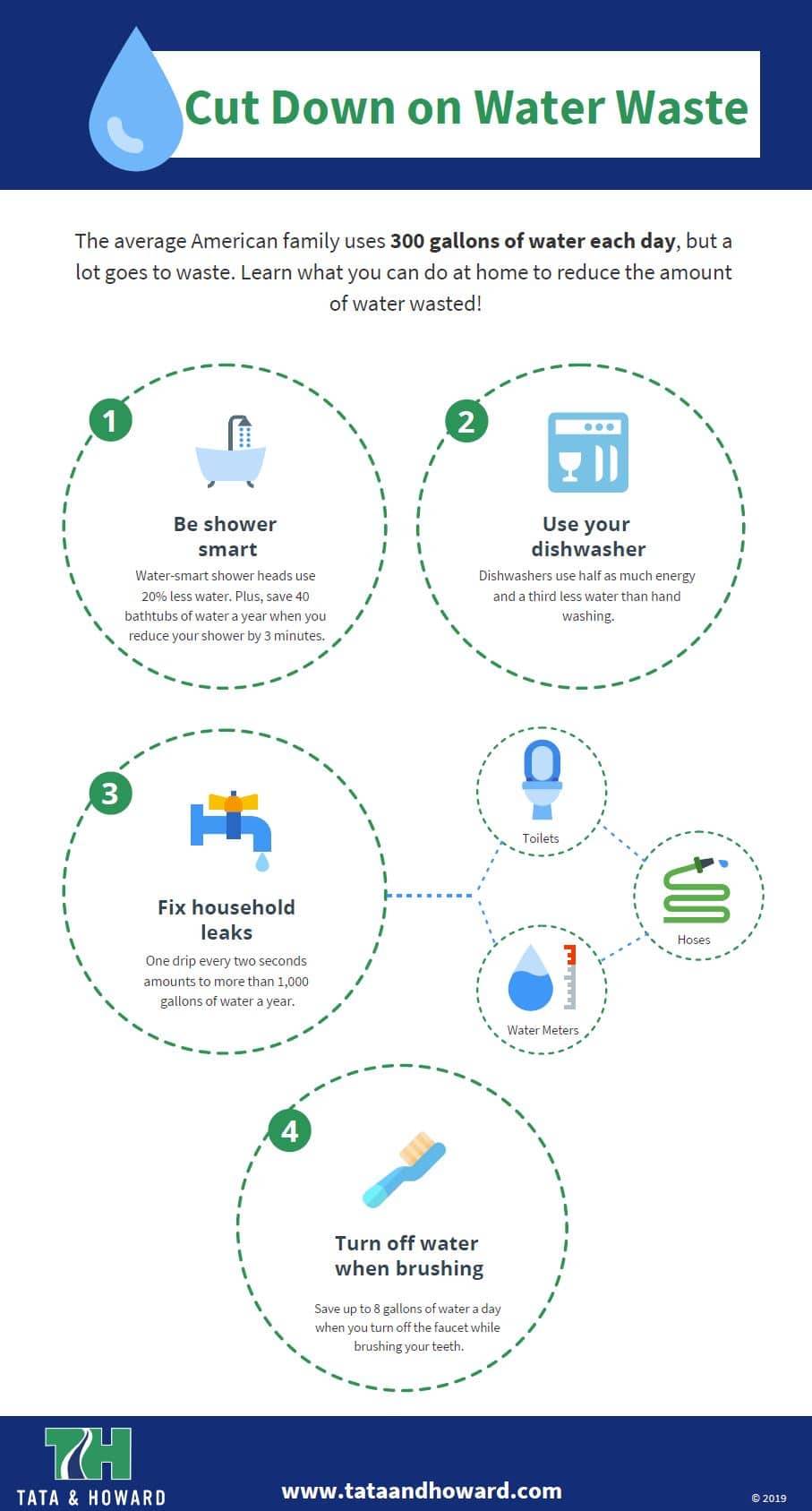
Reclaiming Wastewater on the Space Station has an impact right here on Earth!
Water—it’s essential for all living beings… and water is essential to make life possible. It’s an interesting paradox that has kept scientists searching for life in extreme places.
 When NASA recently announced the discovery of liquid water flowing under an ice cap on Mars, it opened the exciting possibility that life may exist outside our earthly abode. While it is conceivable scientists may eventually discover life somewhere in our galaxy, a reliable source of water outside earth is fundamental for the possibility of establishing a colony on Mars, exploring the universe and even visiting distant planets in search of life outside earth.
When NASA recently announced the discovery of liquid water flowing under an ice cap on Mars, it opened the exciting possibility that life may exist outside our earthly abode. While it is conceivable scientists may eventually discover life somewhere in our galaxy, a reliable source of water outside earth is fundamental for the possibility of establishing a colony on Mars, exploring the universe and even visiting distant planets in search of life outside earth.
This is the stuff of science fiction…or is it?
Well, let’s get the stars out of our eyes and return to earth. First, we need to get to Mars and therein lies the challenge. Top on the list is how to provide the essentials for life, such as water, air and the entire habitat for the astronauts to live in as they journey among the stars.
Getting to Space
Establishing a sustainable long-term flight program requires a base to launch manned operations in space. The International Space Station (ISS), which was put into orbit in 1998 and has been continuously occupied since 2000, currently provides a habitable place for astronauts to live and conduct scientific experiments.
 But hauling tons of supplies and materials to the International Space Station (ISS) is inefficient and extremely expensive. Sustaining a crew of four astronauts on the ISS with water, power and other supplies, costs nearly one million dollars a day. Even with the reusable SpaceX rocket which regularly provides supplies to the ISS, it costs $2,500 per pound to launch into space. With four astronauts living on the ISS needing approximately 12 gallons of water a day, it is impractical to stock the ISS with the tons of water needed for long periods of time.
But hauling tons of supplies and materials to the International Space Station (ISS) is inefficient and extremely expensive. Sustaining a crew of four astronauts on the ISS with water, power and other supplies, costs nearly one million dollars a day. Even with the reusable SpaceX rocket which regularly provides supplies to the ISS, it costs $2,500 per pound to launch into space. With four astronauts living on the ISS needing approximately 12 gallons of water a day, it is impractical to stock the ISS with the tons of water needed for long periods of time.
It’s no wonder then that rationing, and recycling is an essential part of daily life on the ISS. The Space Station must provide not only clean water, but air to breath, power, and ideal atmospheric conditions to sustain life outside earth.
And every drop of liquid is important!
Reclaiming Water for Life Support
The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) on the ISS is a life support system that provides atmospheric pressure, oxygen levels, waste management and water supply, and fire detection and suppression. The most important function for ECLSS is controlling the atmosphere for the crew, but the system also collects, processes, and stores waste and water produced by the crew…including the furry lab passengers too.
Yes, even mice waste is recycled.
 If the idea of drinking reclaimed water from mice urine and other waste sources sounds unappetizing, consider this, the water the astronauts drink is often cleaner that what many earthlings drink. NASA regularly checks the water quality and it is monitored for bacteria, pollutants and proper pH (60 – 8.5).
If the idea of drinking reclaimed water from mice urine and other waste sources sounds unappetizing, consider this, the water the astronauts drink is often cleaner that what many earthlings drink. NASA regularly checks the water quality and it is monitored for bacteria, pollutants and proper pH (60 – 8.5).
This highly efficient reclamation system processes and recycles fluid from the sink, shower, toilet, sweat, and even condensation from the air. The ECLSS water recovery system on the ISS uses both physical and chemical processes to remove contaminants, as well as filtration and temperature sterilization to ensure the water is safe to drink.
More Innovation for the Future
Providing the astronauts with clean water from reclaimed wastewater at the Space Station is working fine for what they need right now, but it’s not perfect. The ISS system recovers water at a rate of approximately 74 percent. For longer missions to Mars and beyond, this rate must increase to at least 98 percent to sustain longer journeys into space. Scientists are continuously working on better and more efficient close-looped support systems to reduce water loss and improve ways to reclaim water from all waste products.
 Recently, NASA invested in a new, lower cost solution to biologically recycle and reuse water developed by Pancopia. Pancopia is a small environmental and energy engineering company located in Virginia that focuses on wastewater treatment and research and development projects. Engineers at the firm have discovered an innovative technology that makes use of a group of bacteria called anammox. Anammox when combined with two other types of bacteria commonly used in conventional wastewater treatment (nitrifiers and denitrifiers), can remove high levels of organic carbon and nitrogen, the two primary pollutants in wastewater.
Recently, NASA invested in a new, lower cost solution to biologically recycle and reuse water developed by Pancopia. Pancopia is a small environmental and energy engineering company located in Virginia that focuses on wastewater treatment and research and development projects. Engineers at the firm have discovered an innovative technology that makes use of a group of bacteria called anammox. Anammox when combined with two other types of bacteria commonly used in conventional wastewater treatment (nitrifiers and denitrifiers), can remove high levels of organic carbon and nitrogen, the two primary pollutants in wastewater.
The combination of these three organisms naturally adjust to changes in the system and eliminates pollutants faster and more reliably than traditional wastewater treatment operations. And, the cost is significantly less to operate than conventional systems, which requires a lot of energy and consumables to run. In addition, the stability of the anammox process reduces costs by requiring fewer manpower hours to monitor and operate.
Back on Earth
What does all this water and wastewater reclamation innovation mean for us on earth?
 Pancopia is currently working on a similar system used on the ISS for municipal wastewater facilities. Using the technology developed for the Space Station, other areas in the world with limited access to clean drinking water, will soon be able to utilize this advanced water filtration and purification system.
Pancopia is currently working on a similar system used on the ISS for municipal wastewater facilities. Using the technology developed for the Space Station, other areas in the world with limited access to clean drinking water, will soon be able to utilize this advanced water filtration and purification system.
This innovative water recycling system initially intended for the astronauts, now has the potential to cut treatment expenses to less than half the current costs for municipal customers, while providing sustainable crystal-clear drinking water especially in arid and drought-stricken communities across the globe.
Man’s search for extraterrestrial life and desire to travel through space may actually have its greatest impact right here on Earth—clean water!








 When NASA recently announced the discovery of liquid water flowing under an ice cap on Mars, it opened the exciting possibility that life may exist outside our earthly abode. While it is conceivable scientists may eventually discover life somewhere in our galaxy, a reliable source of water outside earth is fundamental for the possibility of establishing a colony on Mars, exploring the universe and even visiting distant planets in search of life outside earth.
When NASA recently announced the discovery of liquid water flowing under an ice cap on Mars, it opened the exciting possibility that life may exist outside our earthly abode. While it is conceivable scientists may eventually discover life somewhere in our galaxy, a reliable source of water outside earth is fundamental for the possibility of establishing a colony on Mars, exploring the universe and even visiting distant planets in search of life outside earth. But hauling tons of supplies and materials to the International Space Station (ISS) is inefficient and extremely expensive. Sustaining a crew of four astronauts on the ISS with water, power and other supplies, costs nearly one million dollars a day. Even with the reusable SpaceX rocket which regularly provides supplies to the ISS, it costs $2,500 per pound to launch into space. With four astronauts living on the ISS needing approximately 12 gallons of water a day, it is impractical to stock the ISS with the tons of water needed for long periods of time.
But hauling tons of supplies and materials to the International Space Station (ISS) is inefficient and extremely expensive. Sustaining a crew of four astronauts on the ISS with water, power and other supplies, costs nearly one million dollars a day. Even with the reusable SpaceX rocket which regularly provides supplies to the ISS, it costs $2,500 per pound to launch into space. With four astronauts living on the ISS needing approximately 12 gallons of water a day, it is impractical to stock the ISS with the tons of water needed for long periods of time. If the idea of drinking reclaimed water from mice urine and other waste sources sounds unappetizing, consider this, the water the astronauts drink is often cleaner that what many earthlings drink. NASA regularly checks the water quality and it is monitored for bacteria, pollutants and proper pH (60 – 8.5).
If the idea of drinking reclaimed water from mice urine and other waste sources sounds unappetizing, consider this, the water the astronauts drink is often cleaner that what many earthlings drink. NASA regularly checks the water quality and it is monitored for bacteria, pollutants and proper pH (60 – 8.5). Recently, NASA invested in a new, lower cost solution to biologically recycle and reuse water developed by
Recently, NASA invested in a new, lower cost solution to biologically recycle and reuse water developed by  Pancopia is currently working on a similar system used on the ISS for municipal wastewater facilities. Using the technology developed for the Space Station, other areas in the world with limited access to clean drinking water, will soon be able to utilize this advanced water filtration and purification system.
Pancopia is currently working on a similar system used on the ISS for municipal wastewater facilities. Using the technology developed for the Space Station, other areas in the world with limited access to clean drinking water, will soon be able to utilize this advanced water filtration and purification system.
 Even so, that millimeter of enamel making up the outer part of the tooth is the hardest substance of the human body and can outlast even the human skeleton when interred. In fact, the oldest vertebrate fossil relics going back 500 million years are teeth. Despite these details, teeth can be surprisingly fragile and prone to decay.
Even so, that millimeter of enamel making up the outer part of the tooth is the hardest substance of the human body and can outlast even the human skeleton when interred. In fact, the oldest vertebrate fossil relics going back 500 million years are teeth. Despite these details, teeth can be surprisingly fragile and prone to decay. Still, with these advances in dentistry, tooth loss and decay persisted. Since ancient times, it was widely thought that toothaches were caused by worms that destroyed teeth. It wasn’t until 1890, when a dentist named Willoughby Miller identified that tooth decay was caused by a certain type of bacteria that thrives on sugar, creating an acid that ate away at tooth enamel.
Still, with these advances in dentistry, tooth loss and decay persisted. Since ancient times, it was widely thought that toothaches were caused by worms that destroyed teeth. It wasn’t until 1890, when a dentist named Willoughby Miller identified that tooth decay was caused by a certain type of bacteria that thrives on sugar, creating an acid that ate away at tooth enamel.

 Financing for The Clean Water SRF Program helps municipalities with federal and state compliance water-quality requirements, focusing on stormwater and watershed management priorities, and green infrastructure. The Drinking Water SRF Program, provides low-interest loans to communities to improve their drinking water safety and water supply infrastructure.
Financing for The Clean Water SRF Program helps municipalities with federal and state compliance water-quality requirements, focusing on stormwater and watershed management priorities, and green infrastructure. The Drinking Water SRF Program, provides low-interest loans to communities to improve their drinking water safety and water supply infrastructure.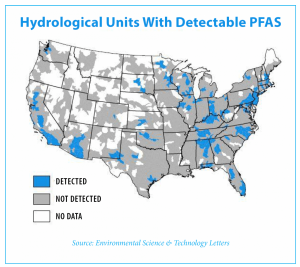 According the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all these UCMR 3 PFAS compounds have been detected in public water supplies across the US. Since PFAS are considered emerging contaminants, there are currently no established regulatory limits for levels in drinking water. However, in 2016, the EPA set Health Advisory levels (HA) of 0.07 micrograms per liter (µg/L) or 70 parts per trillion (ppt) for the combined concentrations of two PFAS compounds, PFOS and PFOA.
According the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), all these UCMR 3 PFAS compounds have been detected in public water supplies across the US. Since PFAS are considered emerging contaminants, there are currently no established regulatory limits for levels in drinking water. However, in 2016, the EPA set Health Advisory levels (HA) of 0.07 micrograms per liter (µg/L) or 70 parts per trillion (ppt) for the combined concentrations of two PFAS compounds, PFOS and PFOA. The EPA also recommends that treatment be implemented for all five PFAS when one or more of these compounds are present.
The EPA also recommends that treatment be implemented for all five PFAS when one or more of these compounds are present. Most research on the effects of PFAS on human health is based on animal studies. And, although there is no conclusive evidence that PFAS cause cancer, animal studies have shown there are possible links. However, PFAS ill-health effects are associated with changes in thyroid, kidney and liver function, as well as affects to the immune system. These chemicals have also caused fetal development effects during pregnancy and low birth weights.
Most research on the effects of PFAS on human health is based on animal studies. And, although there is no conclusive evidence that PFAS cause cancer, animal studies have shown there are possible links. However, PFAS ill-health effects are associated with changes in thyroid, kidney and liver function, as well as affects to the immune system. These chemicals have also caused fetal development effects during pregnancy and low birth weights.