The Johnstown Flood of 1889
It had been raining heavily for several days in late May of 1889. People living below in the narrow Conemaugh Valley were eager for the spring rains to end. Just a month earlier, deep snow had lined the steep ravines of the Allegheny Mountains range and the ground was sodden with the heavy spring runoff. Floodwaters at the South Fork Dam high above the City of Johnstown, Pennsylvania were causing the lake level to rise, threatening to overtop the large earth embankment dam.
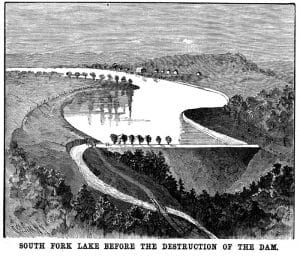 As the spring rains continued, life was about to change for the working-class city of 30,000 and other communities beneath the South Fork Dam.
As the spring rains continued, life was about to change for the working-class city of 30,000 and other communities beneath the South Fork Dam.
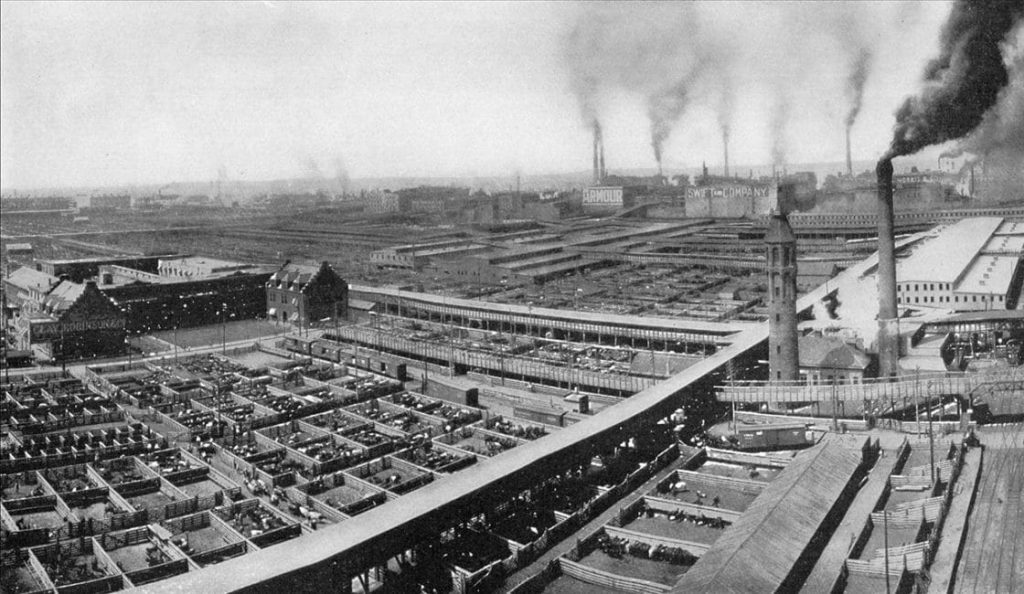
Originally constructed in 1852, the South Fork Dam provided a source of water for a division of the Pennsylvania Canal. After a minor breach in 1862, the dam was hastily rebuilt creating Lake Conemaugh. By 1881, the dam was owned and maintained by the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club, who created a recreational area by the large lake, enjoyed by their elite clientele from nearby Pittsburgh.
 For the pleasure of their private members, club owners soon began modifications to the dam. Fish screens were installed across the spillway to keep the expensive game fish from escaping. The dam was lowered by a few feet so that two carriages could navigate the carriage road to the clubhouse. Relief pipes and valves that controlled the water level and spill off from the original dam were sold off for scrap, and rustic cottages were built nearby.
For the pleasure of their private members, club owners soon began modifications to the dam. Fish screens were installed across the spillway to keep the expensive game fish from escaping. The dam was lowered by a few feet so that two carriages could navigate the carriage road to the clubhouse. Relief pipes and valves that controlled the water level and spill off from the original dam were sold off for scrap, and rustic cottages were built nearby.
Ignored Warnings
Notoriously leaky, repairs to the earthen dam had been neglected for years. As torrential rains came down, swollen waters from the lake put tremendous pressure on the poorly maintained dam. With fish screens trapping debris that kept the spillway from flowing and with no other way to control the lake level, the water kept rising.
 Club officials struggled to reinforce the earthen dam, but it continued to disintegrate. When the lake’s water began to pour over the top, it was apparent that a catastrophic collapse was inevitable and imminent. Frantic riders were sent down the valley to alert the local communities and tell them to evacuate. Sadly, few residents heeded the alarm being so often used to the minor seasonal flooding from the Little Conemaugh river.
Club officials struggled to reinforce the earthen dam, but it continued to disintegrate. When the lake’s water began to pour over the top, it was apparent that a catastrophic collapse was inevitable and imminent. Frantic riders were sent down the valley to alert the local communities and tell them to evacuate. Sadly, few residents heeded the alarm being so often used to the minor seasonal flooding from the Little Conemaugh river.
This time, however, the flood danger was much more serious and deadly.
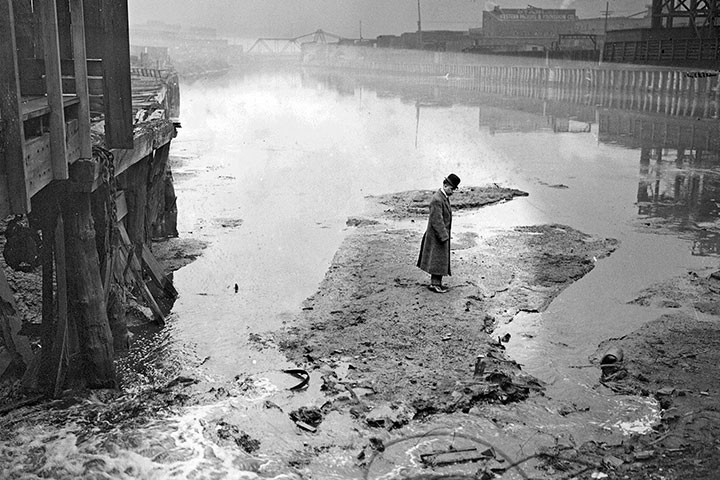
On May 31, 1889 at 3:10pm, the South Fork Dam washed away, leaving a wake of destruction that killed 2,209 people and wiped the City of Johnstown off the map forever. It took only 10 minutes for the raging torrent of 20 million tons or about 4.8 billion gallons of water to rip through the communities of South Fork, Mineral Point, Woodvale, and East Conemaugh.
 Along the way, the deluge accumulated everything in its path, including all sorts of debris—from city buildings, houses, and barns. Piles of boulders, trees, farm equipment, rolls of barbed wire, horse carriages, and railroad cars churned in the turmoil. Embroiled in the devastation were also animals and people—both dead and alive.
Along the way, the deluge accumulated everything in its path, including all sorts of debris—from city buildings, houses, and barns. Piles of boulders, trees, farm equipment, rolls of barbed wire, horse carriages, and railroad cars churned in the turmoil. Embroiled in the devastation were also animals and people—both dead and alive.
By the time the raging waters reached Johnstown at 4:07 pm, the mass of debris was a wave 45-feet-tall, nearly a half mile wide and traveling at 40 miles per hour.
Despite the shocking immensity of this tragedy, relief efforts to the ravaged communities began almost immediately. Emergency shelters for homeless residents popped up and the grim task of cleaning up began. Volunteers and donations poured in from across the country and world, sending tons of supplies and help. One of the first to arrive was Clara Barton, who had founded the American Red Cross just a few years earlier.
 It would take months to sift through all the wreckage to find the bodies and years to fully recover from the aftermath.
It would take months to sift through all the wreckage to find the bodies and years to fully recover from the aftermath.
Lessons Learned
It is widely thought the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club was to blame for the catastrophic failure of the South Fork Dam. Members of the club neglected to properly maintain the dam and made numerous dangerous modifications. Lowering the dam crest to only about four feet above the spillway severely impaired the ability of the structure to withhold stormwater overflow. The missing discharge pipes and relief valves prevented the reservoir from being drained for repairs and the elaborate fish screens clogged the spillway with debris. The club had also been warned by engineers that the dam was unsafe.
 A hydraulic analysis published in 2016 confirmed what had long been suspected, that the changes made to the dam by the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club severely reduced the ability of the dam to withstand major storms.1
A hydraulic analysis published in 2016 confirmed what had long been suspected, that the changes made to the dam by the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club severely reduced the ability of the dam to withstand major storms.1
The South Fork Dam was simply unable to withstand the large volume of stormwater that occurred on that fateful day on May 31, 1889.
Although the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club failed to maintain the dam, club members were never legally held responsible for the Johnstown Flood after successfully arguing that the disaster was an “act of God.”
Due to what many perceived as an injustice and outrage towards the wealthy club members, American law was ultimately challenged and “a non-negligent defendant could be held liable for damage caused by the unnatural use of land”. This legal action eventually imposed laws for the acceptance of strict liability for damages and loss.
National Dam Safety Awareness Day
On May 31st, we commemorate the catastrophic failure of the South Fork Dam by recognizing this day as National Dam Safety Awareness Day.
The Johnstown flood or the Great Flood of 1889, as it was later known as, was the single deadliest disaster in the U.S at the time. This tragedy, 129 years later, is still a harsh reminder of the critical importance of the proper maintenance and safe operation of dams.
Earth embankment dams may fail due to overtopping by flood water, erosion of the spillway discharge channel, seepage, settling, and cracking or movement of the embankment.
Routine dam evaluations and inspections, as required by law, can identify problems with dams before conditions become unsafe. Dams embankments, gatehouses and spillways, like other structures, can deteriorate due to weather, vandalism, and animal activity. Qualified engineering firms can perform soil borings, soil testing, stability analyses, hydrologic and hydraulic modeling for evaluating spillway sizing and downstream hazard potential, arrange for under water inspections by divers, permitting, and assistance in applying for funding for repairs. Also required, are Emergency Action Plans (EAP) that identifies potential emergency conditions and specifies preplanned actions to be followed in the case of a dam failure to minimize property damage or loss of life.
The required frequency of dam inspections will vary depending on the state, but generally are based on hazard classification, with high hazard dams requiring more frequent inspection. Generally dam inspections should be performed every two years for high hazard dams, unless the state requires more frequent inspections. The best time of year for inspections is in the fall, when reservoir levels are typically low, and when foliage and tree leaves are reduced, allowing improved visibility around the dam.
A wealth of information on dam safety awareness, can be found at the Association of State Dam Safety Officials website
1Wikipedia.com



 T&H kicked off EOM with our Employee Breakfast & Presentation on October 1st. We are encouraging our employees to participate in weekly hosted games and activities to gain points for their teams – which will be modeled after the Houses of Harry Potter’s Hogwarts School. The House with the most points at the end of the month will win the House Cup! Other fun activities include a cornhole tournament, poker night, lunchtime Jeopardy, pumpkin decorating, the firm’s Anniversary Lunch, and wrapping up with the Pie in the Eye Day.
T&H kicked off EOM with our Employee Breakfast & Presentation on October 1st. We are encouraging our employees to participate in weekly hosted games and activities to gain points for their teams – which will be modeled after the Houses of Harry Potter’s Hogwarts School. The House with the most points at the end of the month will win the House Cup! Other fun activities include a cornhole tournament, poker night, lunchtime Jeopardy, pumpkin decorating, the firm’s Anniversary Lunch, and wrapping up with the Pie in the Eye Day.
 The most alarming news is the hottest temperature ever reliably recorded reached 124.3 degrees in Algeria this July.
The most alarming news is the hottest temperature ever reliably recorded reached 124.3 degrees in Algeria this July. Wastewater treatment plants that use aerobic bacteria must provide oxygen with huge and costly electrically powered blowers for these microorganisms to survive. Anaerobic bacteria treatment processes do not need oxygen and use considerably less energy, making the wastewater treatment process more economical to operate. In addition to saving money, engineers believe these anaerobes can filter household and industrial chemicals better than conventional treatment plants.
Wastewater treatment plants that use aerobic bacteria must provide oxygen with huge and costly electrically powered blowers for these microorganisms to survive. Anaerobic bacteria treatment processes do not need oxygen and use considerably less energy, making the wastewater treatment process more economical to operate. In addition to saving money, engineers believe these anaerobes can filter household and industrial chemicals better than conventional treatment plants.

 When NASA recently announced the discovery of liquid water flowing under an ice cap on Mars, it opened the exciting possibility that life may exist outside our earthly abode. While it is conceivable scientists may eventually discover life somewhere in our galaxy, a reliable source of water outside earth is fundamental for the possibility of establishing a colony on Mars, exploring the universe and even visiting distant planets in search of life outside earth.
When NASA recently announced the discovery of liquid water flowing under an ice cap on Mars, it opened the exciting possibility that life may exist outside our earthly abode. While it is conceivable scientists may eventually discover life somewhere in our galaxy, a reliable source of water outside earth is fundamental for the possibility of establishing a colony on Mars, exploring the universe and even visiting distant planets in search of life outside earth. But hauling tons of supplies and materials to the International Space Station (ISS) is inefficient and extremely expensive. Sustaining a crew of four astronauts on the ISS with water, power and other supplies, costs nearly one million dollars a day. Even with the reusable SpaceX rocket which regularly provides supplies to the ISS, it costs $2,500 per pound to launch into space. With four astronauts living on the ISS needing approximately 12 gallons of water a day, it is impractical to stock the ISS with the tons of water needed for long periods of time.
But hauling tons of supplies and materials to the International Space Station (ISS) is inefficient and extremely expensive. Sustaining a crew of four astronauts on the ISS with water, power and other supplies, costs nearly one million dollars a day. Even with the reusable SpaceX rocket which regularly provides supplies to the ISS, it costs $2,500 per pound to launch into space. With four astronauts living on the ISS needing approximately 12 gallons of water a day, it is impractical to stock the ISS with the tons of water needed for long periods of time. If the idea of drinking reclaimed water from mice urine and other waste sources sounds unappetizing, consider this, the water the astronauts drink is often cleaner that what many earthlings drink. NASA regularly checks the water quality and it is monitored for bacteria, pollutants and proper pH (60 – 8.5).
If the idea of drinking reclaimed water from mice urine and other waste sources sounds unappetizing, consider this, the water the astronauts drink is often cleaner that what many earthlings drink. NASA regularly checks the water quality and it is monitored for bacteria, pollutants and proper pH (60 – 8.5). Recently, NASA invested in a new, lower cost solution to biologically recycle and reuse water developed by
Recently, NASA invested in a new, lower cost solution to biologically recycle and reuse water developed by  Pancopia is currently working on a similar system used on the ISS for municipal wastewater facilities. Using the technology developed for the Space Station, other areas in the world with limited access to clean drinking water, will soon be able to utilize this advanced water filtration and purification system.
Pancopia is currently working on a similar system used on the ISS for municipal wastewater facilities. Using the technology developed for the Space Station, other areas in the world with limited access to clean drinking water, will soon be able to utilize this advanced water filtration and purification system.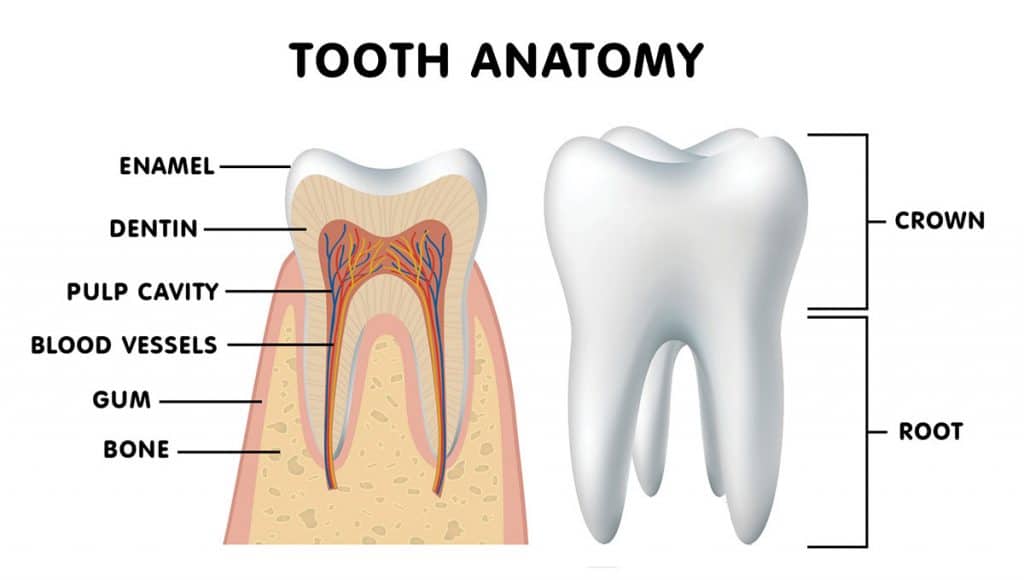 Even so, that millimeter of enamel making up the outer part of the tooth is the hardest substance of the human body and can outlast even the human skeleton when interred. In fact, the oldest vertebrate fossil relics going back 500 million years are teeth. Despite these details, teeth can be surprisingly fragile and prone to decay.
Even so, that millimeter of enamel making up the outer part of the tooth is the hardest substance of the human body and can outlast even the human skeleton when interred. In fact, the oldest vertebrate fossil relics going back 500 million years are teeth. Despite these details, teeth can be surprisingly fragile and prone to decay. Still, with these advances in dentistry, tooth loss and decay persisted. Since ancient times, it was widely thought that toothaches were caused by worms that destroyed teeth. It wasn’t until 1890, when a dentist named Willoughby Miller identified that tooth decay was caused by a certain type of bacteria that thrives on sugar, creating an acid that ate away at tooth enamel.
Still, with these advances in dentistry, tooth loss and decay persisted. Since ancient times, it was widely thought that toothaches were caused by worms that destroyed teeth. It wasn’t until 1890, when a dentist named Willoughby Miller identified that tooth decay was caused by a certain type of bacteria that thrives on sugar, creating an acid that ate away at tooth enamel.

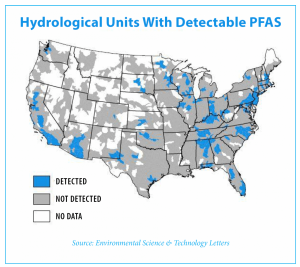 According the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all these UCMR 3 PFAS compounds have been detected in public water supplies across the US. Since PFAS are considered emerging contaminants, there are currently no established regulatory limits for levels in drinking water. However, in 2016, the EPA set Health Advisory levels (HA) of 0.07 micrograms per liter (µg/L) or 70 parts per trillion (ppt) for the combined concentrations of two PFAS compounds, PFOS and PFOA.
According the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all these UCMR 3 PFAS compounds have been detected in public water supplies across the US. Since PFAS are considered emerging contaminants, there are currently no established regulatory limits for levels in drinking water. However, in 2016, the EPA set Health Advisory levels (HA) of 0.07 micrograms per liter (µg/L) or 70 parts per trillion (ppt) for the combined concentrations of two PFAS compounds, PFOS and PFOA. The EPA also recommends that treatment be implemented for all five PFAS when one or more of these compounds are present.
The EPA also recommends that treatment be implemented for all five PFAS when one or more of these compounds are present. Most research on the effects of PFAS on human health is based on animal studies. And, although there is no conclusive evidence that PFAS cause cancer, animal studies have shown there are possible links. However, PFAS ill-health effects are associated with changes in thyroid, kidney and liver function, as well as affects to the immune system. These chemicals have also caused fetal development effects during pregnancy and low birth weights.
Most research on the effects of PFAS on human health is based on animal studies. And, although there is no conclusive evidence that PFAS cause cancer, animal studies have shown there are possible links. However, PFAS ill-health effects are associated with changes in thyroid, kidney and liver function, as well as affects to the immune system. These chemicals have also caused fetal development effects during pregnancy and low birth weights.
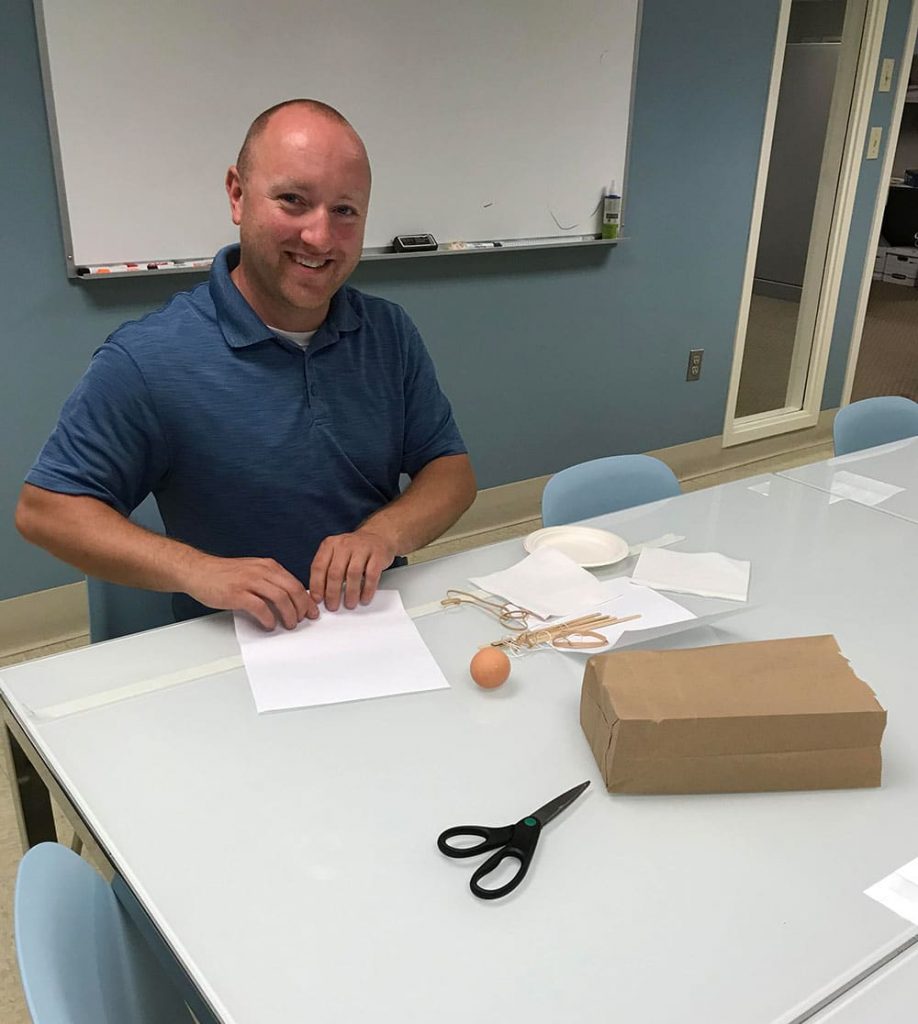
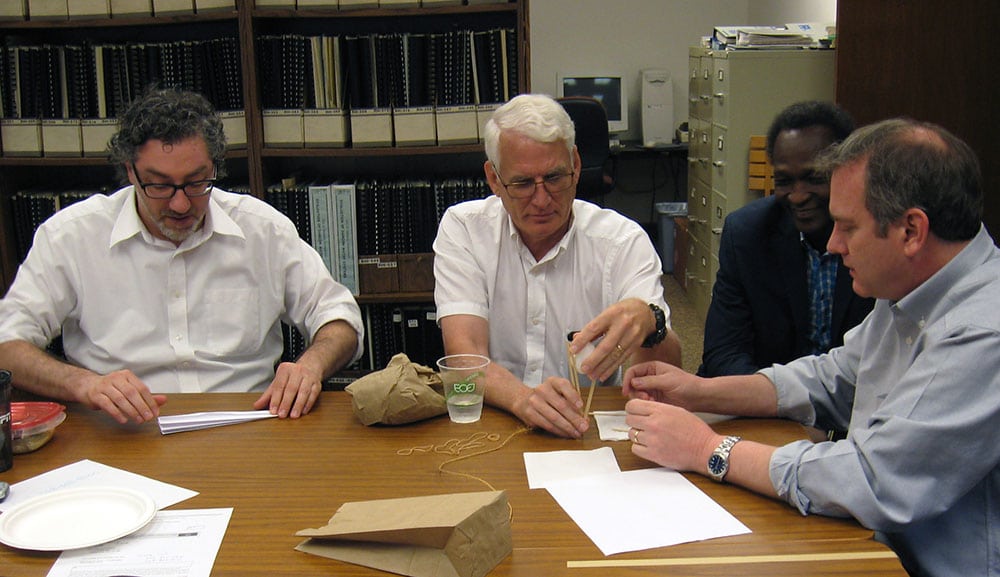
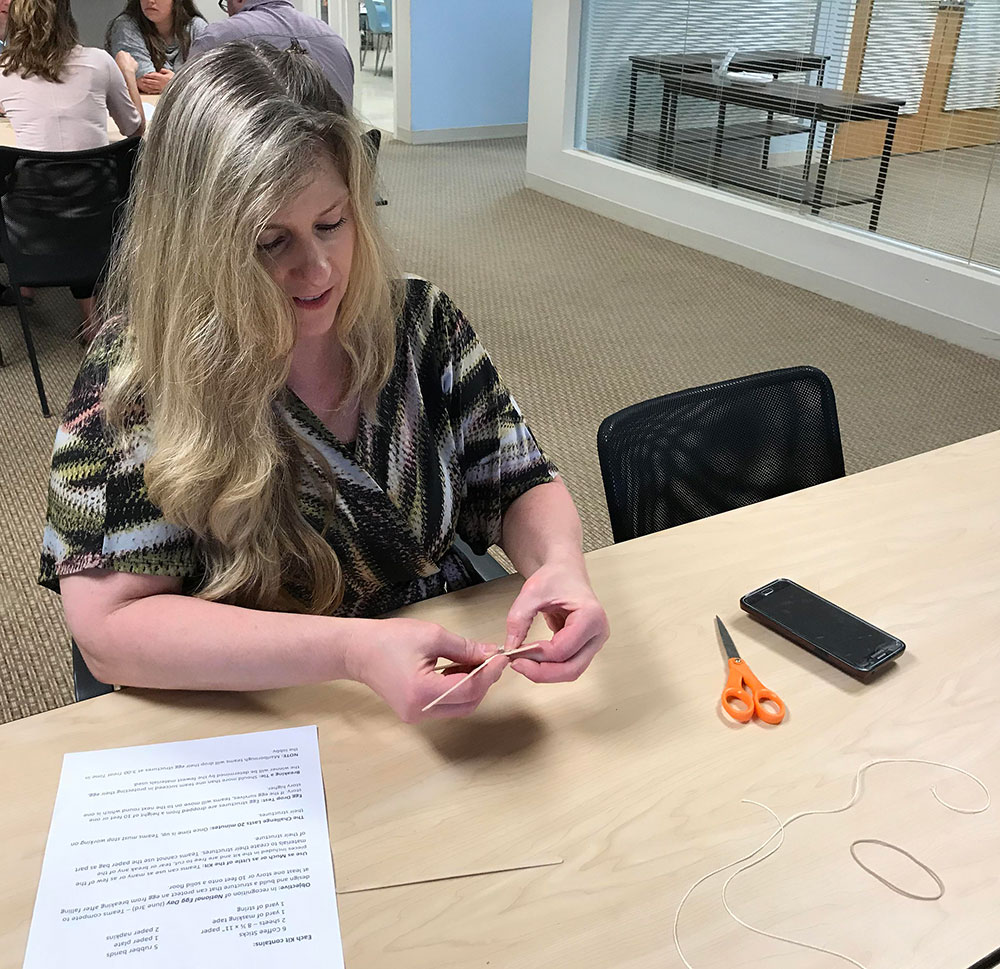
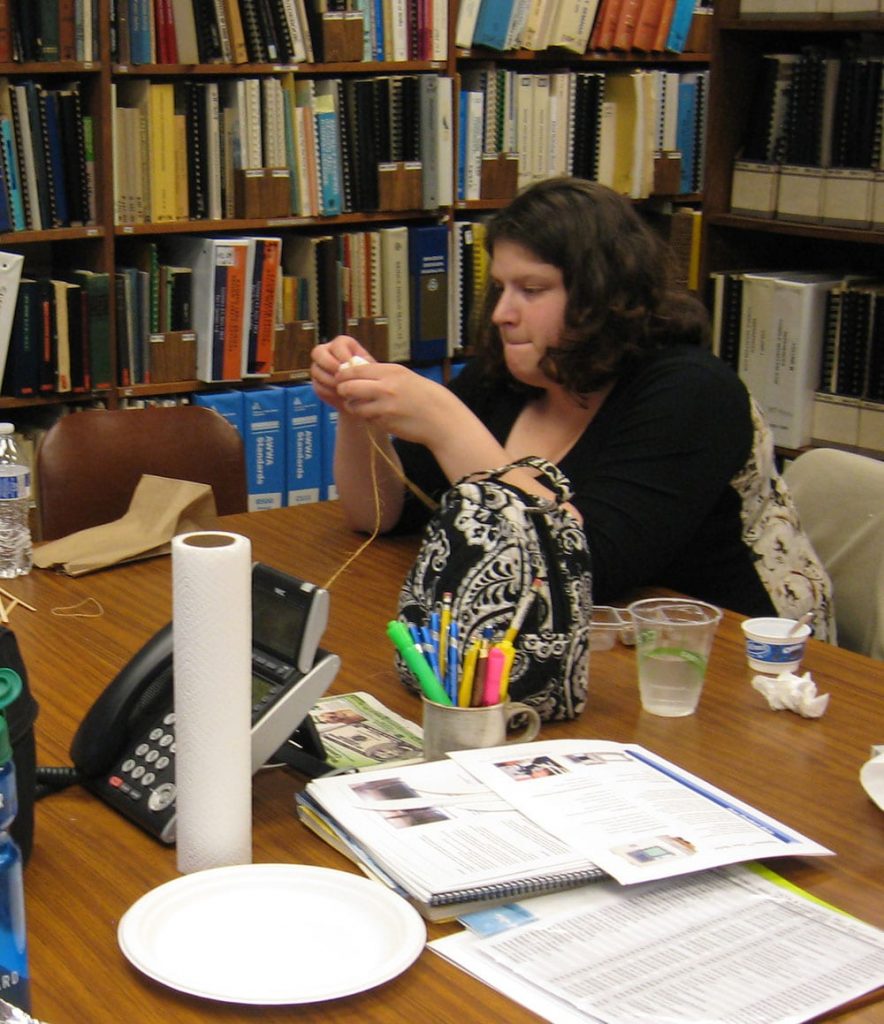
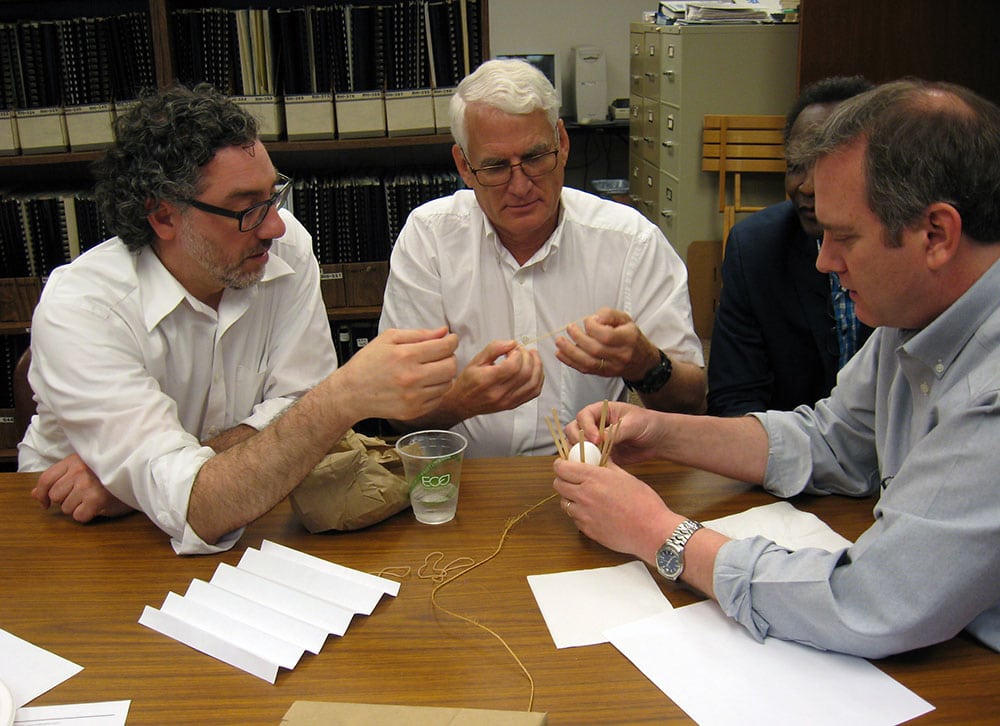
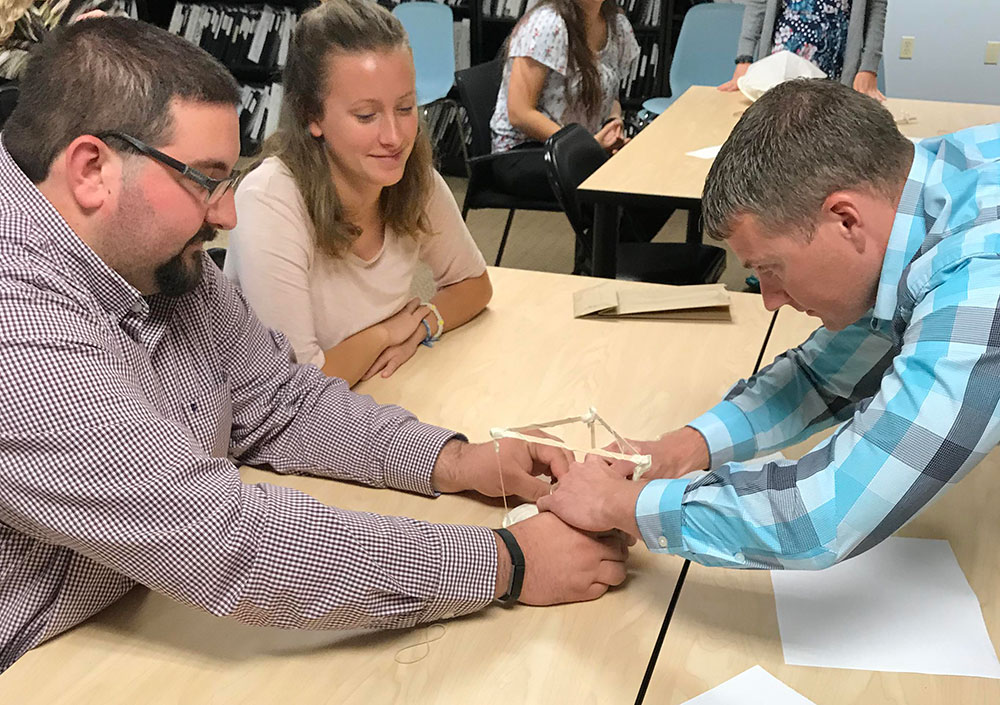
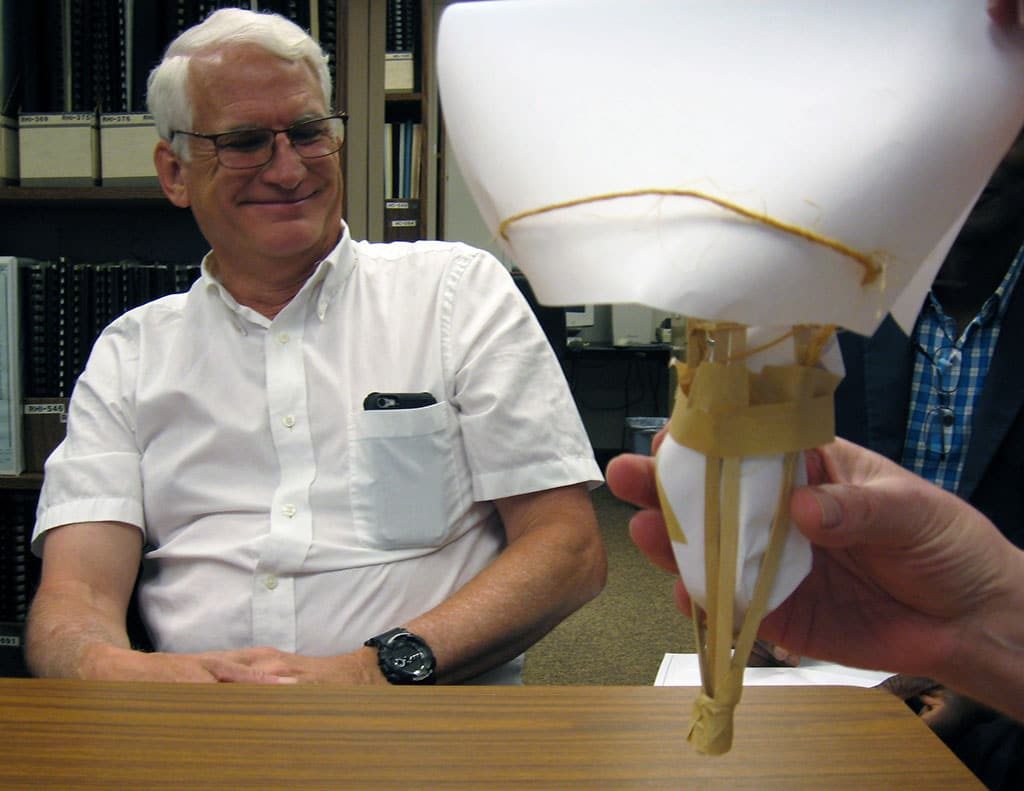
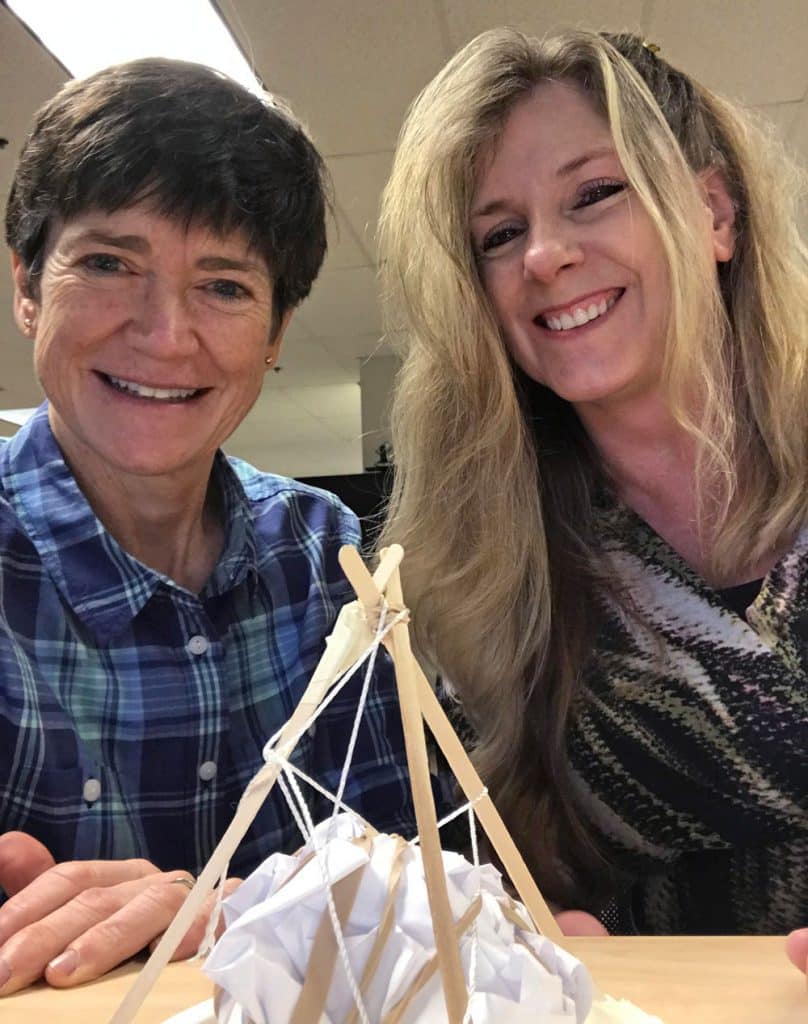
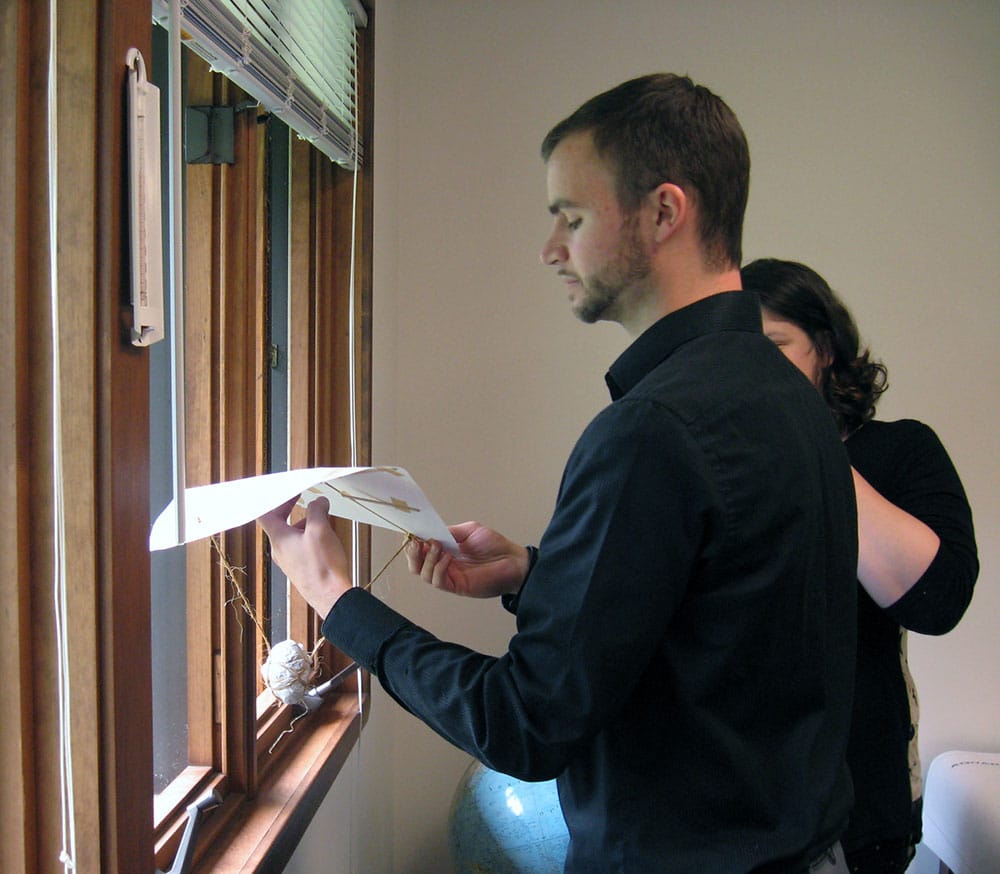
 Using ordinary office supplies (plus an uncooked chicken egg), to build their egg protective packages, teams could use as many or as few of the materials and were free to cut, tear, or break any of the pieces. The time to create the egg structures lasted 20 minutes. After the creating phase was over, it was time to drop the eggs.
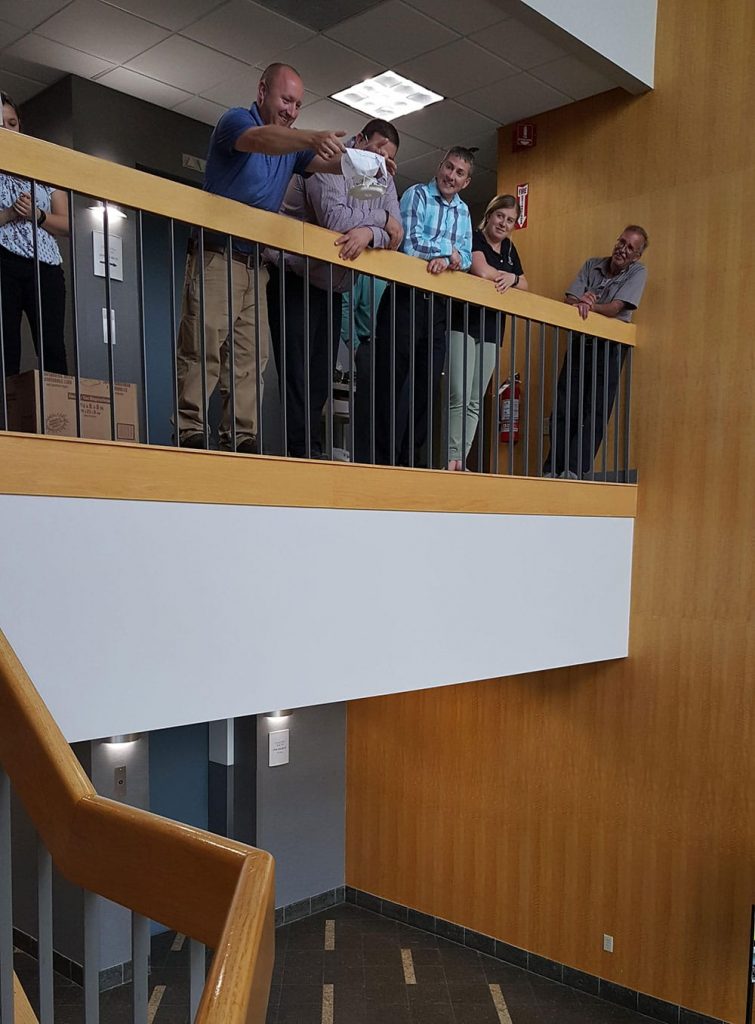
Using ordinary office supplies (plus an uncooked chicken egg), to build their egg protective packages, teams could use as many or as few of the materials and were free to cut, tear, or break any of the pieces. The time to create the egg structures lasted 20 minutes. After the creating phase was over, it was time to drop the eggs. From the second floor of our Waterbury, CT office, two teams dropped their eggs onto the sidewalk below. Upon closer examination, not one of the eggs survived the fall. In the case of a tie, as in this case since both eggs broke on impact, the team using the least amount of materials was declared the winners. Congratulations to Chelsea, Will, Kevin and Sal who used fewer pieces in the design of their egg packages.
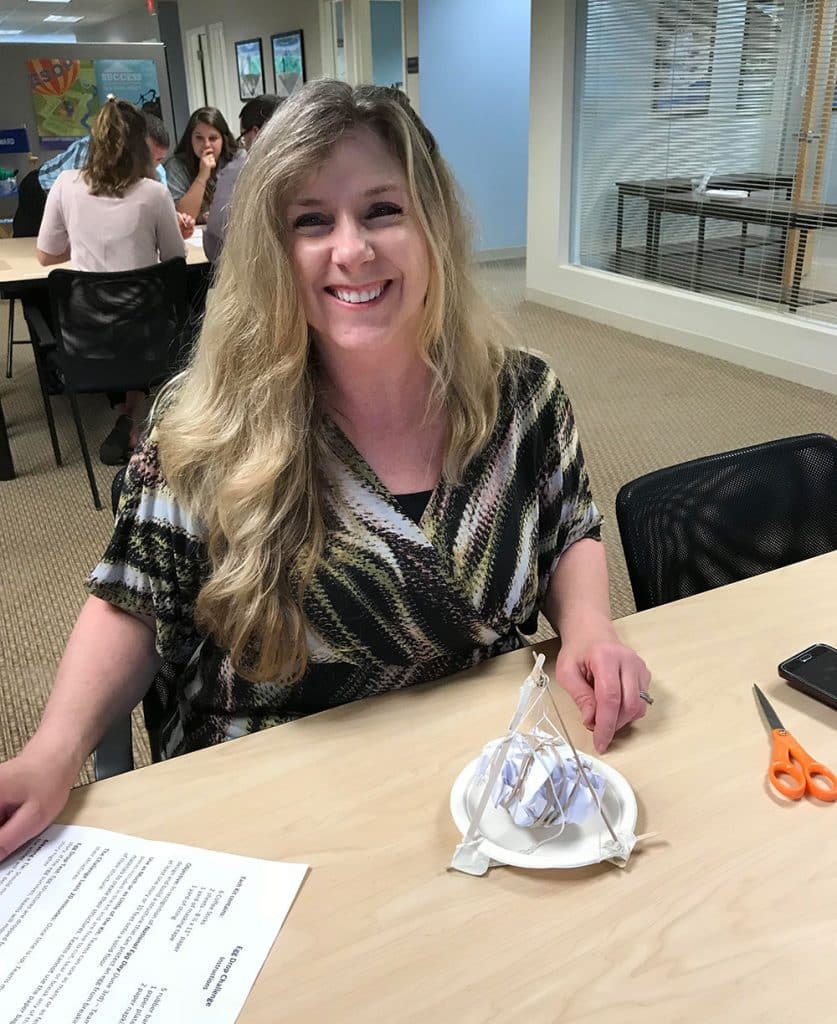
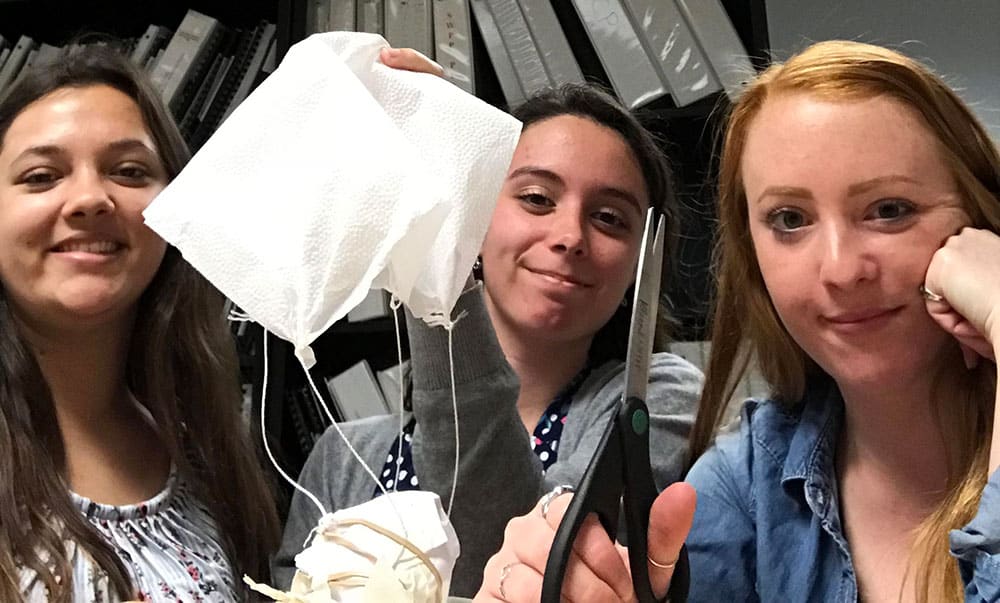
From the second floor of our Waterbury, CT office, two teams dropped their eggs onto the sidewalk below. Upon closer examination, not one of the eggs survived the fall. In the case of a tie, as in this case since both eggs broke on impact, the team using the least amount of materials was declared the winners. Congratulations to Chelsea, Will, Kevin and Sal who used fewer pieces in the design of their egg packages. Those three teams then ventured to the third floor and dropped their eggs again. Sadly, none of the eggs survived the fall from the nearly 30-foot fall. And, although many of the egg structures were still intact, it was clear from the misshapen, leaking packages, the eggs broke on contact. Fortunately, there was very little mess to clean up since the eggs were all overly wrapped and packaged. It was a tough call, but team Chris and Chrissie shared the winning honors.
Those three teams then ventured to the third floor and dropped their eggs again. Sadly, none of the eggs survived the fall from the nearly 30-foot fall. And, although many of the egg structures were still intact, it was clear from the misshapen, leaking packages, the eggs broke on contact. Fortunately, there was very little mess to clean up since the eggs were all overly wrapped and packaged. It was a tough call, but team Chris and Chrissie shared the winning honors. The materials used for the egg drop challenge can be whatever you choose. We opted to use common items found around the office. Of course, don’t forget the egg!
The materials used for the egg drop challenge can be whatever you choose. We opted to use common items found around the office. Of course, don’t forget the egg!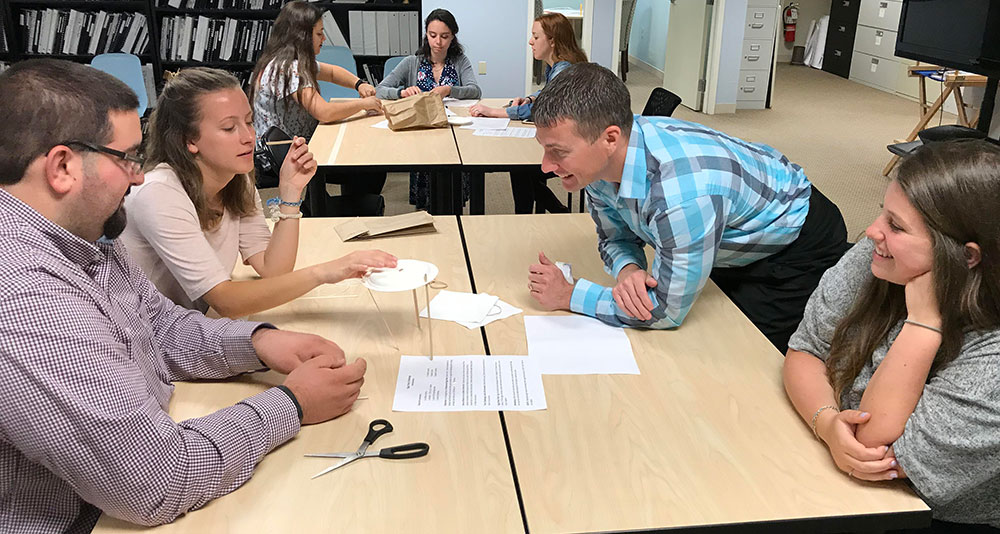

























 As the spring rains continued, life was about to change for the working-class city of 30,000 and other communities beneath the South Fork Dam.
As the spring rains continued, life was about to change for the working-class city of 30,000 and other communities beneath the South Fork Dam. For the pleasure of their private members, club owners soon began modifications to the dam. Fish screens were installed across the spillway to keep the expensive game fish from escaping. The dam was lowered by a few feet so that two carriages could navigate the carriage road to the clubhouse. Relief pipes and valves that controlled the water level and spill off from the original dam were sold off for scrap, and rustic cottages were built nearby.
For the pleasure of their private members, club owners soon began modifications to the dam. Fish screens were installed across the spillway to keep the expensive game fish from escaping. The dam was lowered by a few feet so that two carriages could navigate the carriage road to the clubhouse. Relief pipes and valves that controlled the water level and spill off from the original dam were sold off for scrap, and rustic cottages were built nearby. Club officials struggled to reinforce the earthen dam, but it continued to disintegrate. When the lake’s water began to pour over the top, it was apparent that a catastrophic collapse was inevitable and imminent. Frantic riders were sent down the valley to alert the local communities and tell them to evacuate. Sadly, few residents heeded the alarm being so often used to the minor seasonal flooding from the Little Conemaugh river.
Club officials struggled to reinforce the earthen dam, but it continued to disintegrate. When the lake’s water began to pour over the top, it was apparent that a catastrophic collapse was inevitable and imminent. Frantic riders were sent down the valley to alert the local communities and tell them to evacuate. Sadly, few residents heeded the alarm being so often used to the minor seasonal flooding from the Little Conemaugh river. Along the way, the deluge accumulated everything in its path, including all sorts of debris—from city buildings, houses, and barns. Piles of boulders, trees, farm equipment, rolls of barbed wire, horse carriages, and railroad cars churned in the turmoil. Embroiled in the devastation were also animals and people—both dead and alive.
Along the way, the deluge accumulated everything in its path, including all sorts of debris—from city buildings, houses, and barns. Piles of boulders, trees, farm equipment, rolls of barbed wire, horse carriages, and railroad cars churned in the turmoil. Embroiled in the devastation were also animals and people—both dead and alive. It would take months to sift through all the wreckage to find the bodies and years to fully recover from the aftermath.
It would take months to sift through all the wreckage to find the bodies and years to fully recover from the aftermath. A hydraulic analysis published in 2016 confirmed what had long been suspected, that the changes made to the dam by the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club severely reduced the ability of the dam to withstand major storms.1
A hydraulic analysis published in 2016 confirmed what had long been suspected, that the changes made to the dam by the South Fork Fishing and Hunting Club severely reduced the ability of the dam to withstand major storms.1