 Last month, Massachusetts Governor Deval Patrick signed into law the Commercial Food Waste Ban, which will go into effect on October 1, 2014. This law targets commercial institutions who produce more than one ton of organic waste per week, such as hospitals, restaurants, schools, hotels, and supermarkets. Once the ban takes effect, this waste food, which accounts for 25% of the waste stream in the Commonwealth, will need to be recycled rather than discarded. Recycling food waste has many advantages. First, it brings awareness to businesses to simply be more mindful in food ordering, preparation, and potential donation in order to decrease the overall amount of food waste they produce. Next, it decreases food waste in landfills, and thus mitigates the amount of greenhouse gas entering the atmosphere from decomposition. Finally, it provides a clean energy source. And that is something this country desperately needs.
Last month, Massachusetts Governor Deval Patrick signed into law the Commercial Food Waste Ban, which will go into effect on October 1, 2014. This law targets commercial institutions who produce more than one ton of organic waste per week, such as hospitals, restaurants, schools, hotels, and supermarkets. Once the ban takes effect, this waste food, which accounts for 25% of the waste stream in the Commonwealth, will need to be recycled rather than discarded. Recycling food waste has many advantages. First, it brings awareness to businesses to simply be more mindful in food ordering, preparation, and potential donation in order to decrease the overall amount of food waste they produce. Next, it decreases food waste in landfills, and thus mitigates the amount of greenhouse gas entering the atmosphere from decomposition. Finally, it provides a clean energy source. And that is something this country desperately needs.
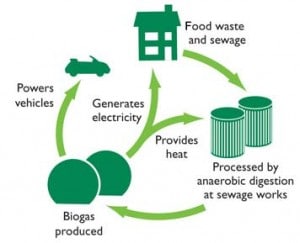
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is one way to dispose of organic waste that has the added benefit of producing clean energy. AD uses microbes to break down organic waste in an oxygen-deprived chamber, producing biogas, a clean and potent energy. Biogas is produced not just from food waste, but from any organic waste matter, including human waste, and is a clean energy option for heating and cooling, electricity, and powering vehicles. Wastewater treatment facilities that currently incorporate AD in their treatment processes could potentially be modified to handle food waste as well, and the Commonwealth is offering up $1M in grant funding for public facilities to do just that. In fact, the first grant of $100,000 has already been awarded to Massachusetts Water Resources Agency (MWRA) to process food waste at its wastewater treatment plant on Deer Island.

Connecticut and Vermont have passed similar laws, but they are using a more gradual approach. Both states currently only require businesses that are located within 20 miles of a suitable recycling facility and produce more than two tons of food waste per week to recycle, but expect full compliance by 2020. New York City is also implementing a food waste ban as a result of the success of its recently completed Food Waste Challenge, a six-month trial in which businesses voluntarily participated by donating unused food as well as diverting their scraps to a local treatment plant. The City noted that a key part of the initiative was food donation, as more than 25% of food waste diversion was a result of donations to local food banks. And businesses are supportive. Melissa Autilio Fleischut, president and CEO of the New York State Restaurant Association, commended the program and supported the litigation. “The Food Waste Challenge proves that sending less to landfills is good for both business and the planet,” Fleischut said in a press release. “The New York State Restaurant Association looks forward to working with the city to advance this initiative in a responsible way that works for everyone.”
On the other side of the country, waste-powered cars are swiftly becoming a reality. Hyundai, who has been working with the University of California, plans to begin leasing a fuel-cell version of its Tucson crossover that can travel about 480 kilometers on a tank of hydrogen, which is produced from AD and has zero emissions. The eco-friendly Tucson, which will only be available to California residents, has low lease rates which include free fuel from nearly a dozen hydrogen pumps around the state. Toyota, Honda, Mercedes-Benz and GM are starting to sell hydrogen cars in California as well.

California has long been a pioneer in green technologies. However, Massachusetts is the first state in the nation to actually implement a comprehensive ban on organic waste. While utilizing waste for energy has largely been voluntary and thus slow-moving, this legal mandate will force large-scale organic waste processing facilities into production, either through retrofitting of existing facilities or new construction. And these new processing centers will produce large amounts of biogas. So will the east coast finally start seeing the alternative fuel filling stations and vehicles that are currently reserved only for the west coast? Let’s hope so. If we could combine east coast legal mandates with west coast alternative fuel technology, the nation could see zero emissions vehicles running on discarded organic scraps and sewerage. Keep excess garbage from our landfills while powering pollutant-free vehicles? Now that’s a win-win.