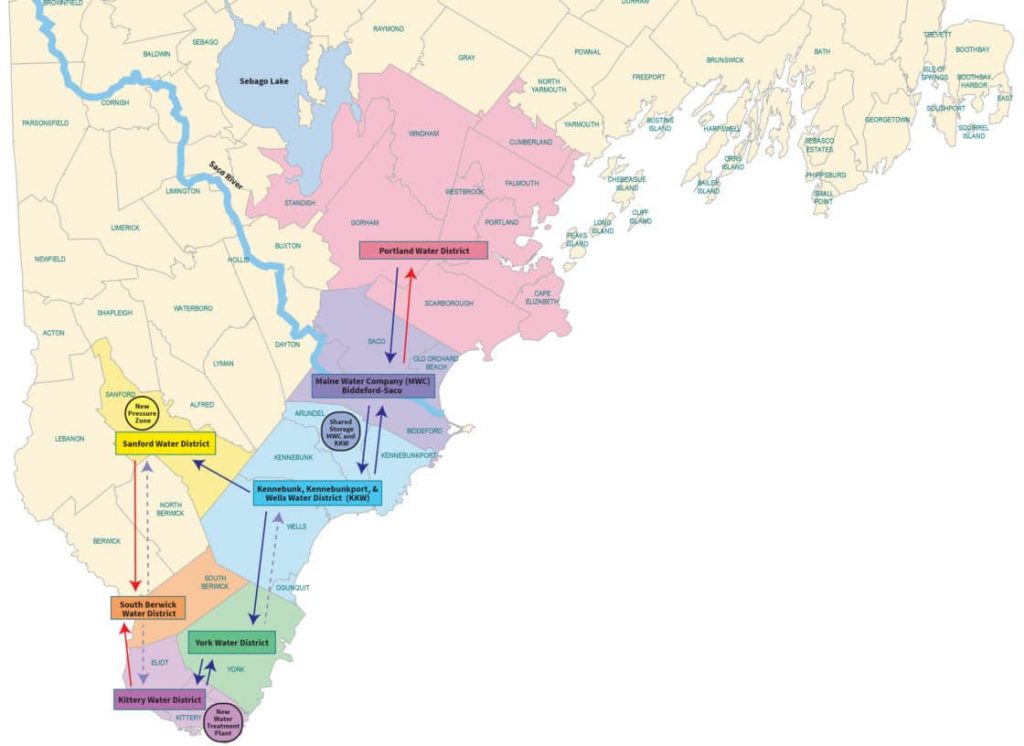
Tata & Howard was retained by the Southern Maine Regional Water Council (SMRWC) to complete a Regional System Study for the Portland Water District (PWD), Maine Water Company – Biddeford & Saco (MWCB&S), Kennebunk, Kennebunkport, Wells Water District (KKWWD), Sanford Water District (SWD), South Berwick Water District (SBWD), York Water District (YWD), and Kittery Water District (KWD).
The purpose of the study was to provide a detailed update to their 2008 Regional Water System Master Plan Study, which studied possible interconnections between the water systems within the SMRWC. A combined water distribution system regional hydraulic model was developed using the hydraulic models of each individual water system. The regional hydraulic model was used to evaluate the hydraulic feasibility and impacts of the proposed interconnections as well as the potential of transferring water from northern systems to southern systems through a completely connected and open system. The PWD and MWCB&S have large water sources and are interested in exploring the option of providing water to southern systems. The study evaluated the needed infrastructure improvements, each system’s available water supply, and demands through the potential and existing interconnections.
The study also examined the effects that the proposed system improvements and interconnections would have on water quality. Not all water systems treat water in the same way; therefore, finished water is unique to the chemicals and treatment techniques used by each system. Specifically, pertinent available data was collected and chemicals used for coagulation, sequestering, primary disinfection, secondary disinfection, corrosion control, pH adjustment, and dental health were reviewed. Raw and finished water parameters such as turbidity, alkalinity, temperature, pH, and total hardness were also collected. Of the seven participating water systems in the study, three disinfect with chloramines and four disinfect with only chlorine solution. Operating the systems together as a permanent solution to water supply concerns would require modifications to the treatment processes in some if not all of the systems. Ideally, each water system involved in water sharing would need to agree to a treatment method to give each system acceptable water quality and eliminate concerns with blending systems.
The identified improvements were based on hydraulic feasibility. Infrastructure recommendations at the interconnection locations include construction of new water mains, pressure reducing valves, and booster pumping stations.