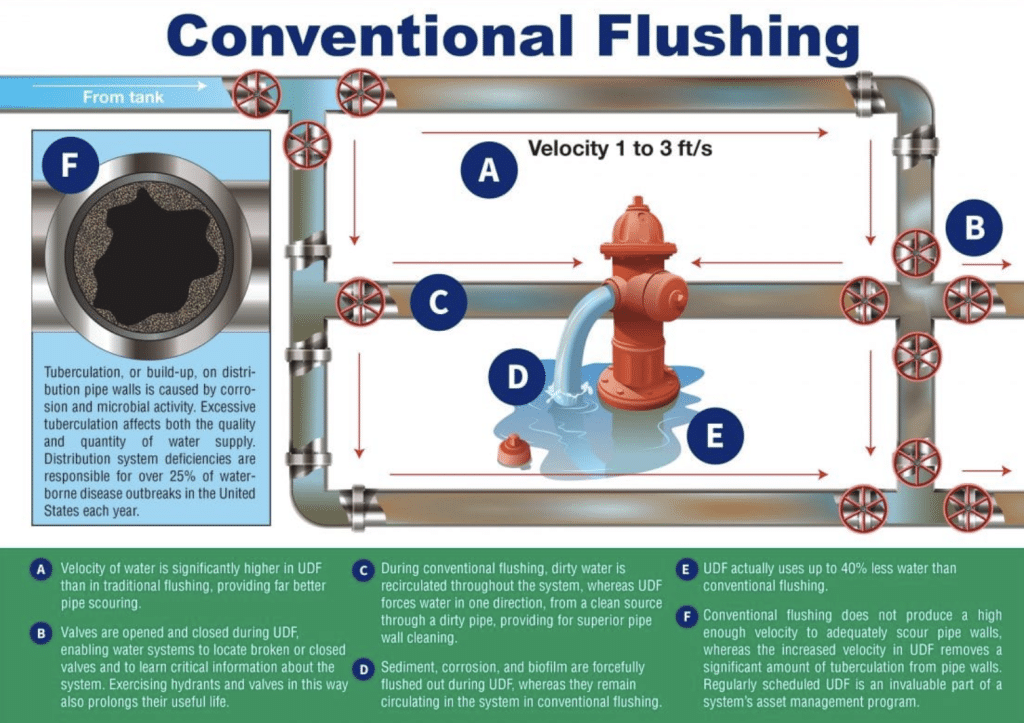
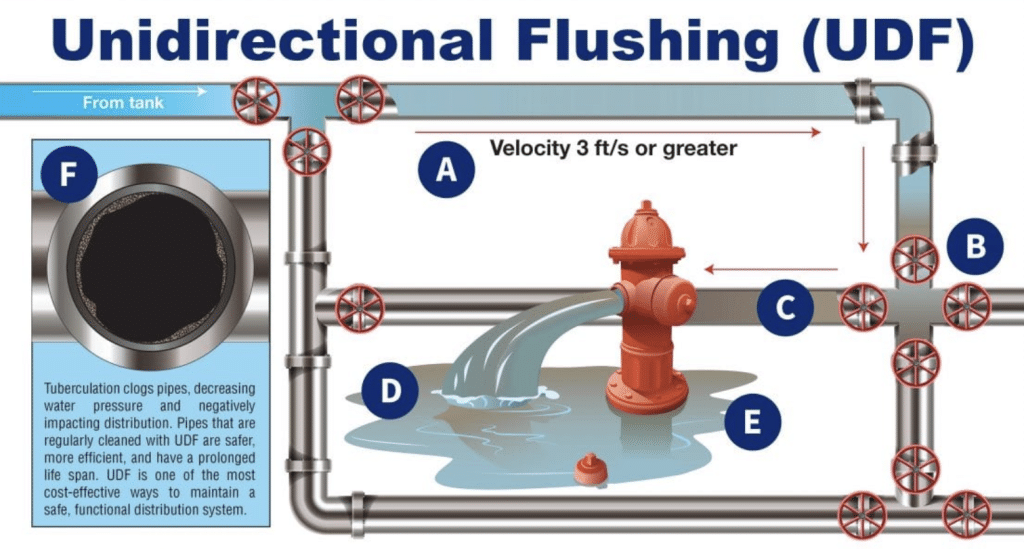
Perfluorinated alkyl substances, also known as PFAS, are a group of manufactured compounds that include perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS), perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), perffluorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS), perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA), perflouroheptanoic acid (PFHpA), and perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS). (Talk about a mouthful.)
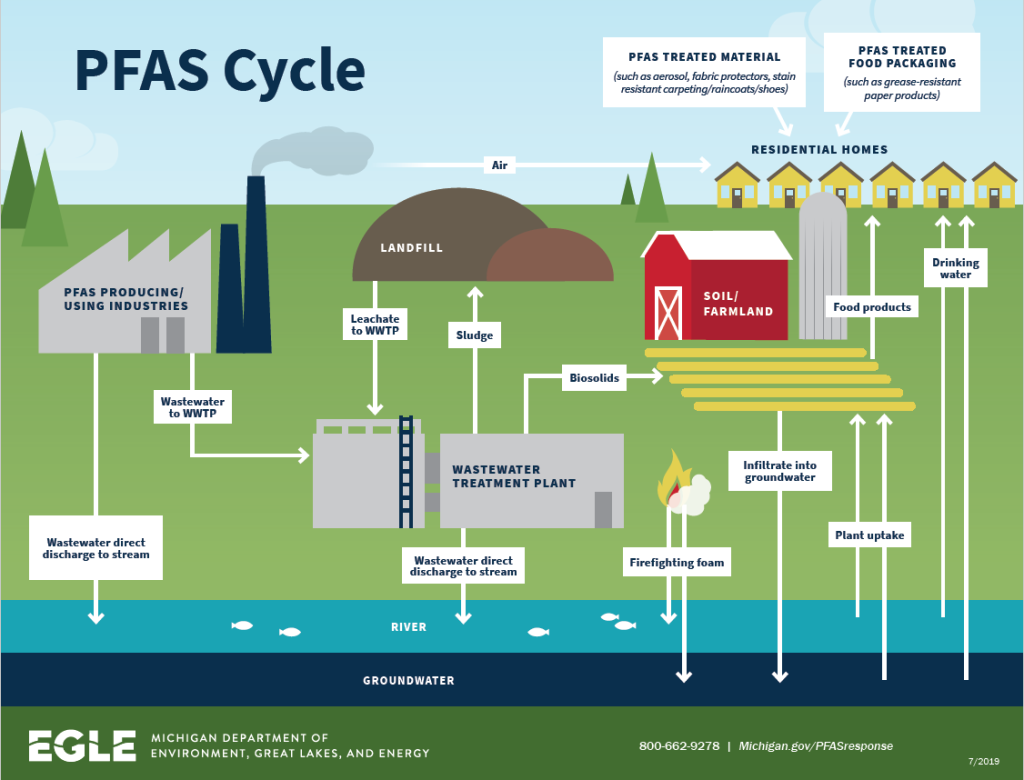 PFAS have been on the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) radar for quite some time now. The question is, why is the EPA so focused on these compounds? Well, for starters, they are human-made, widely used, and nearly impossible to dissolve and break down, which means that over time they start to spread and grow, more and more, both within the human body and in our environment. These compounds are also resistant to heat, oil, grease, and water, and —what’s worse — is that the EPA has found traces of all the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule 3 (UCMR 3) (i.e., the long p-words mentioned earlier) in our country’s water supply in recent years.
PFAS have been on the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) radar for quite some time now. The question is, why is the EPA so focused on these compounds? Well, for starters, they are human-made, widely used, and nearly impossible to dissolve and break down, which means that over time they start to spread and grow, more and more, both within the human body and in our environment. These compounds are also resistant to heat, oil, grease, and water, and —what’s worse — is that the EPA has found traces of all the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule 3 (UCMR 3) (i.e., the long p-words mentioned earlier) in our country’s water supply in recent years.
Even with a history of use dating back to the 1940s, these manufactured toxins are still considered emerging contaminants, meaning that there aren’t any already established regulatory limits for how much of these compounds can legally be in our drinking water. These seemingly forever-lasting compounds can in turn have adverse side effects and cause complications in our planet’s ecology and within the human body.
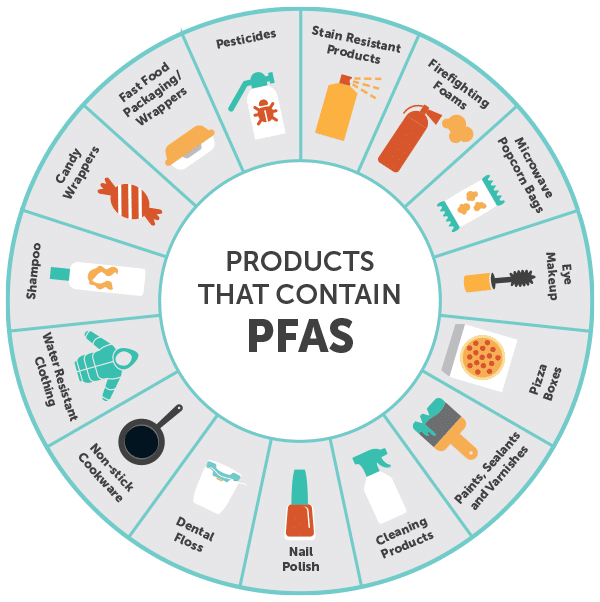 Today, PFAS can be found in the following:
Today, PFAS can be found in the following:
- PFAS-grown agricultural products result in contaminated soil, water, and/or handled with PFAS-containing equipment and materials.
- Drinking water contaminated from polluted groundwater from stormwater runoff near landfills, wastewater treatment plants, and firefighter training facilities.
- Household products, including nonstick products (e.g., Teflon), polishes, waxes, paints, cleaning products, and stain and water-repellent fabrics.
- Firefighting foams, which is a major source of groundwater contamination at airports and military bases where firefighting training occurs.
- Industrial facilities that utilize PFAS when manufacturing chrome plating, electronics, and oil recovery.
When looking at the bigger picture, it is clear there is an immense need and opportunity for further research to see how PFAS can affect humans, as most of the research so far has been in animals. While PFAS aren’t even manufactured in the country anymore (thankfully), they are just as present across the globe and are still shipped in products and food from overseas.
All of this is to show that PFAS are…definitely not something we want near our food, water, and goods. So what has the EPA been doing to help?
Well, in 2016, the EPA set Health Advisory (HA) levels of how many micrograms per liter (µg/L) for the combined concentrations of two PFAS compounds, PFOS and PFOA. The Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) also took action and established drinking water guidelines that were required to follow the EPA’s HA levels, but applied them to all five PFAS chemicals (PFOS, PFOA, PFNA, PFHXS, and PFHpA). If the level of risk was then raised due to potential health risks, the Public Water Systems (PWS) must take action in order to restore safe HA levels.
During the summer of 2022, the EPA announced four new drinking water health advisories for PFAS as part of President Biden’s action plan to deliver clean drinking water to the American people. In addition, a $1 billion grant (the first of $5 billion) has been offered to territories and states across the country to pay for quality water testing, technical assistance, contractor training, and more.
MassDEP, EPA, and other federal agencies have been continuing their testing and research on PFAS both in the lab and in the field, PWS have been running tests on local water, and partnerships have been made between MassDEP and PWS in order to identify areas where our environment has been affected by PFAS.
All seemingly good things.
So let’s repeat the question: what has the EPA been doing to help?
All of these efforts are necessary in order to begin to identify the presence and consequences of PFAS, restore clean drinking water, help those affected, and more. That said, we also must get to the root of the problem: we need corporations to end the manufacturing of man-made toxins and compounds.
 At the end of the day, our planet’s drinking water has been affected on a national and global level thanks to the work of PFAS manufacturers. People, animals, and our entire ecosystem have been tainted. Now, water utilities are tasked with cleaning up the mess (literally). Grants are helpful but they’re not guaranteed and, frankly, $1-5 billion isn’t nearly enough for testing on a national scale, which is necessary due to the almost 100 years of damage PFAS have caused.
At the end of the day, our planet’s drinking water has been affected on a national and global level thanks to the work of PFAS manufacturers. People, animals, and our entire ecosystem have been tainted. Now, water utilities are tasked with cleaning up the mess (literally). Grants are helpful but they’re not guaranteed and, frankly, $1-5 billion isn’t nearly enough for testing on a national scale, which is necessary due to the almost 100 years of damage PFAS have caused.
Water utilities are already at a disadvantage when it comes to limited capital resources and are not adequately equipped to fix contaminated waterways. The responsibility should fall on the corporations who created PFAS to help clean up our land and water. After all, they profited off the manufacturing of these compounds for years, while PWS are now left holding the bill.
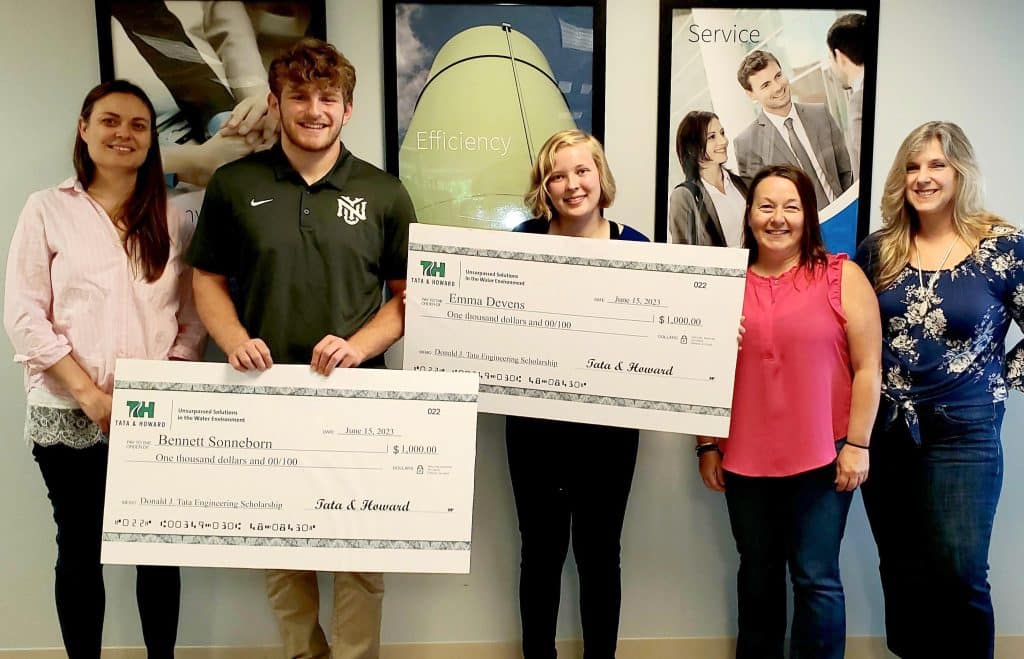

 Tata & Howard presented the Donald J. Tata Engineering Scholarship Award to two deserving high school seniors this spring: Bennett Sonneborn from Natick High School and Emma Devens from Marlborough High School. Both are pursuing engineering degrees and exhibited not only exemplary GPA and grades in their classes, but were also involved in extracurricular activites and philanthropic initiatives. We had so much fun presenting them their big checks, and we wish them all the best on their college journeys. In the fall, Bennett is attending New York University and Emma is attending the Rochester Institute of Technology.
Tata & Howard presented the Donald J. Tata Engineering Scholarship Award to two deserving high school seniors this spring: Bennett Sonneborn from Natick High School and Emma Devens from Marlborough High School. Both are pursuing engineering degrees and exhibited not only exemplary GPA and grades in their classes, but were also involved in extracurricular activites and philanthropic initiatives. We had so much fun presenting them their big checks, and we wish them all the best on their college journeys. In the fall, Bennett is attending New York University and Emma is attending the Rochester Institute of Technology.
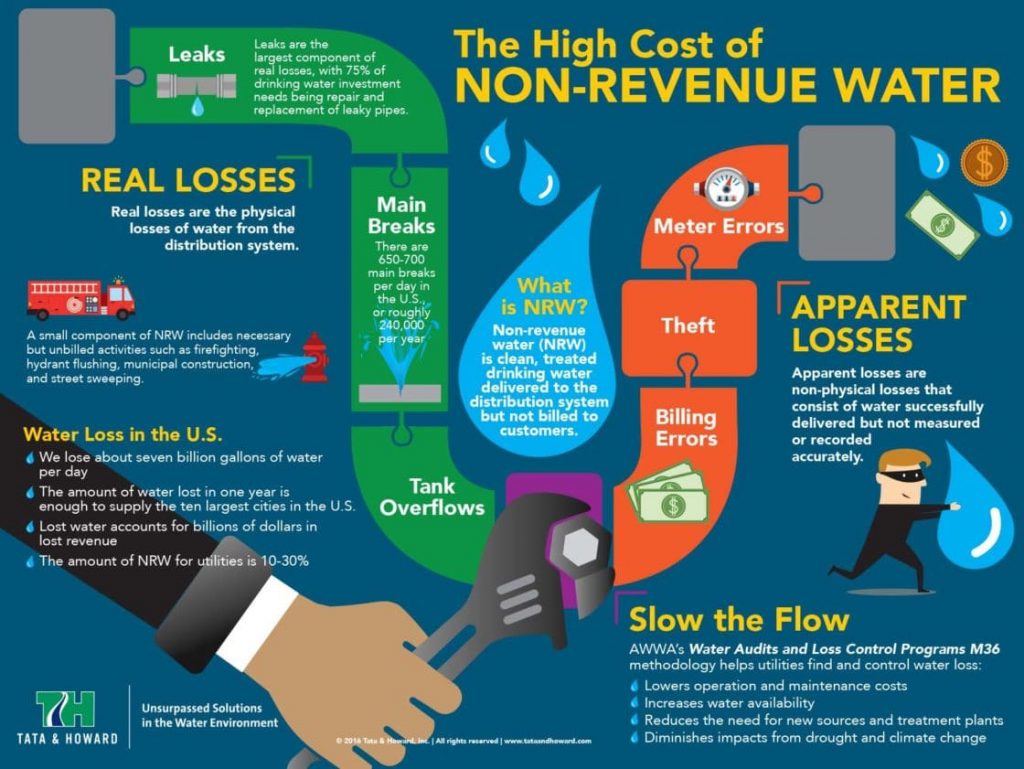
 Every year during the first week of May, the American Water Works Association (AWWA) and members of the water community celebrate Drinking Water Week, a week-long campaign dedicated to educating the public about the critical role clean water plays in our daily lives.
Every year during the first week of May, the American Water Works Association (AWWA) and members of the water community celebrate Drinking Water Week, a week-long campaign dedicated to educating the public about the critical role clean water plays in our daily lives.
 The Tata & Howard Capital Efficiency Plan (CEP) helps you do just that. Our CEP method is an accelerated and progressive approach to asset management. Our program allows municipalities, with the assistance and guidance of expert field staff and project managers, to do the following: (1) identify areas of their water, stormwater, and wastewater systems that are in need of repair, replacement, and/or rehabilitation; and (2) create a prioritized plan of action that is easily justified. In addition, the entire plan is conducted and completed in a way that makes the most bang out of municipalities’ limited infrastructure bucks.
The Tata & Howard Capital Efficiency Plan (CEP) helps you do just that. Our CEP method is an accelerated and progressive approach to asset management. Our program allows municipalities, with the assistance and guidance of expert field staff and project managers, to do the following: (1) identify areas of their water, stormwater, and wastewater systems that are in need of repair, replacement, and/or rehabilitation; and (2) create a prioritized plan of action that is easily justified. In addition, the entire plan is conducted and completed in a way that makes the most bang out of municipalities’ limited infrastructure bucks.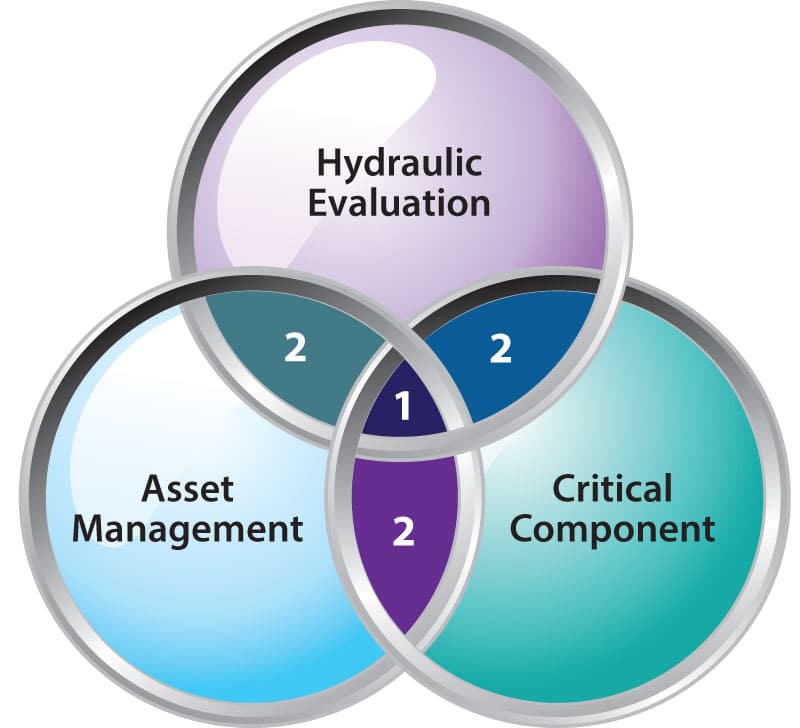 Once the plan is completed, systems receive their CEP report, complete with Geographic Information System (GIS) representation for each pipe segment within their individual underground piping system, along with a database. Each report will detail what issues are critical and should be prioritized, and includes estimated costs for the repairs, replacements, or rehabilitations that need to be made, so critical and less-critical projects alike can be part of the conversation when preparing annual budgets.
Once the plan is completed, systems receive their CEP report, complete with Geographic Information System (GIS) representation for each pipe segment within their individual underground piping system, along with a database. Each report will detail what issues are critical and should be prioritized, and includes estimated costs for the repairs, replacements, or rehabilitations that need to be made, so critical and less-critical projects alike can be part of the conversation when preparing annual budgets. It has been no secret that federal and state funding has been on a steady decline for several decades now, starting in the mid-1970s. With already limited funding, state and local governments are unable to meet full capital expenditures and to prioritize projects, and are frankly falling behind, leaving their residents to bear the burden of crumbling infrastructure.
It has been no secret that federal and state funding has been on a steady decline for several decades now, starting in the mid-1970s. With already limited funding, state and local governments are unable to meet full capital expenditures and to prioritize projects, and are frankly falling behind, leaving their residents to bear the burden of crumbling infrastructure. Asset management planning is absolutely critical to the current and future health and maintenance of our water supplies. This highly structured, three-circle approach to capital planning is one of the most effective ways for systems to conclusively prioritize those that are in most need of repair, replacement, or rehabilitation. Each CEP approach is specifically tailored to each project, as each system and project have varying needs.
Asset management planning is absolutely critical to the current and future health and maintenance of our water supplies. This highly structured, three-circle approach to capital planning is one of the most effective ways for systems to conclusively prioritize those that are in most need of repair, replacement, or rehabilitation. Each CEP approach is specifically tailored to each project, as each system and project have varying needs.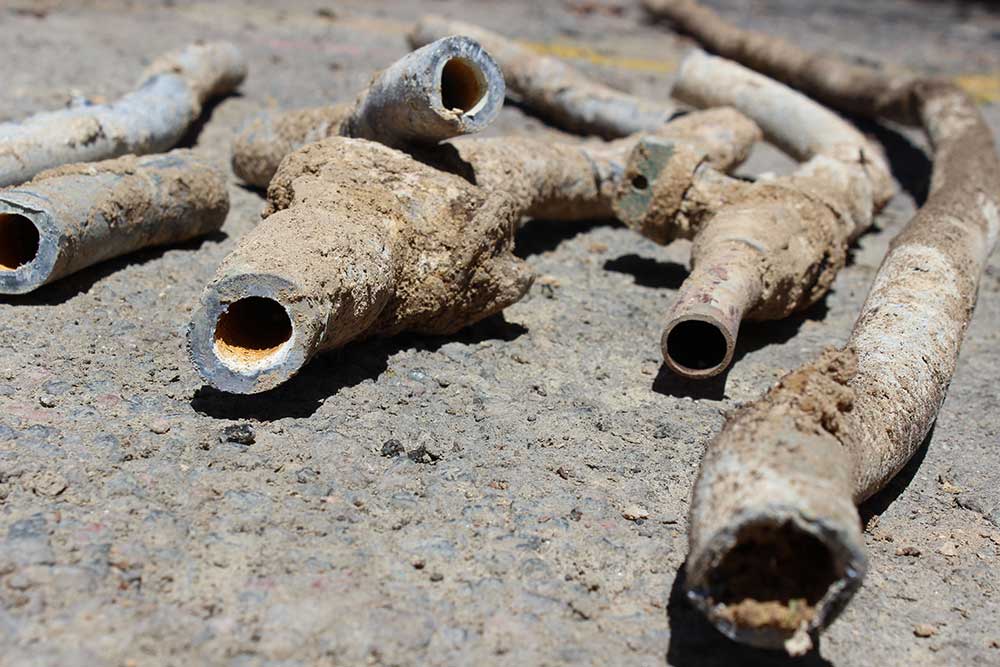 For example, in an effort to help remove lead pipes from Massachusetts turf, in the past we have partnered with the city of Marlborough, MA and
For example, in an effort to help remove lead pipes from Massachusetts turf, in the past we have partnered with the city of Marlborough, MA and For starters, let’s start with why lead is bad for us. Exposing one to lead, whether by contaminated drinking water or ingestion, can lead to severe brain and nervous system damage, kidney damage, can drastically affect children and those who are pregnant, and can cause death.
For starters, let’s start with why lead is bad for us. Exposing one to lead, whether by contaminated drinking water or ingestion, can lead to severe brain and nervous system damage, kidney damage, can drastically affect children and those who are pregnant, and can cause death.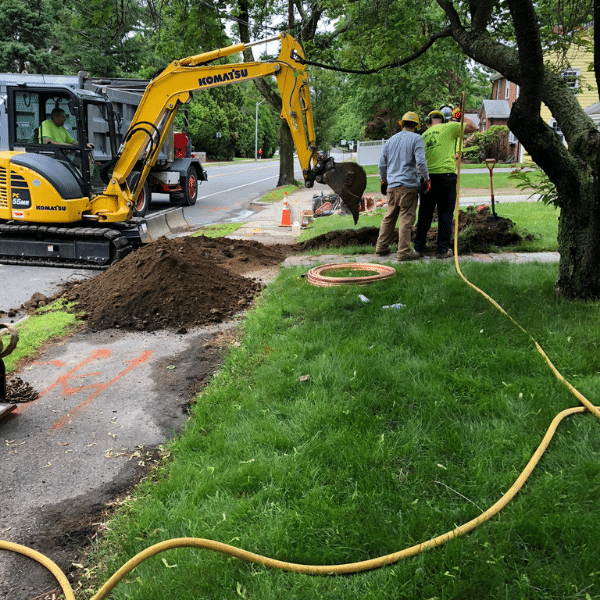
 PFAS have been on the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) radar for quite some time now. The question is, why is the EPA so focused on these compounds? Well, for starters, they are human-made, widely used, and nearly impossible to dissolve and break down, which means that over time they start to spread and grow, more and more, both within the human body and in our environment. These compounds are also resistant to heat, oil, grease, and water, and —what’s worse — is that the EPA has found traces of all the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule 3 (UCMR 3) (i.e., the long p-words mentioned earlier) in our country’s water supply in recent years.
PFAS have been on the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) radar for quite some time now. The question is, why is the EPA so focused on these compounds? Well, for starters, they are human-made, widely used, and nearly impossible to dissolve and break down, which means that over time they start to spread and grow, more and more, both within the human body and in our environment. These compounds are also resistant to heat, oil, grease, and water, and —what’s worse — is that the EPA has found traces of all the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule 3 (UCMR 3) (i.e., the long p-words mentioned earlier) in our country’s water supply in recent years. Today,
Today,  At the end of the day, our planet’s drinking water has been affected on a national and global level thanks to the work of PFAS manufacturers. People, animals, and our entire ecosystem have been tainted. Now, water utilities are tasked with cleaning up the mess (literally). Grants are helpful but they’re not guaranteed and, frankly, $1-5 billion isn’t nearly enough for testing on a national scale, which is necessary due to the almost 100 years of damage PFAS have caused.
At the end of the day, our planet’s drinking water has been affected on a national and global level thanks to the work of PFAS manufacturers. People, animals, and our entire ecosystem have been tainted. Now, water utilities are tasked with cleaning up the mess (literally). Grants are helpful but they’re not guaranteed and, frankly, $1-5 billion isn’t nearly enough for testing on a national scale, which is necessary due to the almost 100 years of damage PFAS have caused.