As the days grow shorter and the air turns crisp, November offers a gentle reminder to pause and reflect. At Tata & Howard (T&H), this season is a time to express gratitude for the people and partnerships that support us and to recognize the essential work that keeps our communities thriving. Gratitude is at the heart of what we do, inspired by our deep appreciation for the vital natural resource we work every day to protect — from maintaining clean, reliable water systems to fostering a company culture grounded in collaboration, respect, and shared purpose.
This month, we’re embracing a “Month of Gratitude,” a celebration that acknowledges the human and technical sides of what we do. While Thanksgiving often sparks intentional reflection, our gratitude extends far beyond a single holiday. It’s a chance to highlight the unsung heroes, the behind-the-scenes processes, and the people who make our mission possible every day.
Behind the Tap
When people turn on the tap, they rarely think about what it takes to make that possible. At T&H, we’re grateful for not just the systems that deliver clean, safe water to every home and business, but for the dedicated teams who make it happen.
For example, something as routine as unidirectional flushing plays a crucial role in maintaining water quality. This process clears out sediment and improves system performance, keeping distribution networks running smoothly and giving our communities confidence in their water supply. While it’s easy to overlook these technical acts, they represent the behind-the-scenes dedication that defines our industry.
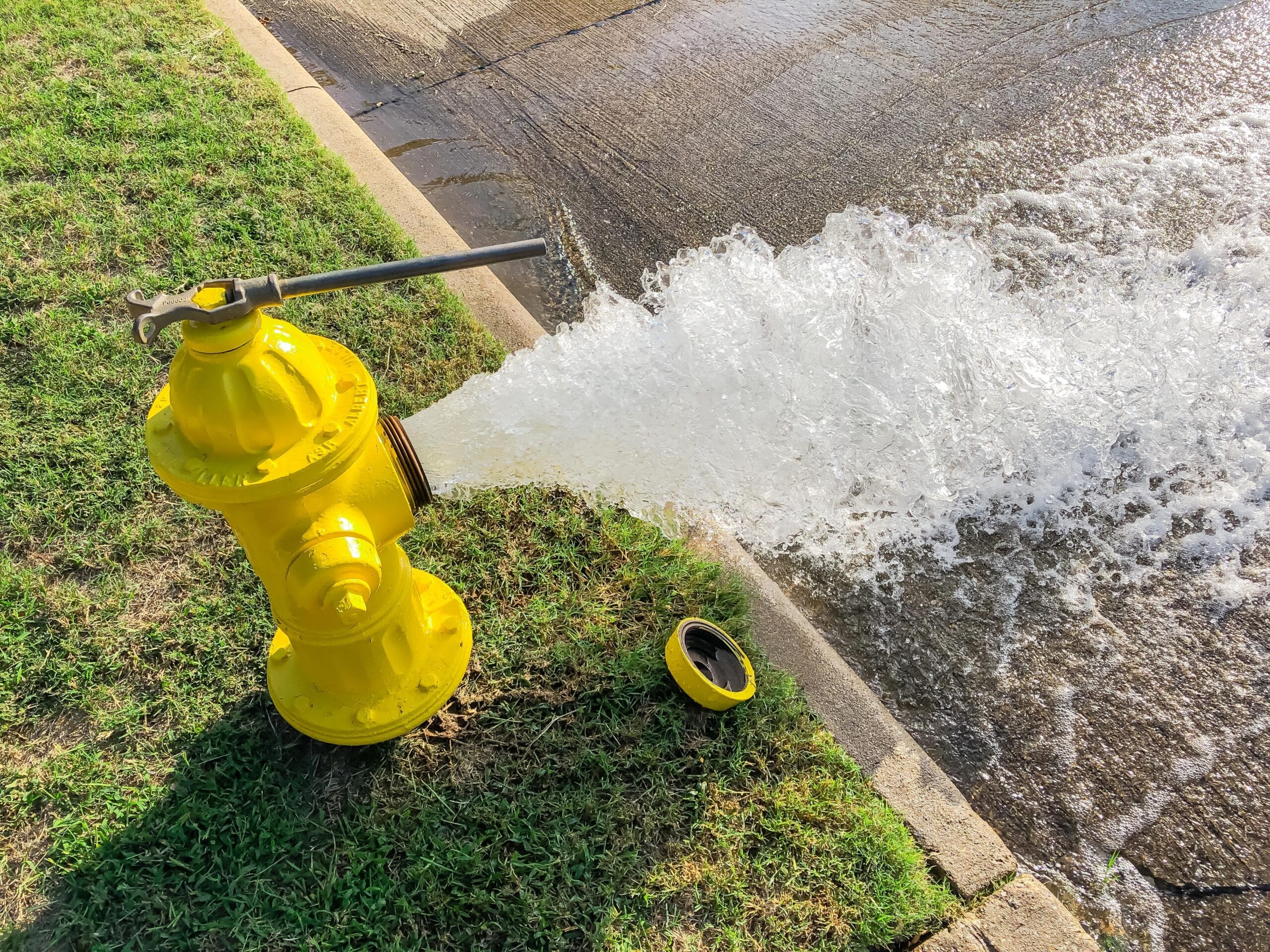

Being grateful for our community’s water infrastructure may sound unusual to most people, but for us, it’s about valuing the systems that keep us healthy and thriving. Each hydrant test, water main replacement, and treatment plant upgrade is a testament to intentional foresight and teamwork. While these efforts often take place behind the scenes, they ensure that clean water remains one of the most reliable and trusted public services.
Our People, Our Strength
Of course, our gratitude isn’t limited to just pipes and pumps. It also extends to the people who design, build, and maintain these systems, along with the communities that place their trust in us. Our ownership team exemplifies what it means to lead with integrity and shared responsibility. As an employee-owned company, T&H’s success is a collective achievement powered by a team that takes personal pride in its work. This culture of ownership strengthens our organization and also deepens our gratitude for one another.
Throughout November, we also reflect on the many relationships that shape our work. We’re thankful for our clients, whose collaboration and trust allow us to pursue meaningful solutions. We’re grateful for our partners who share our commitment to quality and sustainability. Most of all, we’re thankful for our colleagues — engineers, scientists, technicians, and support staff — who bring creativity, dedication, and heart to every project. Together, we build something greater than the sum of our parts.
Our gratitude also extends beyond our immediate circle to the communities we serve. Whether we’re improving water systems in a small town or enhancing infrastructure for a growing city, we’re reminded that our work has a lasting impact on people’s lives. Knowing that our efforts help ensure safe drinking water for families, schools, and businesses is profoundly rewarding. It’s what motivates us to innovate, collaborate, and keep learning.
Gratitude in Action
This “Month of Gratitude” also reminds us that appreciation and stewardship are interconnected. As we give thanks for the systems that sustain us, we also recognize that our responsibility to care for them goes hand-in-hand. It’s critical to remember that sustainability is not just a professional focus but a moral commitment. By promoting efficient water use, investing in resilient infrastructure, and adopting environmentally conscious practices, we express our gratitude through action, ensuring future generations inherit the same resources and opportunities we enjoy today.
Small Acts, Big Impact
Internally, our culture of gratitude shows up in a number of ways: in morning conversations over coffee, mentoring between colleagues, and shared pride when a project is complete. It’s in celebrating milestones and the collective support when faced with challenges. We believe that gratitude creates connection, and connection strengthens our ability to serve.
As we reflect on this month, we’re reminded that gratitude doesn’t have to be grand to be meaningful. Sometimes it’s as simple as appreciating the clarity of a well-maintained water line, the dedication of a field crew in challenging weather, or the innovation sparked in a brainstorming session. Other times, it’s about recognizing the values that guide us — collaboration, quality, and service — and the people who embody them each day.
Guided by Thanks
At T&H, gratitude is more than a seasonal sentiment. It’s a guiding principle that shapes our relationships, informs our decisions, and inspires our ongoing commitment to excellence. As we move through this month of reflection and thanks, we’re reminded that every drop of effort matters, from the precision of an engineering design to the trust of a lasting partnership.
So, this November, we pause to say thank you to our colleagues, clients, partners, and communities. We’re grateful for your trust, your collaboration, and your shared vision for a sustainable future. Together, we will continue to protect our most vital resource and the people who depend on it.
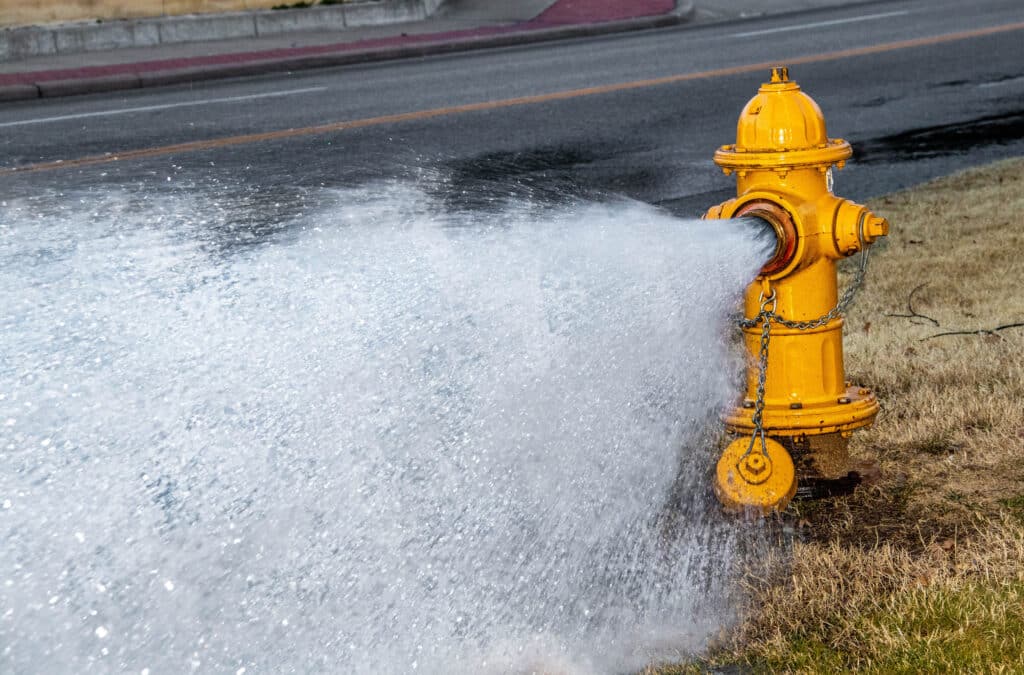



 How it Works
How it Works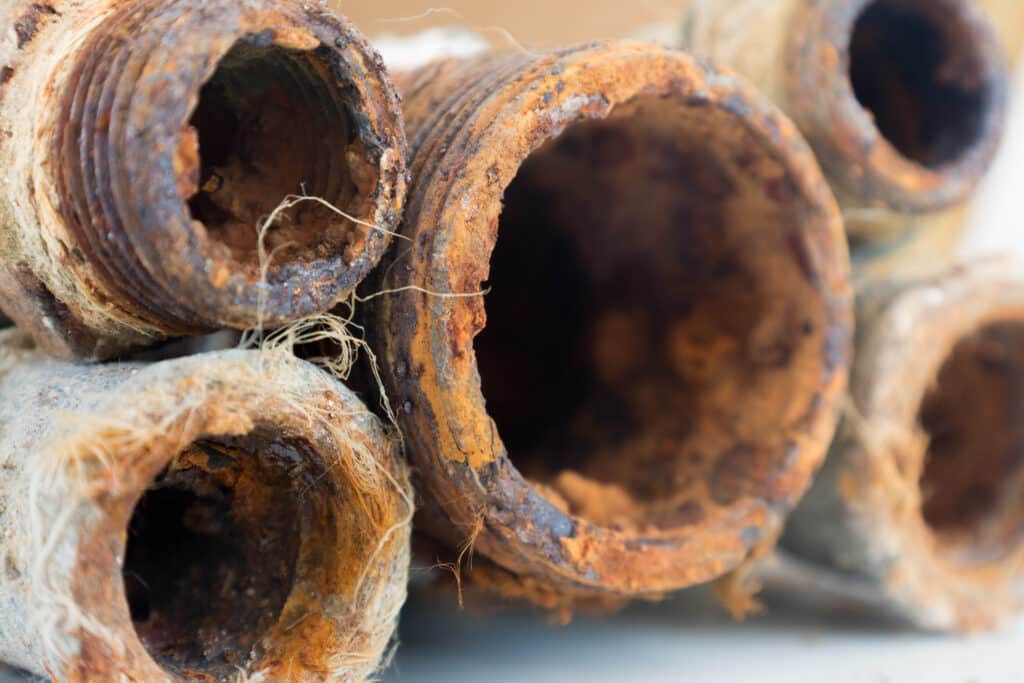 Preserving Aging Pipes
Preserving Aging Pipes Fall’s Perfect Timing: Why UDF Matters Most in the Heat
Fall’s Perfect Timing: Why UDF Matters Most in the Heat 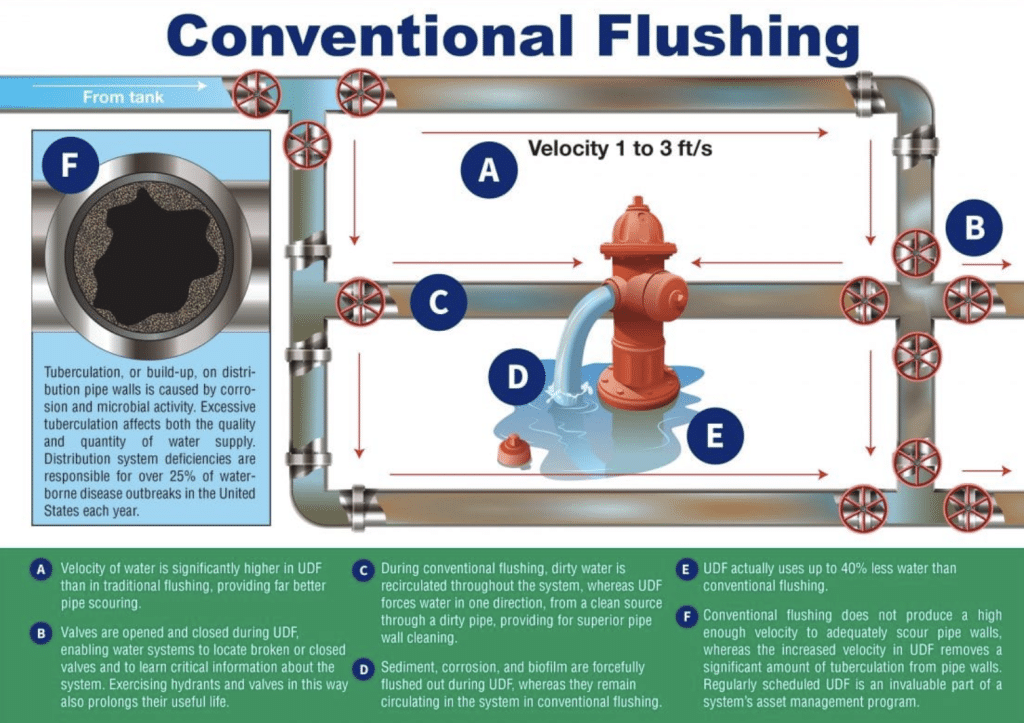
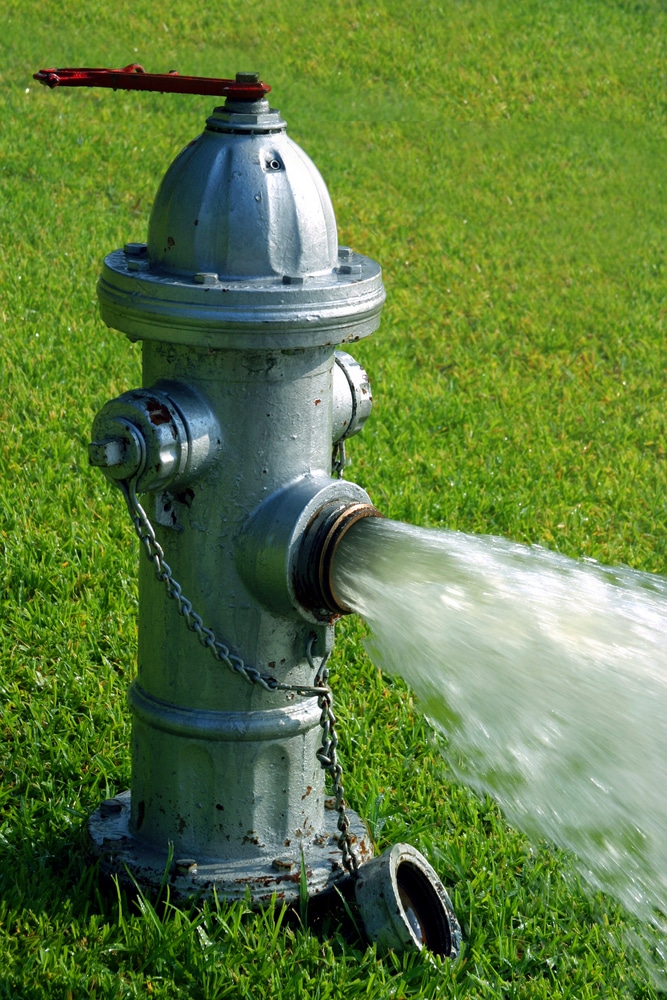
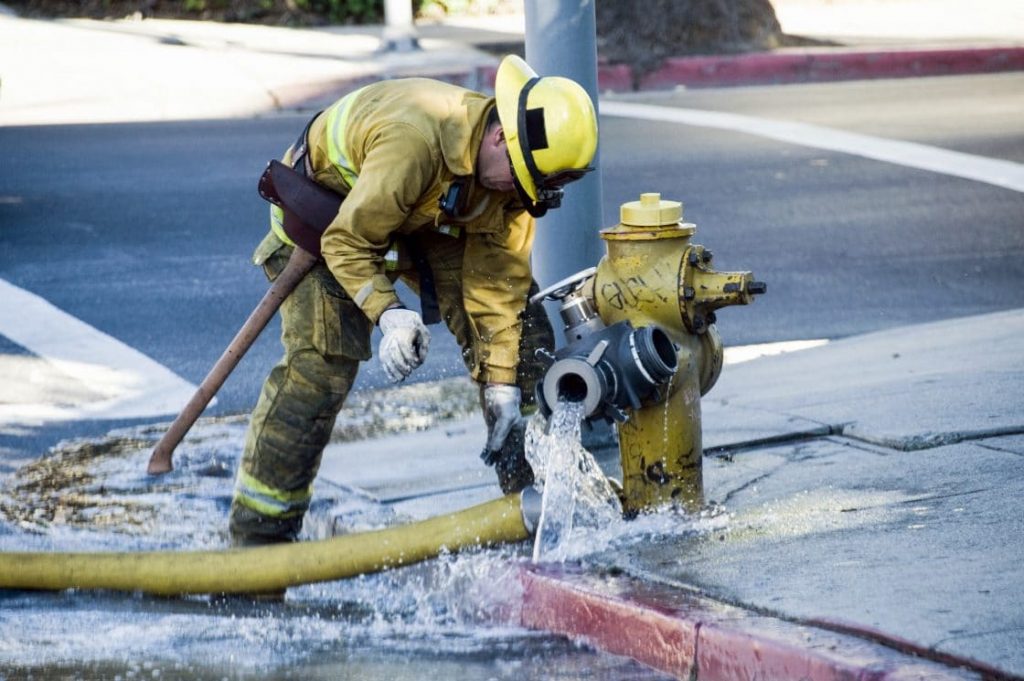
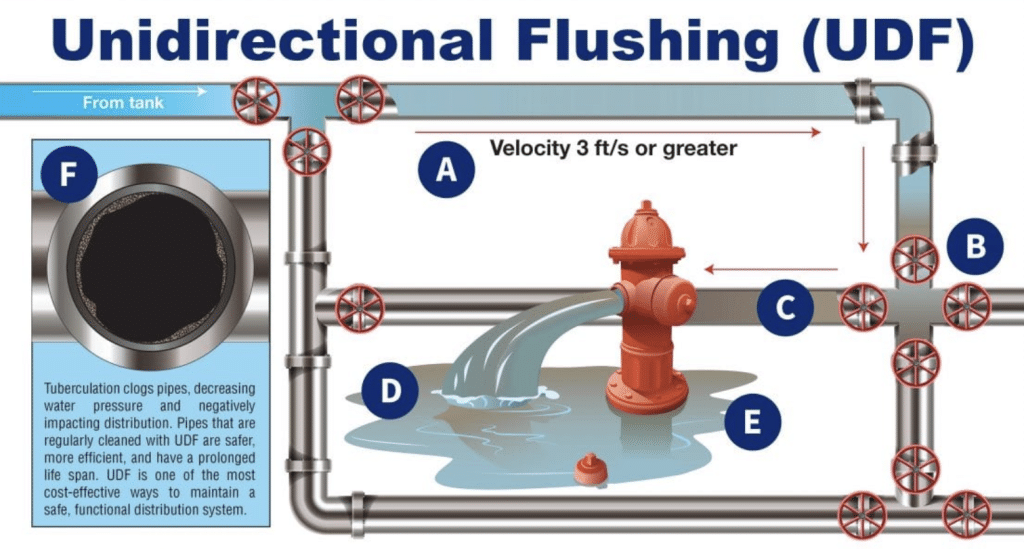



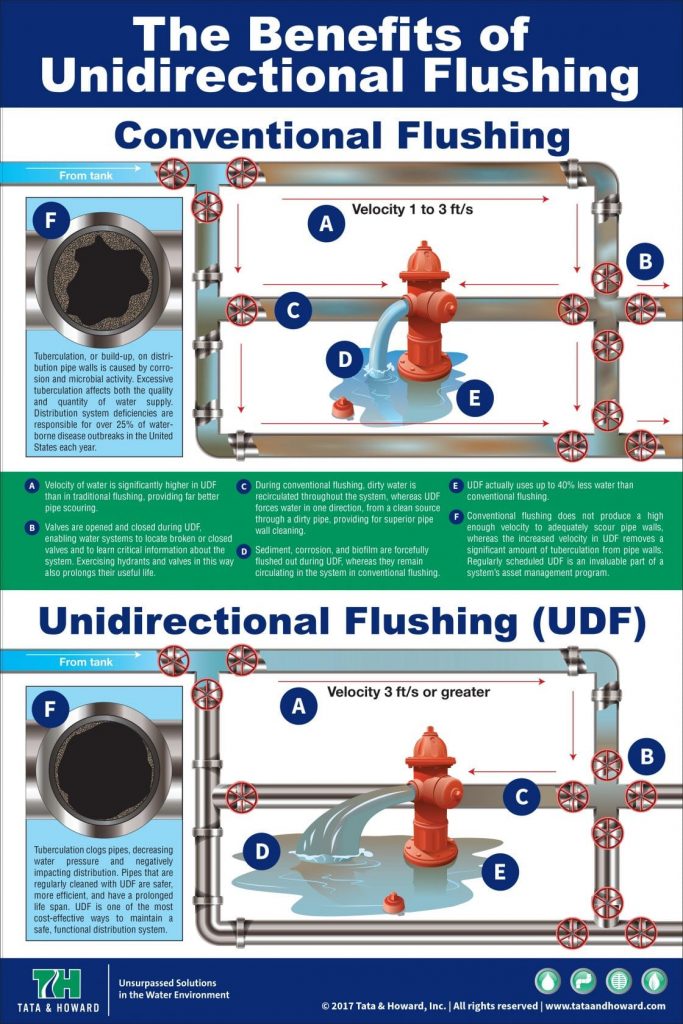
 Water utilities today are faced with a unique set of difficulties. Population growth has resulted in unprecedented demand while climate change has caused supply to dwindle. Increased regulations have forced utilities to invest more and more capital into treatment while budgets have shrunk. In addition, our nation’s aging infrastructure has forced water utilities to heavily invest in repair and replacement of the distribution system. Therefore, it has become critical that utilities utilize the most cost-effective and efficient methodologies in order to maintain and improve their water systems.
Water utilities today are faced with a unique set of difficulties. Population growth has resulted in unprecedented demand while climate change has caused supply to dwindle. Increased regulations have forced utilities to invest more and more capital into treatment while budgets have shrunk. In addition, our nation’s aging infrastructure has forced water utilities to heavily invest in repair and replacement of the distribution system. Therefore, it has become critical that utilities utilize the most cost-effective and efficient methodologies in order to maintain and improve their water systems.
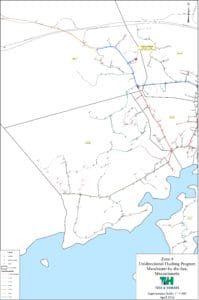 Because demand is highest in summer and would make flushing impractical, and low temperatures in winter would cause unsafe conditions from flushed water freezing on roadways and sidewalks, flushing is typically performed in the spring and fall. Currently, Tata & Howard is assisting the communities of Haverhill and Manchester By The Sea, MA and Norwalk First Taxing District in Norwalk, CT with their annual UDF Programs. Both AWWA and MassDEP recommend that UDF be performed on an annual basis, at a minimum. If a distribution system is too large to perform UDF annually, flushing should instead be scheduled in rotation so that all parts of the distribution system are exercised on a regular basis.
Because demand is highest in summer and would make flushing impractical, and low temperatures in winter would cause unsafe conditions from flushed water freezing on roadways and sidewalks, flushing is typically performed in the spring and fall. Currently, Tata & Howard is assisting the communities of Haverhill and Manchester By The Sea, MA and Norwalk First Taxing District in Norwalk, CT with their annual UDF Programs. Both AWWA and MassDEP recommend that UDF be performed on an annual basis, at a minimum. If a distribution system is too large to perform UDF annually, flushing should instead be scheduled in rotation so that all parts of the distribution system are exercised on a regular basis. With the beginning of each new year come all sorts of resolutions – to eat better, spend less, organize the house, and clean the garage. But the most commonly made resolution by far is to exercise to get into better shape. And while we agree with this resolution 100%, it may not be for the reasons you think. You see, we think you DO need to exercise – your fire hydrants!
With the beginning of each new year come all sorts of resolutions – to eat better, spend less, organize the house, and clean the garage. But the most commonly made resolution by far is to exercise to get into better shape. And while we agree with this resolution 100%, it may not be for the reasons you think. You see, we think you DO need to exercise – your fire hydrants!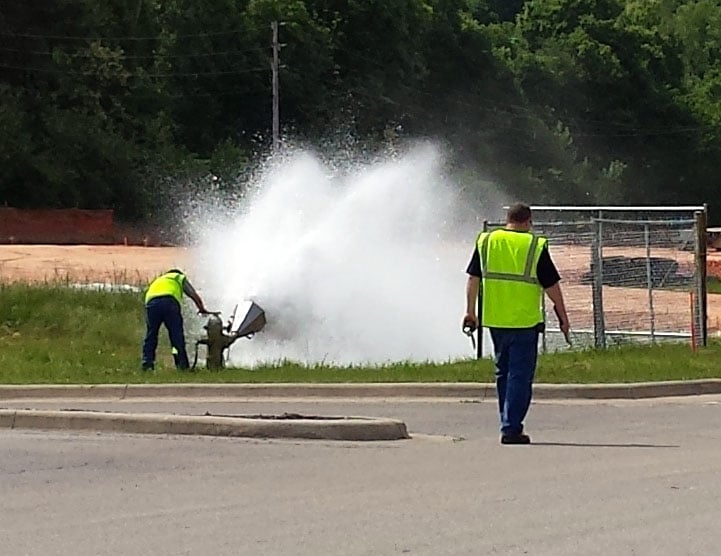 While the primary objective of unidirectional flushing is to clean mains, there are also many secondary goals and benefits. Exercising hydrants and valves prolongs the life of the valves while also locating closed or broken valves. In addition, flushing helps to narrow down a search area when trying to determine the cause of water quality or pressure issues in a specific area of the system. In a best case scenario, the flushing will actually alleviate the water quality issues by flushing out any debris or buildup that is causing the problem. Also, there are often discrepancies between the hydraulic model and the distribution system that can be discovered and addressed during flushing. Lastly, flushing helps to determine or disprove suspected system issues. Frequently, these issues are not of an emergency nature and can either be readily corrected during the flushing process or can be scheduled for repair at a convenient time, BEFORE they require critical attention.
While the primary objective of unidirectional flushing is to clean mains, there are also many secondary goals and benefits. Exercising hydrants and valves prolongs the life of the valves while also locating closed or broken valves. In addition, flushing helps to narrow down a search area when trying to determine the cause of water quality or pressure issues in a specific area of the system. In a best case scenario, the flushing will actually alleviate the water quality issues by flushing out any debris or buildup that is causing the problem. Also, there are often discrepancies between the hydraulic model and the distribution system that can be discovered and addressed during flushing. Lastly, flushing helps to determine or disprove suspected system issues. Frequently, these issues are not of an emergency nature and can either be readily corrected during the flushing process or can be scheduled for repair at a convenient time, BEFORE they require critical attention.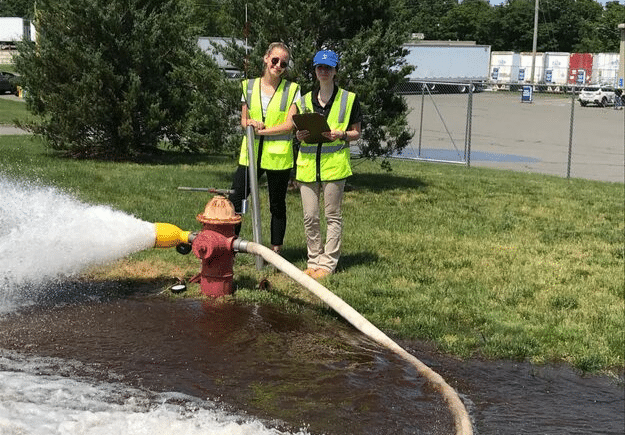 According to The American Water Works Association (AWWA), “distribution system deficiencies continue to be responsible for more then 25 percent of waterborne disease outbreaks in the United States each year, a statistic that underscores the need for water suppliers to effectively control water quality within the distribution system. Flushing is one of the most powerful tools available to a water utility for maintaining this control.” For this reason, AWWA has published a set of guidelines to follow when implementing a unidirectional flushing program. They recommend a minimum velocity of 3.0 feet per second, and also recommend that system pressure in the surrounding area maintain 20 psi, similar to the concept of adequate fire flow availability.
According to The American Water Works Association (AWWA), “distribution system deficiencies continue to be responsible for more then 25 percent of waterborne disease outbreaks in the United States each year, a statistic that underscores the need for water suppliers to effectively control water quality within the distribution system. Flushing is one of the most powerful tools available to a water utility for maintaining this control.” For this reason, AWWA has published a set of guidelines to follow when implementing a unidirectional flushing program. They recommend a minimum velocity of 3.0 feet per second, and also recommend that system pressure in the surrounding area maintain 20 psi, similar to the concept of adequate fire flow availability.