An Introduction to Groundwater
Groundwater is an abundant and renewable natural resource comprised of the water that soaks into the earth from precipitation. This water moves downward to seep into cracks, crevices, and other openings in rock beds and sand. Groundwater makes up 95% of the world\’s freshwater, with surface water (lakes, rivers, and streams) making up only three percent of all freshwater. To put it into perspective, hydrologists estimate there are currently over 33,000 trillion gallons of groundwater in reserve in the U.S. – which is 20 to 30 times greater than the total amount of water in all of the lakes, streams, and rivers of the U.S.
Why It’s Important
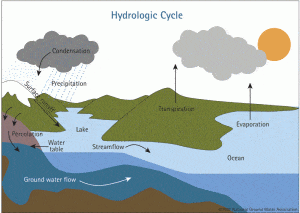 Groundwater is an integral part of the hydrologic cycle, which includes all the water of the Earth including the atmosphere, oceans, surface water, and groundwater. The system is cyclical in that water repeatedly moves through all of these elements. In addition, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that 25% of all U.S. rainfall becomes groundwater, and that 30% of U.S. stream flow originates from groundwater.
Groundwater is an integral part of the hydrologic cycle, which includes all the water of the Earth including the atmosphere, oceans, surface water, and groundwater. The system is cyclical in that water repeatedly moves through all of these elements. In addition, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that 25% of all U.S. rainfall becomes groundwater, and that 30% of U.S. stream flow originates from groundwater.
The U.S. uses about 80 billion gallons of fresh groundwater every day for public and private drinking water, irrigation, livestock, manufacturing, mining, and thermoelectric power. Over 40% of the nation’s population depends on groundwater for their drinking water supply, with private household wells comprising the largest percentage of all wells in the nation. Over 13 million households depend on private well water.
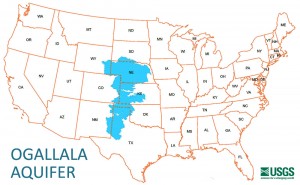
The largest use of groundwater in the U.S. is irrigation. Over 50 billion gallons of groundwater are used per day for agricultural purposes, up from just over 2 billion gallons per day in 1900. The nation’s largest aquifer is the Ogallala, which runs beneath 250,000 square miles stretching from Texas to South Dakota, and 90% of the water pumped from the Ogallala is used for agricultural irrigation. This massive and plentiful aquifer accounts for one-third of all U.S. irrigated agriculture, and creates about $20 billion in food and fiber annually. If the waters of the Ogallala were spread across the surface of the U.S., all 50 states would be covered with 1.5 feet of water. Yet, even though groundwater is plentiful and renewable, it still needs to be respected. Scientists estimate that if the Ogallala were fully withdrawn, it would take a whopping 6,000 years to refill it naturally. So we all need to take steps to conserve the groundwater – indeed, all water – that we have.
Best Conservation Practices
In the Home
- Turn the faucet off when the water isn’t being used, such as while brushing your teeth or doing dishes.
- Don’t pour fresh, unused water down the drain; use it to water plants or to fill a humidifier.
- Install aerators with flow restrictors on household faucets.
- When upgrading, choose water- and energy-efficient appliances, such as low-flow toilets and front-load washing machines.
- Always repair a dripping faucet or leaking toilet; one wasted drop per second adds up to 2,700 gallons per year!
- Only run a fully loaded dishwasher or washing machine, or set the water level to match the load size.

Dennis Nett/The Post-Standard/Landov
In the Yard
- Raise the mower blade to the highest level to allow your lawn to retain its moisture and to strengthen the root system.
- Plant native, drought-resistant grasses, shrubs, and trees.
- Don’t overwater your lawn. Heavy rain eliminates the need to water for up to two weeks, and a bright green lawn is truly overrated. As they say in California, where the drought has reached a critical state, “Brown is the New Green.” A lawn that isn’t perfectly and uniformly dark green indicates a future-minded, caring, and responsible resident.
Groundwater is clearly an extremely important natural resource, and one that deserves our care. Stay tuned later this week as we showcase a Cape Cod aquifer, its uses, safety, sustainability, and protection.
For more information on groundwater, visit https://water.epa.gov/type/groundwater/index.cfm.
For fun and educational kids’ activities, please visit https://water.epa.gov/learn/kids/drinkingwater/index.cfm