Dams: To Remove or Not To Remove?

Dams are an integral part of modern day infrastructure, providing many benefits to society. Yet dams have also come under scrutiny in the past few years as they can potentially have a negative effect on an area’s ecology. Some people, including environmental groups, are vehemently calling for the removal of many dams, while others continue to promote the positive impact that dams have on our culture. To remove or not to remove? That is the question.
The Benefits of Dams
Dams have been in existence for over 5,000 years. The first known dam to be built was the Jawa Dam, which was constructed around 3,000 BCE in Mesopotamia. Since that time, dam engineering has progressed significantly, and there are now about 50,000 large dams in use worldwide. The United States currently has 87,000 dams over six feet in height, 2,000,000 dams in total, and 50 major dams — the most in the world. And though they may have an ecological impact, dams admittedly provide myriad benefits, both economically and socially.
Recreation
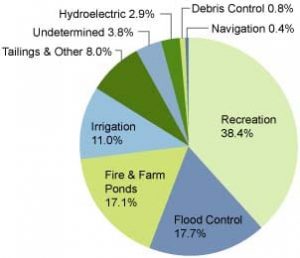 The most prevalent function of America’s dams is to provide recreation. Families flock to our nation’s lakes that are created by dams for vacations and downtime to enjoy boating, camping, picnic areas, water skiing, fishing, and water sports. Some of the most beautiful and enjoyable vacation spots in the nation are lakes created by dams. In fact, of the top ten most popular vacation lakes in the United States, eight are impounded by dams, including number one on the list, Lake Tahoe. These recreational areas bring in millions of dollars of tourist funds and are important to the economic health of the nation.
The most prevalent function of America’s dams is to provide recreation. Families flock to our nation’s lakes that are created by dams for vacations and downtime to enjoy boating, camping, picnic areas, water skiing, fishing, and water sports. Some of the most beautiful and enjoyable vacation spots in the nation are lakes created by dams. In fact, of the top ten most popular vacation lakes in the United States, eight are impounded by dams, including number one on the list, Lake Tahoe. These recreational areas bring in millions of dollars of tourist funds and are important to the economic health of the nation.
Flood Control
Flood control dams impound floodwater to help prevent loss of life and protect property caused by flooding. They also protect farmers’ crops from being destroyed by flood inundation. Protecting people, property, and crops also provides high economic benefit.
Water Storage (Fire & Farm Ponds)
While major dams create massive lakes, thousands of other dams create smaller reservoirs throughout the nation that supply water for industrial, municipal, and agricultural uses. Water from these human-made lakes supply water for livestock and fire protection for cities and towns, as well as industrial uses.
Irrigation

Over ten percent of American crops are irrigated using water impounded by dams. This irrigated farmland provides thousands of jobs to hardworking American people, providing huge economic benefit to our nation.
Mine Tailings
Mine tailings are sometimes overlooked as dams, but there are actually over 1,300 mine tailings impoundments in the United States. The tailings allow for the mining and processing of coal and other minerals while protecting the surrounding environment.
Electrical Generation
While only 2.9% of our nation’s dams provide hydroelectric power, they account for over 35% of our nation’s renewable energy, over 6% of our total electricity, and around 10% of our nation’s total power needs. In fact, the United States is the second largest producer of hydropower in the world, second only to Canada. Hydropower is considered a clean energy source because it does not contribute to air pollution, climate change, or ozone depletion.
Some other uses for dams include debris control and navigation.
Negative Effects of Dams
While our nation’s dams provide many benefits, they also cause many concerns. First, the cost of maintenance sometimes outweighs any positive impact the dam may provide. In addition, dams can also have a negative effect on the environment, and some pose serious hazard to people and property. By 2020, about 70% of our nation’s dams will be over 50 years old and will require significant rehabilitation and repair. In fact, the Association of State Dam Safety Officials has estimated that it could cost over $51 billion to rehabilitate our nation’s non-federally owned dams. Therefore, it is imperative that we consider all aspects of dams and their environmental, economic, and social impact before making any rehabilitation decisions.
Many dams continue to provide benefit to our nation and its communities, while others have simply outlived their useful function. In these cases, it makes sense to remove them rather than to pour increasingly dwindling funds into their repair. Since 1912, over 1,300 American dams have been removed, 62 of these being removed in 2015 alone.
Maintenance vs. Removal

Like all infrastructure, dams require routine and ongoing maintenance to keep them safe and functioning. Frequently, dams are allowed to deteriorate until they pose a threat to public safety, particularly when they have fallen out of usage. In these cases, it is prudent for dam owners to work with state and federal dam experts to determine whether it makes sense to simply remove the dam rather than repair it.
Environmental Impact
One of the most significant impacts that dams have on the environment is interference with migratory fish such as salmon. Dams block the migration of these fish to upstream spawning areas, while also limiting the movement of both sediment and woody debris necessary to the maintenance of downstream spawning grounds. Many environmental activists call for the removal of dams that interfere with fish spawn, citing disruption of local ecology. The good news is that once a dam is removed, species quickly return to their upstream spawning areas, regardless of the length of time that the dam has been in place.
Tourism

While dams provide significant recreational benefits, in some cases they can also hinder them. When a river is returned to its free-flowing state by dam removal, new recreational opportunities arise, including whitewater rafting, kayaking, and fly fishing. These activities can greatly benefit local economies by increasing tourism to these typically remote communities. Also, removing dams can increase the number of recreational and commercial fish species such as trout and salmon. Both commercial fisheries and recreational fishermen benefit from increased catch rates though additional revenue and increased tourism, respectively.
Decreased Cost-Effectiveness
Many aging dams were originally built to supply hydro power to nearby industrial facilities such as mills and factories, and they generate little electricity. Because the nation has shifted away from local power supply to a more regional production, the power generated by these older dams is expensive and, since many of the older factories and mills have permanently shut down, are oftentimes no longer even needed.
Cultural Implications
Many Native American populations place significant spiritual and cultural value on free-flowing rivers and the natural ecology, as evidenced by the long standoff between the federal government and the Standing Rock Sioux tribe. Because dams change the natural ecology and prohibit the free flow of rivers and waters, Native American tribes often view them in a negative light.
Property Value
Dams have the tendency to drive down property values, particularly smaller dams which are no longer used for their original purpose. These dams can present flood risk as well as lower water quality, and removal of these dams improves property values.
In Conclusion

The question remains: to remove or not to remove? The reality is that there is no easy or right answer. The decision on whether to repair or remove a dam is complex, and all contributing factors must be considered carefully before determining the best course of action. The decision must include weighing the current value of the dam, including its social and economic benefits, against the costs of upkeep and the detrimental effects of the dam on the environment. When the dam has little social or economic effect either way, the long-term costs of maintenance versus the cost of removal must be considered.
Thousands of American dams have aged to the point that they require significant repair, while scientific understanding of our world’s delicate ecology and has grown exponentially. Also, advances in economic methodology has highlighted the positive impact that dam removal can have on local and regional communities. Because of these modern-day shifts, it is often considered prudent to remove dams that no longer properly serve their original purpose. At the same time, dams that still function and provide important benefits such as irrigation and flood control are often repaired and maintained. The fact remains that the answer is not clear or definitive. All aspects of a dam, its location, original use, state of repair, social and cultural implications, and surrounding environment must be considered prior to determining the best course of action.
