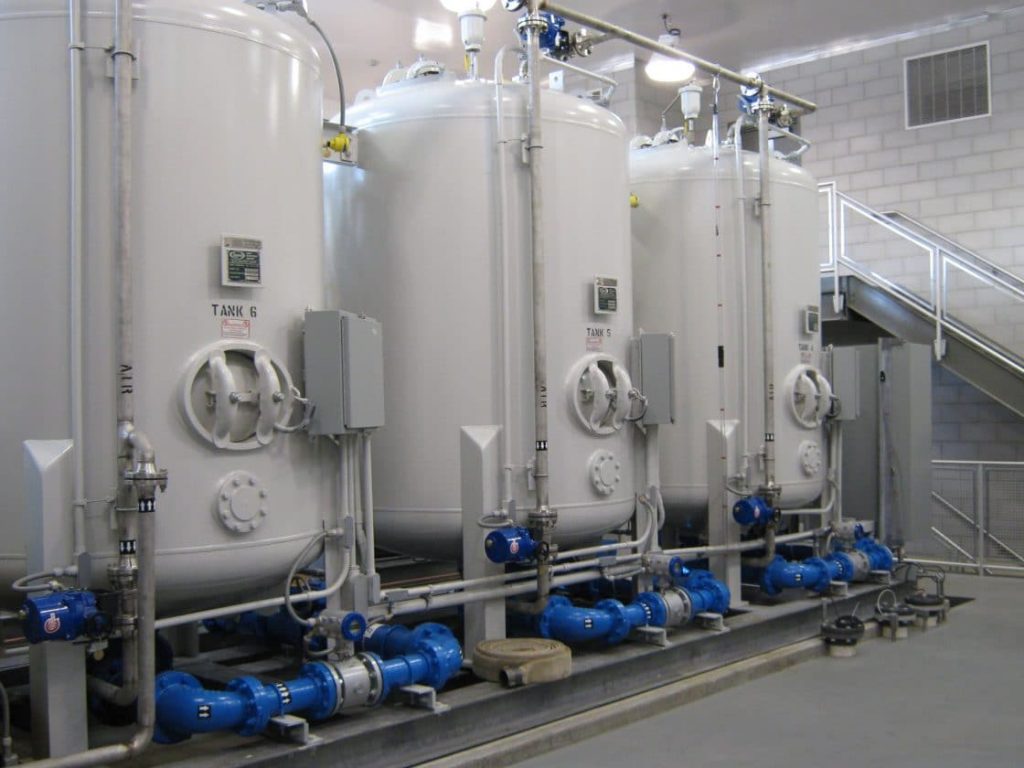
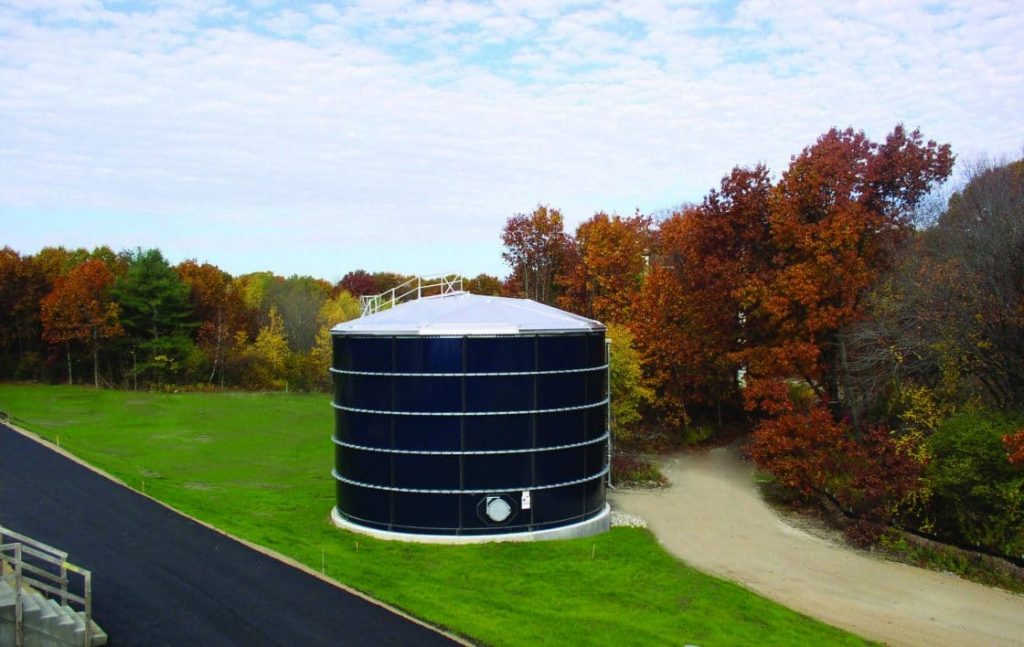
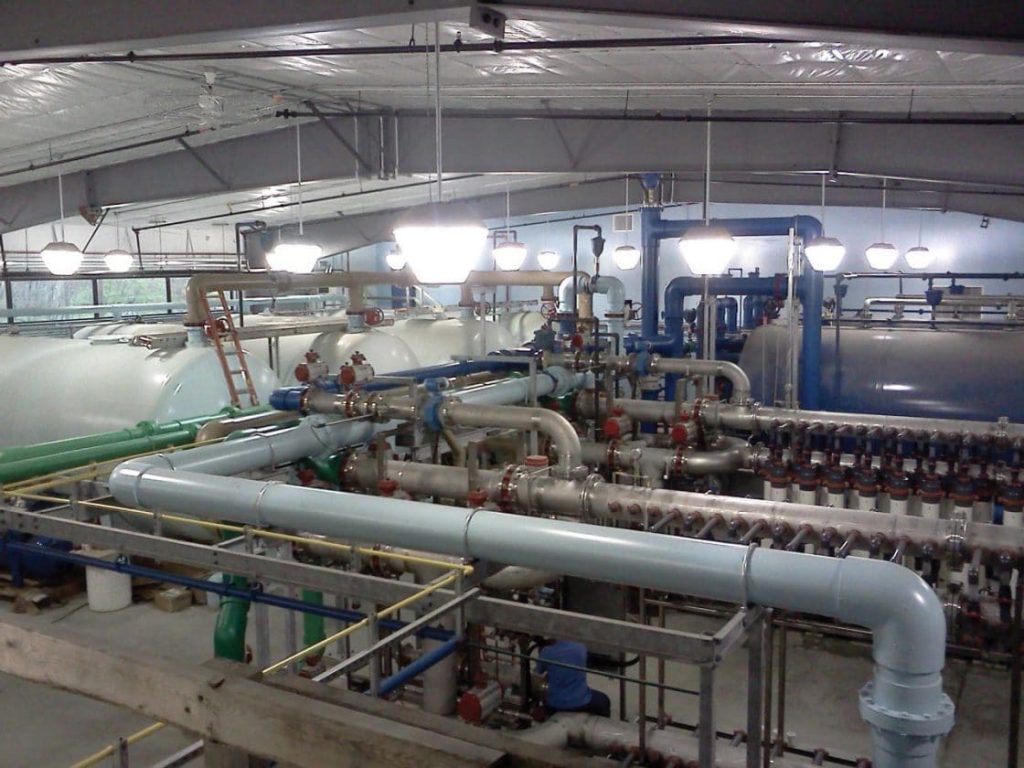
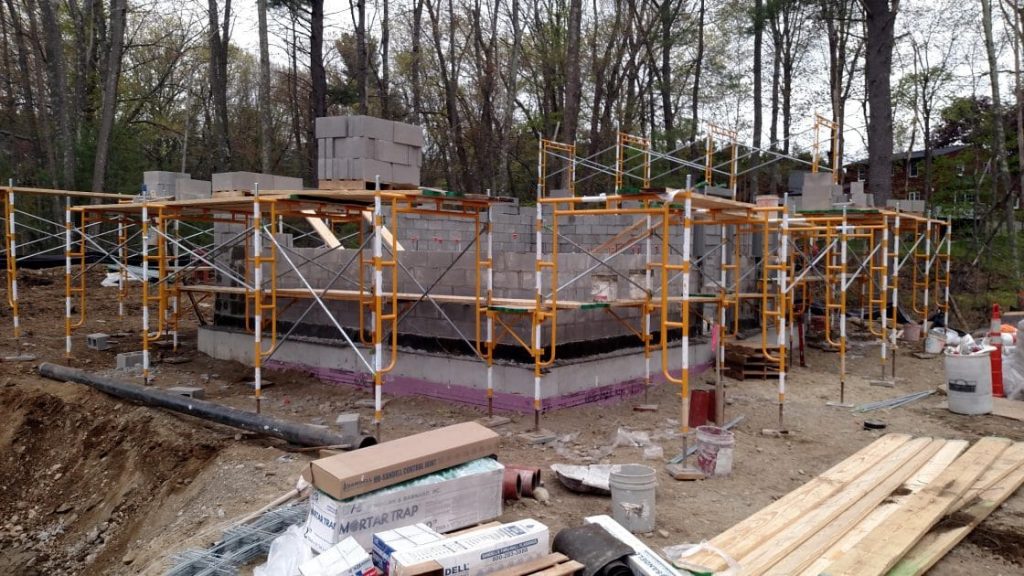
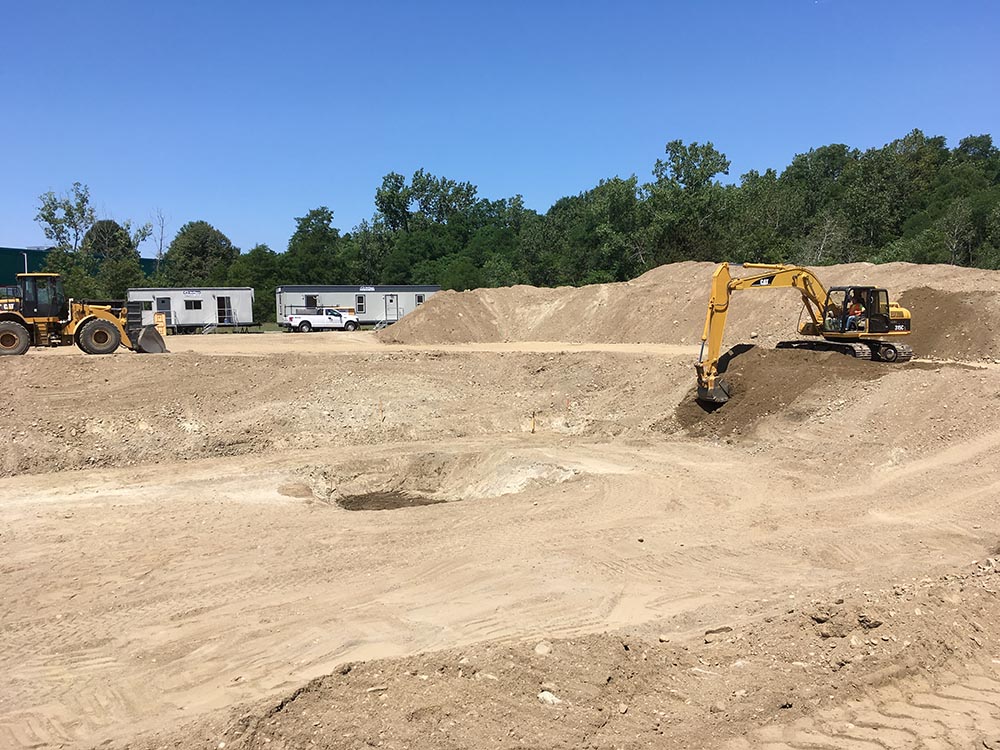
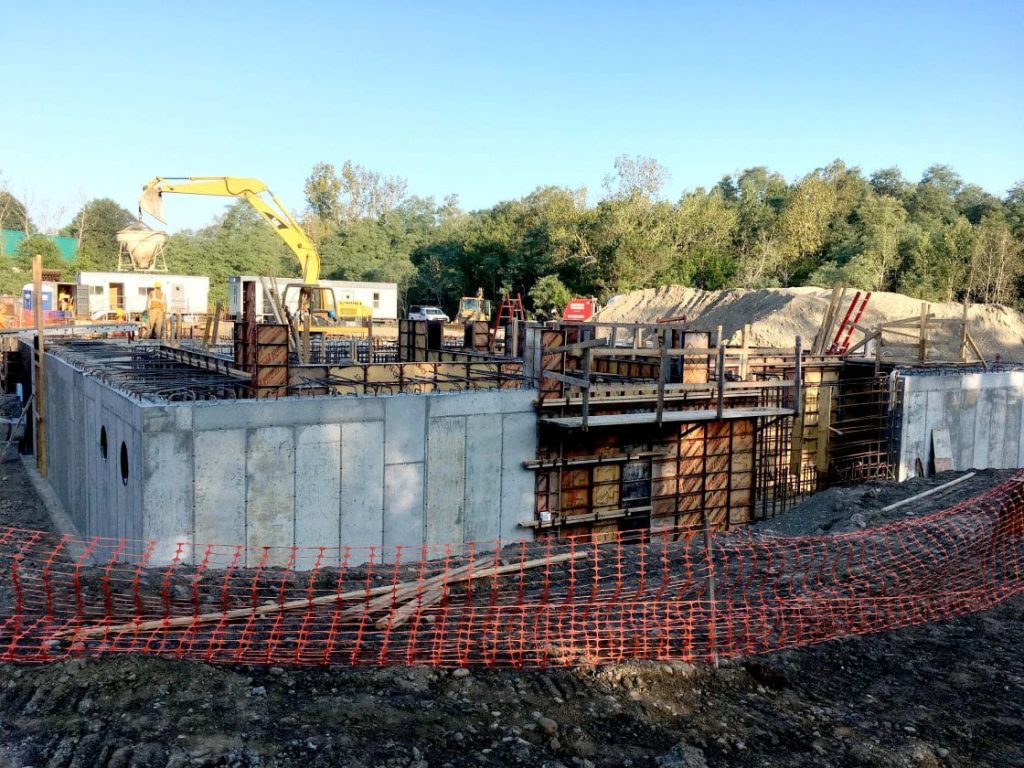
Tata & Howard, Inc. was retained by the First District Water Department (FDWD) to complete a Capital Efficiency Plan™ for the First District water system in the City of Norwalk, CT. Areas of the water distribution system in need of rehabilitation, repair, or replacement, were identified and improvements were prioritized to make the most efficient use of the FDWD’s capital budget. The study evaluated the existing water infrastructure including water transmission and distribution piping and appurtenances. In addition, water storage needs were evaluated and prioritized.
Tata & Howard evaluated the water distribution system using the Three Circle Approach, which consists of evaluation criteria including a system hydraulic evaluation, a critical component assessment, and asset management considerations.
Hydraulic improvements included recommendations that would strengthen the transmission capabilities of the system or provide an ISO recommended fire flow to a certain area. Priority 2 recommendations were identified as part of a system-wide evaluation to improve estimated needed fire flows and system looping.

A critical component assessment was performed for the water distribution system to evaluate the impact of potential water main failures on the system. The critical component assessment includes identification of critical areas served, critical water mains, and the need for redundant mains. Critical areas served were identified by the FDWD and include water department facilities, medical facilities, schools, and business districts. Critical water mains include primary transmission lines as well as water mains that cross over major highways, rivers, and railroad tracks. Factors that affected the decision to replace or rehabilitate a water main include break history, material, age, diameter, soil conditions, water quality, and pressure.
An asset management assessment was completed for the system. A number of factors are considered in the ratings including break history, material, age, diameter, soil conditions, water quality, and pressure, and these factors affect the decision to replace or rehabilitate a water main.
Utilizing the Three Circle Approach, improvements were recommended and prioritized based on the aforementioned criteria. Phase I improvements include any recommended improvements that fall into all three circles and are therefore hydraulically deficient, critical, and have a high asset management score. There are approximately 16,300 linear feet of new main in the Phase I recommended improvements. Phase II improvements include any recommended improvements that fall into two of the circles. There are approximately 81,400 linear feet of new main in the Phase IIa and Phase IIb recommended improvements. Phase III recommendations include any recommended improvements that are needed hydraulically or that have a high asset management score indicating poor condition. The Phase IIIa and Phase IIIb include approximately 157,000 linear feet of new main. In addition, recommendations included soil testing for corrosivity prior to ductile water main installation, implementation of a unidirectional flushing program, and annual updating of the hydraulic model.