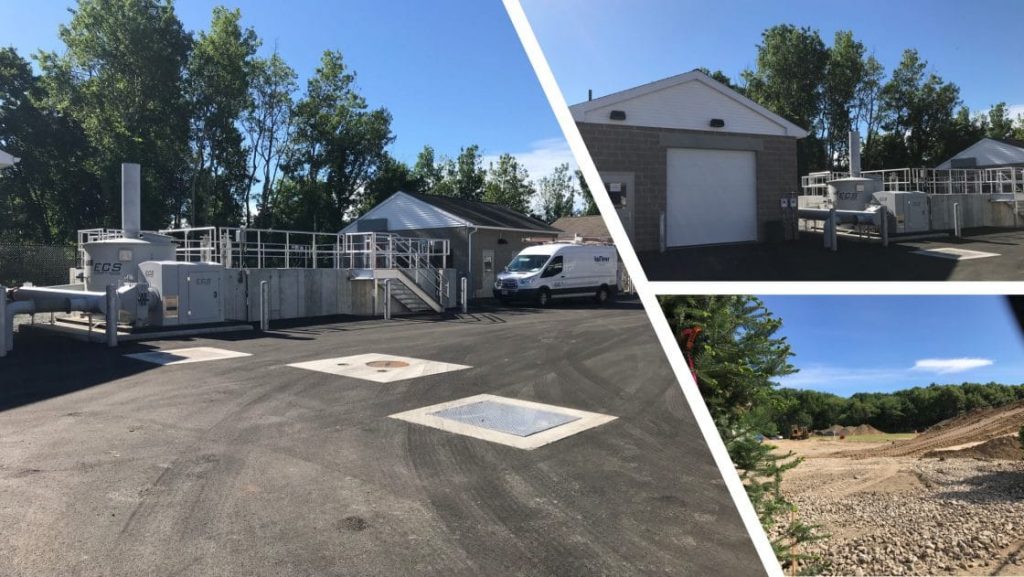
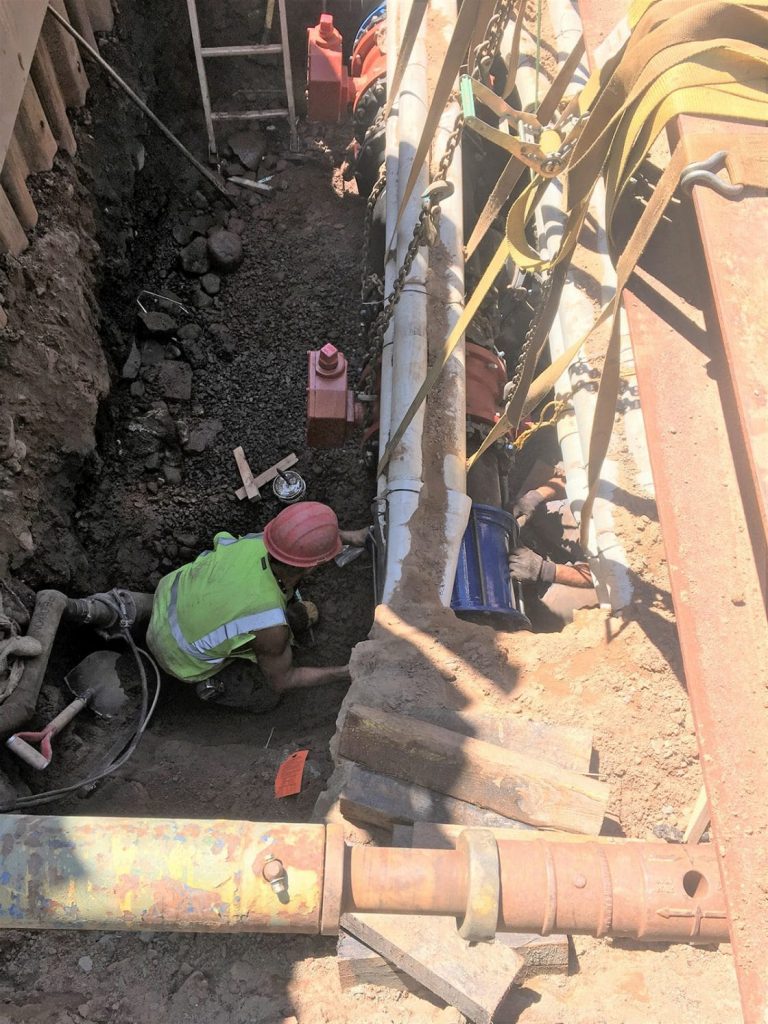
The Wiscasset Water District (WWD) completed its final phase of water main replacements for the Town of Wiscasset, ME. In 2007, Wiscasset, a rural coastal town in Maine, embarked on a long-awaited infrastructure improvement program to replace the Town’s century-old waterlines. The Wiscasset Water District, engaged Tata & Howard’s services in 2010, to prepare a Capital Efficiency Plan™ (CEP), to identify areas to the Town’s water distribution system needing rehabilitation, repair, and/or replacement.
The Capital Efficiency Plan™ report which included hydraulic modeling, system criticality, and an asset management plan, provided the Utility with a database and Geographic Information System (GIS) representation for each pipe segment within their underground piping system. The CEP report also prioritized the water distribution system piping improvements and provided estimated costs to replace or rehabilitate the water mains.
In response to the CEP™ findings, the Wiscasset Water District retained the services of Tata & Howard, to perform design, bidding, construction administration, and resident project representation services for a series of water main projects.

Phased over 10 years, the plan included replacing 33,150 feet of 12-inch and 8-inch piping, installation of a water storage tank mixer, SCADA upgrades, and office landscaping improvements.
The final phase of water main replacements is scheduled to be completed during the summer of 2018 and will fulfill all the Priority I water main improvements identified in the 2010 CEP™ report. The projects were funded in part by a combination of USDA Rural Development grants (6 total) and loans (7 total), as well as coordination with the Maine Department of Transportation and Rural Development.
The final phase of water main replacements that was completed during the summer of 2018 fulfilled all the Priority I water main improvements identified in the 2010 CEP™ report. The projects were funded in part by a combination of USDA Rural Development grants (6 total) and loans (7 total), as well as coordination with the Maine Department of Transportation and Rural Development.