In America, we use about 30% of our nation’s drinking water supply – fresh, treated, clean water – to flush our toilets. We are suffering from one of the worst droughts in recent history, and our nation is literally running out of water. We need to conserve the water we have, and the most efficient way to accomplish this task is through alternative toilet technology. Luckily, engineers work every day designing these eco-conscious toilets, some of which we will showcase here.
In America, we use about 30% of our nation’s drinking water supply – fresh, treated, clean water – to flush our toilets. We are suffering from one of the worst droughts in recent history, and our nation is literally running out of water. We need to conserve the water we have, and the most efficient way to accomplish this task is through alternative toilet technology. Luckily, engineers work every day designing these eco-conscious toilets, some of which we will showcase here.
High Efficiency Toilets
Before we get into the newer technology of High Efficiency Toilets (HET), let’s first take a look at the traditional toilet. The old-fashioned Gravity Feed toilet is certainly reliable. It’s been around for decades and gets the job done. With each flush, a valve opens up and gravity forces water down a tunnel, while the resulting pressure forces waste down another, lower, tunnel called a trapway. However, until recently, this traditional design has used 3.5 gallons per flush (GPF) or more, some models using up to 5 GPF. Once the 1.6 GPF restrictions took effect, the Gravity Feed toilet didn’t perform quite so well, often clogging and requiring multiple flushes – which defeats the purpose of a low-flow toilet in the first place. As a result, engineers started working on water efficient toilets, commonly referred to as HETs. HETs are designed to work with existing plumbing and, while they still use water, they use significantly less water than traditional toilets.
Dual-Flush Toilets
 A step up in effectiveness is the Dual-Flush design. This high efficiency toilet earns the name by offering two ways to eliminate waste, usually by the use of two separate buttons to press. Press one and only about 1.3 gallons is released, which works fine for removing liquid waste. Press the second (or both buttons together in some instances) and 1.6 gallons is released.
A step up in effectiveness is the Dual-Flush design. This high efficiency toilet earns the name by offering two ways to eliminate waste, usually by the use of two separate buttons to press. Press one and only about 1.3 gallons is released, which works fine for removing liquid waste. Press the second (or both buttons together in some instances) and 1.6 gallons is released.
Other models vary the technique. Some use as little as 0.8 GPF to 1.1 GPF. Some allow for a more traditional-style handle but one that can also be pulled up rather than just pushed down. Move it one way and you get the partial flush; the other way releases the larger amount of water.
Pressure Assist Toilets
The next step up, in the sense of efficiency and oomph, is the Pressure Assist design. Here, the toilet doesn’t rely solely on gravity (as do both the Gravity Feed and many Dual-Flush models) but adds artificially generated pressure. Typically, that pressure is supplied by a plastic or metal canister that holds air. With each flush, the air adds additional pressure to that supplied by the force of gravity. And the combination is impressive: they can typically handle 40 feet of toilet paper in a single flush without jamming. Solid human waste is no challenge to these units.
Still, they have a downside. They don’t have motors that create the pressure and they put extra stress on your pipes. Those two facts imply two more: your home water system must supply adequate pressure in the first place and your pipes must be able to withstand the flush pressure. Fortunately, most homes satisfy those requirements, especially those built in the past 40 years.
Power Assist Toilets
A less-common variation on the HET theme is the Power Assist design. It actually incorporates a pump that forces water at higher velocity than is possible from a gravity feed or simple pressure assist method. The flush volumes are usually between one and 1.3 GPF, so they satisfy the legal restrictions.
However, this type typically requires a 120-volt electrical source to power the motor that drives the pump. While they’re safe, many consumers don’t feel comfortable having a water device like a toilet so directly connected to an electrical supply. They’re also generally much more expensive and usually overkill for homeowners. As a consequence, they’re more often found in commercial establishments and even there they are relatively rare.
Waterless Toilets
With our nation’s water crisis looming, waterless toilets make the most sense, because they use literally no water. And the even better news about waterless toilets is that, besides the waterless urinal, they don’t connect to any plumbing or infrastructure, which can save thousands in new construction and on water and sewer bills. But is waterless toilet technology advanced enough to be viable in the typical household or commercial setting? Let’s take a look.
Waterless Urinals
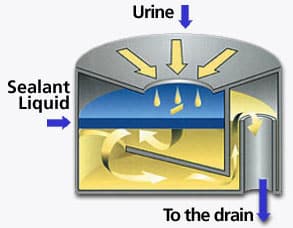 Waterless urinals have gained in popularity and are becoming more widely used in commercial settings, even being approved by the plumbing code since 2006. They use gravity to force urine down through a trap that contains a heavy liquid, which allows urine to pass through while forming a seal against odors. Waterless urinals use zero water, discharge into standard, existing plumbing lines, and are easy to clean. Also, since urine is sterile and bacteria develop only when urine is mixed with water, waterless urinals remain odorless. Waterless urinals are currently used in San Diego schools, the L.A. Coliseum, and the Taj Mahal, and they have been mandated in army facilities since 2010. They also count towards LEED certification points. There really are no drawbacks to the waterless urinal save one – but it’s a big one: half the world’s population is women. Enough said.
Waterless urinals have gained in popularity and are becoming more widely used in commercial settings, even being approved by the plumbing code since 2006. They use gravity to force urine down through a trap that contains a heavy liquid, which allows urine to pass through while forming a seal against odors. Waterless urinals use zero water, discharge into standard, existing plumbing lines, and are easy to clean. Also, since urine is sterile and bacteria develop only when urine is mixed with water, waterless urinals remain odorless. Waterless urinals are currently used in San Diego schools, the L.A. Coliseum, and the Taj Mahal, and they have been mandated in army facilities since 2010. They also count towards LEED certification points. There really are no drawbacks to the waterless urinal save one – but it’s a big one: half the world’s population is women. Enough said.
Composting Toilets
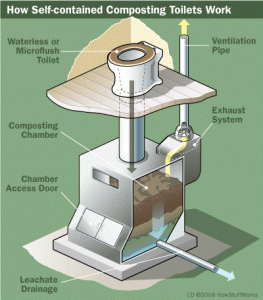 A composting (or biological) toilet system contains and processes excrement, toilet paper, carbon additive, and sometimes, food waste. Unlike a septic system, a composting toilet system relies on unsaturated conditions where aerobic bacteria break down waste. This process is similar to a yard waste composter. If sized and maintained properly, a composting toilet breaks down waste to just 10-30% of its original volume. The resulting soil-like material, called “humus” legally must be either buried or removed by a licensed septage hauler in accordance with state and local regulations.
A composting (or biological) toilet system contains and processes excrement, toilet paper, carbon additive, and sometimes, food waste. Unlike a septic system, a composting toilet system relies on unsaturated conditions where aerobic bacteria break down waste. This process is similar to a yard waste composter. If sized and maintained properly, a composting toilet breaks down waste to just 10-30% of its original volume. The resulting soil-like material, called “humus” legally must be either buried or removed by a licensed septage hauler in accordance with state and local regulations.
Composting toilet systems require no water and have low power consumption. They can also accept kitchen waste, thus reducing household garbage. Composting toilets are the most environmentally friendly of the new generation of toilets. Composting human waste and burying it around tree roots and nonedible plants keeps organic wastes productively cycling in the environment, and composting toilet systems divert nutrient and pathogen-containing effluent from soil, surface water, and groundwater. In many states, installing a composting toilet system allows the property owner to keep a reduced-size leach field, minimizing costs and disruption of landscapes.
Of course, there are a few drawbacks as well. Maintenance of composting toilet systems requires more responsibility and commitment by users and owners than conventional wastewater systems, and improperly installed or maintained systems have the potential to cause some problems. Using an inadequately treated end-product as a soil amendment may have possible health consequences, and improper maintenance makes cleaning difficult and may lead to health hazards and odor problems. Too much liquid residual (leachate) in the composter can disrupt the process if it is not drained and properly managed. In addition, there may be aesthetic issues because the excrement in some systems may be in sight.
Incinerating Toilets
 Incinerating toilets are self-contained units consisting of a traditional commode-type seat connected to a holding tank and a gas-fired or electric heating system to incinerate waste products deposited in the holding tank. The incineration products are primarily water and a fine, non-hazardous ash that can be disposed of easily and without infection hazard. Typically the user drops in a coffee-filter type liner, uses the toilet, then “flushesâ€. The liner drops into a chamber, which heats up to approximately 1200 degrees, and incinerates the waste over a period of time, usually one to two hours. As a safety feature, the incinerator automatically turns itself off if the lid is lifted, thus eliminating the chance of bathroom burns.
Incinerating toilets are self-contained units consisting of a traditional commode-type seat connected to a holding tank and a gas-fired or electric heating system to incinerate waste products deposited in the holding tank. The incineration products are primarily water and a fine, non-hazardous ash that can be disposed of easily and without infection hazard. Typically the user drops in a coffee-filter type liner, uses the toilet, then “flushesâ€. The liner drops into a chamber, which heats up to approximately 1200 degrees, and incinerates the waste over a period of time, usually one to two hours. As a safety feature, the incinerator automatically turns itself off if the lid is lifted, thus eliminating the chance of bathroom burns.
Incinerating toilets use no water at all, and they produce only about a tablespoon per use of a fine, sterile ash that can be disposed of in the trash. They are simple to install, easy to use, and are relatively odorless in comparison to other waterless toilets. However, they do also have some drawbacks. Incinerating destroys nutrients in the waste and also requires energy, resulting in higher than average energy costs for users. In addition, units are not entirely pollution-free, as they require either electricity or propane, both of which produce some air pollutants.
Hope for the Future
If we could save the third of our nation’s drinking water that we are flushing down our toilets, we would actually solve the nation’s water crisis. And researchers and engineers are working every day to do just that: to find a sustainable, cost-effective solution to the wastewater problem facing America. At the moment, there is not yet a universal answer to our nation’s toilet troubles. However, with the abundance of emerging technologies and the combined focus of researchers and engineers, it is only a matter of time before our wastewater – and therefore water – woes are permanently solved.
REFERENCES:
www.epa.gov
www.goarticles.com/finhuge
www.bestratedtoilets.com