For a waterworks system to ensure reliable, long-lasting services, it’s critical that a fundamental component be efficient resource allocation. By incorporating capital efficiency plans, master plans, and a methodical capital planning process, utilities are able to navigate the complexities of their industry, not only by enabling them to strategically allocate resources and address dire infrastructure needs but also by meeting the persistent demands of evolving environmental regulations.
As we forge ahead, smart capital planning remains the compass that guides utilities towards a future where access to clean water is not just a necessity but a sustainable and well-managed reality.

Capital Efficiency Plans (CEPs): The Blueprint for Resource Organization
Capital Efficiency Plans (CEPs) at T&H follow a standard Venn diagram method. For every water main segment, there are three sets of evaluation criteria: key components, asset management, and hydraulic modeling.
With each set comes its own set of unique drawbacks, and it’s where the three overlap that the system’s weak points are put on display. If it seems that the weaknesses meet more than one set of criteria, then they are swiftly prioritized above the others as they require the most attention. By choosing this type of visual method, CEPs can quickly and justifiably pinpoint areas of criticality, allowing utilities to make a targeted plan of attack.
To put it simply, CEPs are a vital element of smart capital planning because they provide utilities with a strategic roadmap leading them towards the treasure trove of resource optimization. CEPs prioritize resource allocation by identifying the projects that will offer the greatest impact on efficiency (in other words, the ones that require the most attention), while also evaluating any potential risks such as regulatory changes and environmental challenges.
By streamlining capital investments, utilities can ensure cost-efficiency while also maintaining and improving their service standards and mitigating any potential, unforeseen issues.
Master Plans: The “What, When, and How” for Sustainable Development
A water master plan is essentially what it sounds like: a blueprint for sustainably managing and using water resources within a specific region. Diving deeper, a water master plan is a detailed framework that takes a variety of factors into account, like evaluating the current water supply, demand forecasts, infrastructure development, conservation tactics, financial planning, and environmental impact evaluations, to name a few.
Water, after all, is our lifeblood; without it, we could not sustain ourselves, our ecosystems, or our industries. It’s no secret that water utilities are often the ones on the front lines battling mitigation efforts, a lack of funding, and a complex web of other responsibilities. This juggling act often means that they need to know the “what, when, and how” as soon as possible: what do they need to do? When do they need to do it? How are they going to pay for it?
A water master plan has three main components: infrastructure assessment, data collection and analysis, and long-term goals. The first step is an infrastructure assessment that will evaluate the current water systems and infrastructure, including a review of pipelines, treatment plants, distribution networks, storage facilities, etc. This comprehensive evaluation will also be able to identify any infrastructure needs, such as maintenance, upgrades, or expansions.
The second step in any effective master plan is data collection and analysis. The master plan is constructed by using the initial assessment’s findings as its foundation—everything from demographic trends to industry developments can provide crucial information that can lead the plan down the path of success or failure. This step is important because it will influence the master plan. After all, bad data equals bad resource allocation. Thirdly, water master planning needs to extend far beyond the immediate needs; long-term goals are absolutely critical in ensuring the future of sustainable water management and utilization.
The heart of a water master plan is straightforward: ensure that water resources are allocated fairly, address critical issues like population growth and climate change, and establish a robust, accessible, and dependable water delivery system. Because at the end of the day, a water master plan promotes long-term water security, the health of people and ecosystems, and effective water management by integrating technical, economic, and environmental concerns.
Capital Planning
Utilities use the capital planning process, a structured methodology, to identify, prioritize, and allocate resources for capital projects. By addressing present demands and preparing for upcoming obstacles, this strategy helps utilities to align investments with strategic objectives. It starts with a thorough evaluation of the state of the infrastructure, which paves the way for the identification of priority projects that solve short-term issues and support long-term objectives.
An essential part of the planning process is estimating the price of proposed capital projects. Utilities use financial analysis to evaluate project viability and pinpoint possible funding sources, and a detailed risk assessment is carried out in order to identify and minimize any issues that could affect the success of capital projects. Investment resilience is increased by proactive risk management.
A financial analysis can help utilities determine just how feasible their projects are and aid in the search for funding by assessing their weaknesses in order to foresee any challenges that could impact the project’s success. Important stakeholders are then consulted to ensure the process takes into account a variety of viewpoints and community requirements. This cooperative and collaborative strategy not only promotes transparency, but it also has the power to greatly increase stakeholder trust.
Conclusion
In the face of a constantly evolving environment while meeting complex regulatory and social dynamics, there is no denying that smart capital planning is essential for the sustainable development of water and wastewater utilities. To put it succinctly, in order to have sustainable development, management, protection, and distribution of water and wastewater utilities, extensive planning is non-negotiable. Combined with ever-changing technology, utilities are further empowered to adapt and thrive.
By incorporating capital efficiency plans, master plans, and a methodical capital planning process, utilities can navigate the complexities with far more ease and effectively meet the needs of their communities.





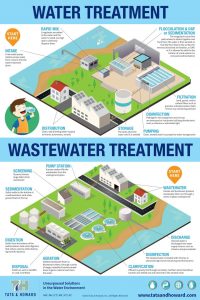
 It is widely known how important water is to our lives and the world we live in. Our body and planet is comprised of about 70% water – making it seem like it is easily accessible and plentiful. However, when you rule out our oceans and ice caps, less than 1% of all the water on Earth is drinkable. Of that less than 1%, groundwater only accounts for 0.28% of fresh water around the globe. Safe drinking water is a privilege we often take for granted while we brush our teeth or drink a glass of water in the morning. While we are giving thanks to our family, friends, and food during Thanksgiving, we should also give big thanks for our clean drinking water and the people who make it happen.
It is widely known how important water is to our lives and the world we live in. Our body and planet is comprised of about 70% water – making it seem like it is easily accessible and plentiful. However, when you rule out our oceans and ice caps, less than 1% of all the water on Earth is drinkable. Of that less than 1%, groundwater only accounts for 0.28% of fresh water around the globe. Safe drinking water is a privilege we often take for granted while we brush our teeth or drink a glass of water in the morning. While we are giving thanks to our family, friends, and food during Thanksgiving, we should also give big thanks for our clean drinking water and the people who make it happen.