In the United States, there are approximately 170,000 public drinking water systems, with 54,000 of them collectively delivering water to more than 264 million people, more than half of the country’s population. Unfortunately, due to the state of our nation’s drinking water system, limited infrastructure funds, and climate change, we are losing approximately seven billion gallons of water a day.
So where exactly is that water going?
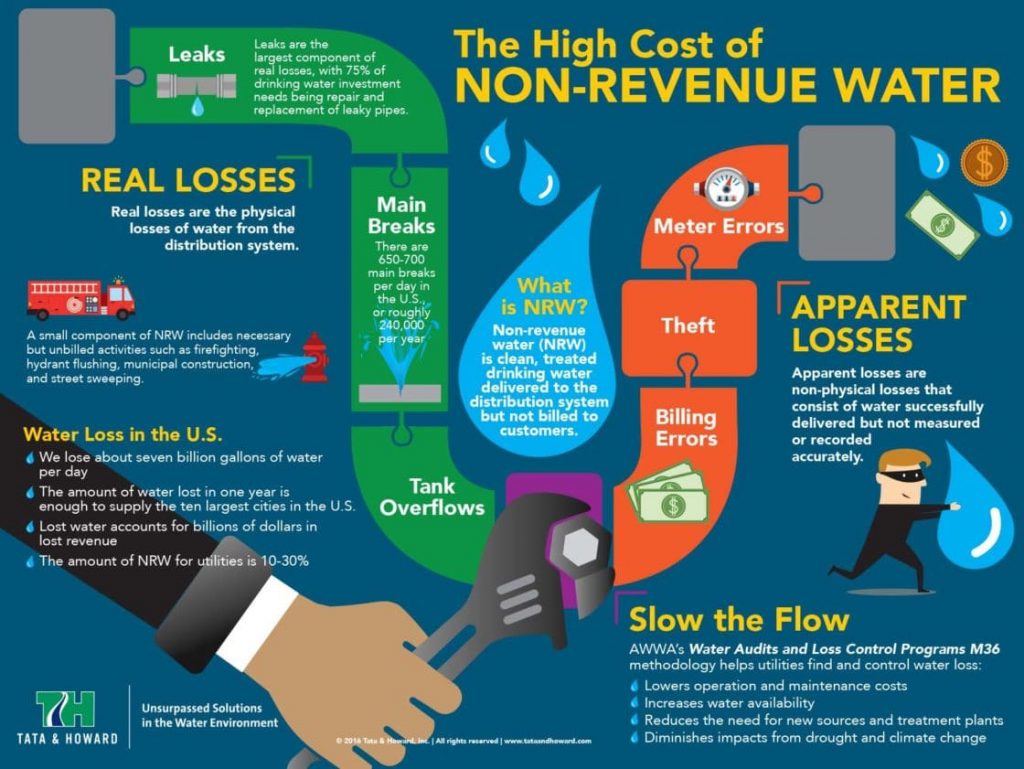
Non-Revenue Water Crisis
Non-revenue water (NRW) is water that has been, essentially, dined and dashed, or water that has been consumed but not paid for by way of inaccurate meter reads or theft. Additionally, leaks in the system can be a major contributor to NRW.
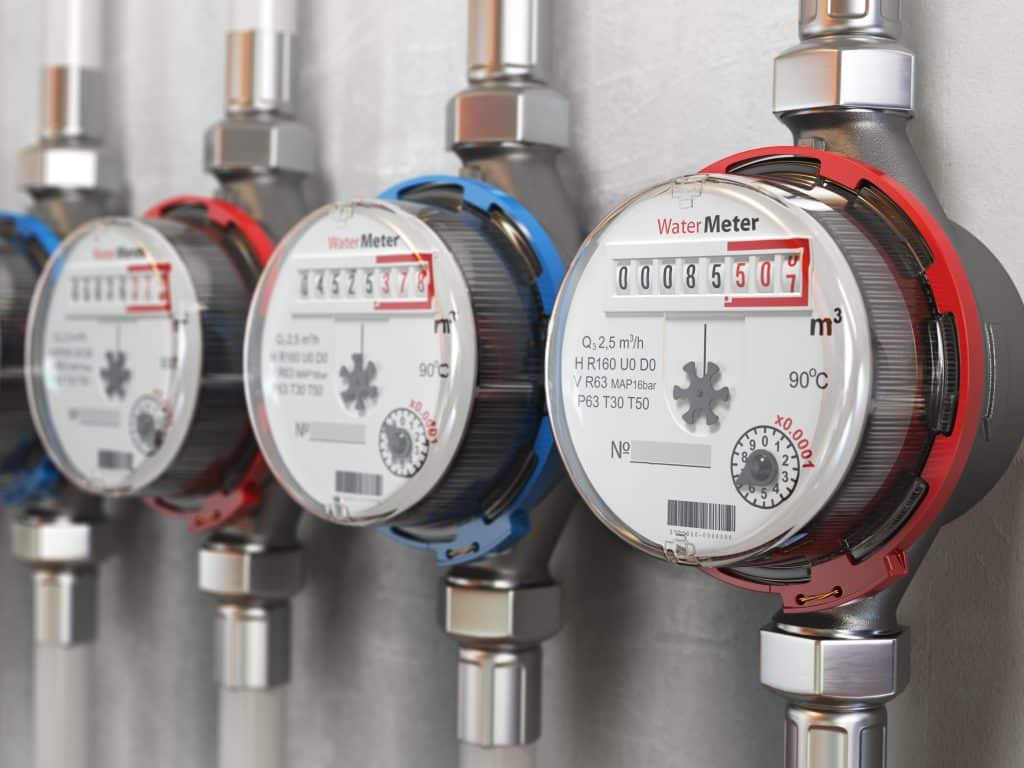

With NRW comes two main types of loss: apparent and real loss. Apparent losses occur when water is delivered to the consumer but is either measured or metered incorrectly. Real losses occur when water is physically lost and never makes it to the consumer. While a very small amount of NRW comes from firefighting, hydrant flushing, municipal construction, and street sweeping, this is considered to be an “unbilled metered” source of NRW and is not considered a part of the “real loss” crisis. (You can find more information on different forms of NRW here.)
So, how does this affect the general public? Well, if you use less water, your monthly bill will go down, as with any typical utility. However, if water is being lost within the plumbing in your house, and there is a higher demand, your monthly bill will be raised. In fact, the average household in the US loses approximately 10,000 gallons of water a year, meaning NRW affects, quite literally, everyone.
Hundred-Year-Old Pipes
In the United States, there are an average of 240,000 water main breaks every year, with approximately 650 to 700 happening per day. Unfortunately, this information isn’t entirely shocking given that a large amount of our nation’s pipes and mains are over a hundred years old and in need of critical replacement in order to prevent further breaks. As it turns out, 75% of drinking water investment needs are for repairing and replacing leaky pipes.
Drinking water system component parts have an average life expectancy of fifteen to ninety-five years, so while new pipes are being added to expand our current systems, other parts are continuing to degrade. Degrading leads to water main and pipe leaks, which not only disrupt service to customers, but can also cause the subsurface of our roads and public infrastructures to erode which, when untreated, can eventually lead to road collapses and deteriorating building foundations. Just as concerning, broken or leaking pipes invite the potential for toxins and disease-causing pathogens to enter the water supply, causing water quality issues that require mitigation — yet another expense.
Why Water Audits?
To fix all of our water distribution systems, it would cost the United States approximately $200 billion, and almost half of that money would be allocated for water loss control. With water audits, the most critical areas can be identified first so the (already limited) funds can be dedicated solely to repairing the infrastructure. From there, water audits can help municipalities develop strategies and courses of action for future problem areas; recapture lost water; decrease the need for new sources, treatment plants, facility upgrades and expansions; and reduce the number of entry points to disease-causing pathogens.
Water audits follow the M36 Water Audit methodology from American Water Works Association (AWWA) and are an affordable and efficient solution to increasing water availability and helping to identify the costs and causes of water loss. In the past, Tata & Howard has been retained by the Towns of Wayland and Grafton, MA, and South Central Connecticut Regional Water Authority (SCCRWA) to complete water audits to determine the volume at which NRW is occurring, potential sources of the lost water, and make recommendations on how to reduce future water loss.
For more information on water loss control and the M36 methodology, take a look at our webinar here.

 Every year during the first week of May, the American Water Works Association (AWWA) and members of the water community celebrate Drinking Water Week, a week-long campaign dedicated to educating the public about the critical role clean water plays in our daily lives.
Every year during the first week of May, the American Water Works Association (AWWA) and members of the water community celebrate Drinking Water Week, a week-long campaign dedicated to educating the public about the critical role clean water plays in our daily lives.




 Don not only supported the Water For People organization individually, he also shared his passionate support with the employees of the firm he co-founded, Tata & Howard, Inc. Employees continue to support WFP through a payroll deduction program, which Don initiated. At the end of each year, the company matches the employee’s donations.
Don not only supported the Water For People organization individually, he also shared his passionate support with the employees of the firm he co-founded, Tata & Howard, Inc. Employees continue to support WFP through a payroll deduction program, which Don initiated. At the end of each year, the company matches the employee’s donations.
 As Drinking Water Week continues, T&H joins the American Water Works Association and water professionals across North America in encouraging homeowners to check and fix leaks inside and outside the home.
As Drinking Water Week continues, T&H joins the American Water Works Association and water professionals across North America in encouraging homeowners to check and fix leaks inside and outside the home. As Drinking Water Week continues, Tata & Howard joins the American Water Works Association and water professionals across North America in encouraging households to identify and replace lead-based water pipes and plumbing. Lead presents health concerns for people of all ages, particularly pregnant women, infants, and young children. In children, low exposure levels have been linked to learning disabilities, behavioral problems, and other issues.
As Drinking Water Week continues, Tata & Howard joins the American Water Works Association and water professionals across North America in encouraging households to identify and replace lead-based water pipes and plumbing. Lead presents health concerns for people of all ages, particularly pregnant women, infants, and young children. In children, low exposure levels have been linked to learning disabilities, behavioral problems, and other issues. Tata & Howard, the American Water Works Association (AWWA), and water professionals across North America are kicking off Drinking Water Week today with the theme “Your Water – To Know It Is To Love It”.
Tata & Howard, the American Water Works Association (AWWA), and water professionals across North America are kicking off Drinking Water Week today with the theme “Your Water – To Know It Is To Love It”. Water utilities today are faced with a unique set of difficulties. Population growth has resulted in unprecedented demand while climate change has caused supply to dwindle. Increased regulations have forced utilities to invest more and more capital into treatment while budgets have shrunk. In addition, our nation’s aging infrastructure has forced water utilities to heavily invest in repair and replacement of the distribution system. Therefore, it has become critical that utilities utilize the most cost-effective and efficient methodologies in order to maintain and improve their water systems.
Water utilities today are faced with a unique set of difficulties. Population growth has resulted in unprecedented demand while climate change has caused supply to dwindle. Increased regulations have forced utilities to invest more and more capital into treatment while budgets have shrunk. In addition, our nation’s aging infrastructure has forced water utilities to heavily invest in repair and replacement of the distribution system. Therefore, it has become critical that utilities utilize the most cost-effective and efficient methodologies in order to maintain and improve their water systems.
 Because demand is highest in summer and would make flushing impractical, and low temperatures in winter would cause unsafe conditions from flushed water freezing on roadways and sidewalks, flushing is typically performed in the spring and fall. Currently, Tata & Howard is assisting the communities of Haverhill and Manchester By The Sea, MA and Norwalk First Taxing District in Norwalk, CT with their annual UDF Programs. Both AWWA and MassDEP recommend that UDF be performed on an annual basis, at a minimum. If a distribution system is too large to perform UDF annually, flushing should instead be scheduled in rotation so that all parts of the distribution system are exercised on a regular basis.
Because demand is highest in summer and would make flushing impractical, and low temperatures in winter would cause unsafe conditions from flushed water freezing on roadways and sidewalks, flushing is typically performed in the spring and fall. Currently, Tata & Howard is assisting the communities of Haverhill and Manchester By The Sea, MA and Norwalk First Taxing District in Norwalk, CT with their annual UDF Programs. Both AWWA and MassDEP recommend that UDF be performed on an annual basis, at a minimum. If a distribution system is too large to perform UDF annually, flushing should instead be scheduled in rotation so that all parts of the distribution system are exercised on a regular basis.