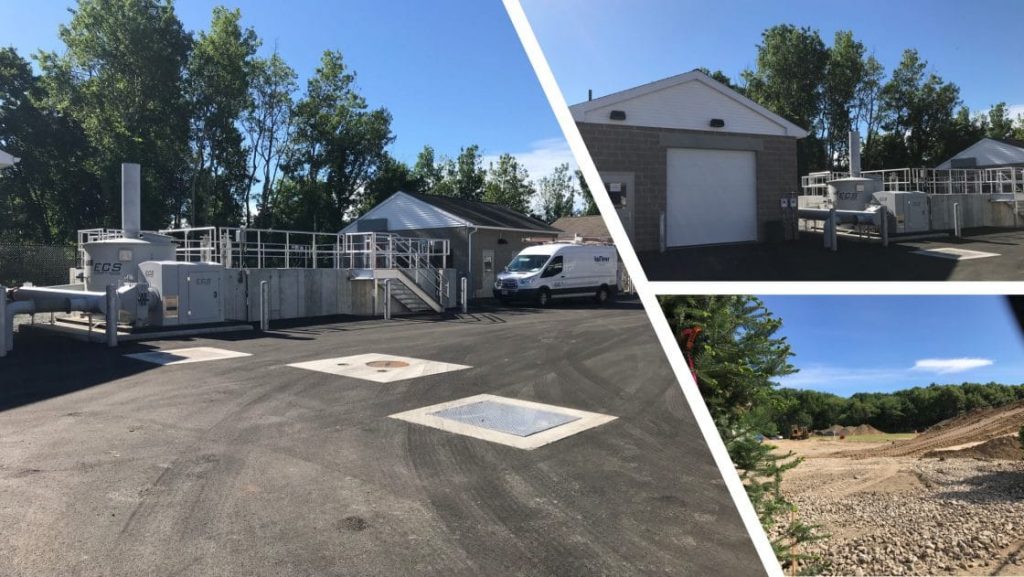
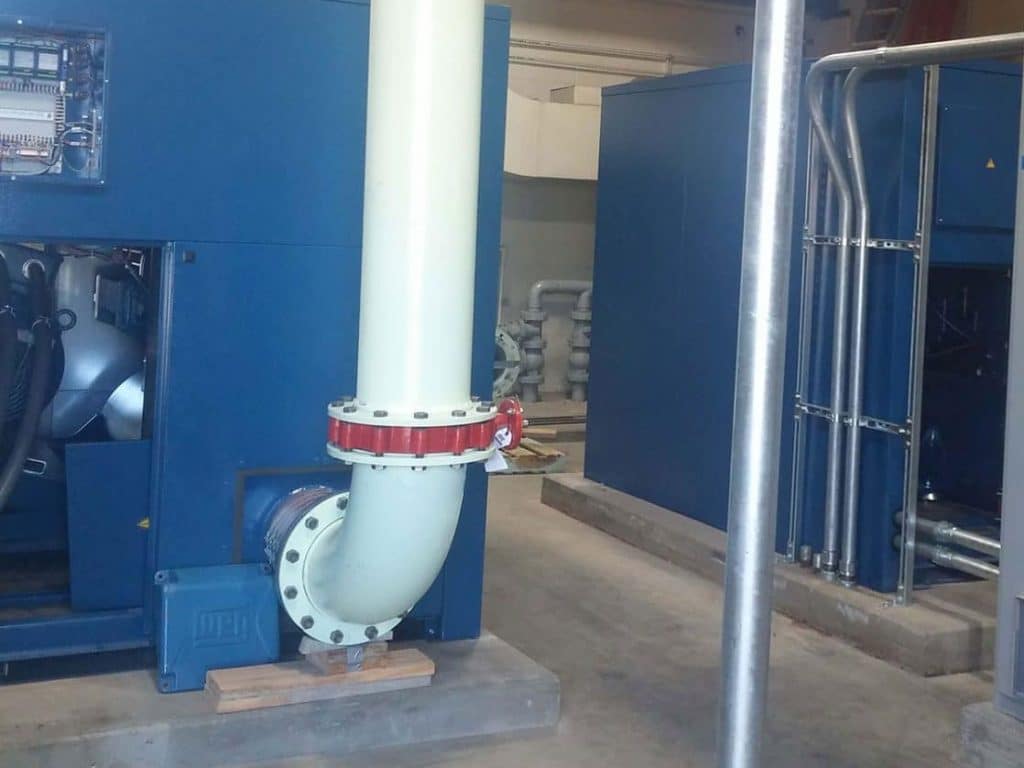
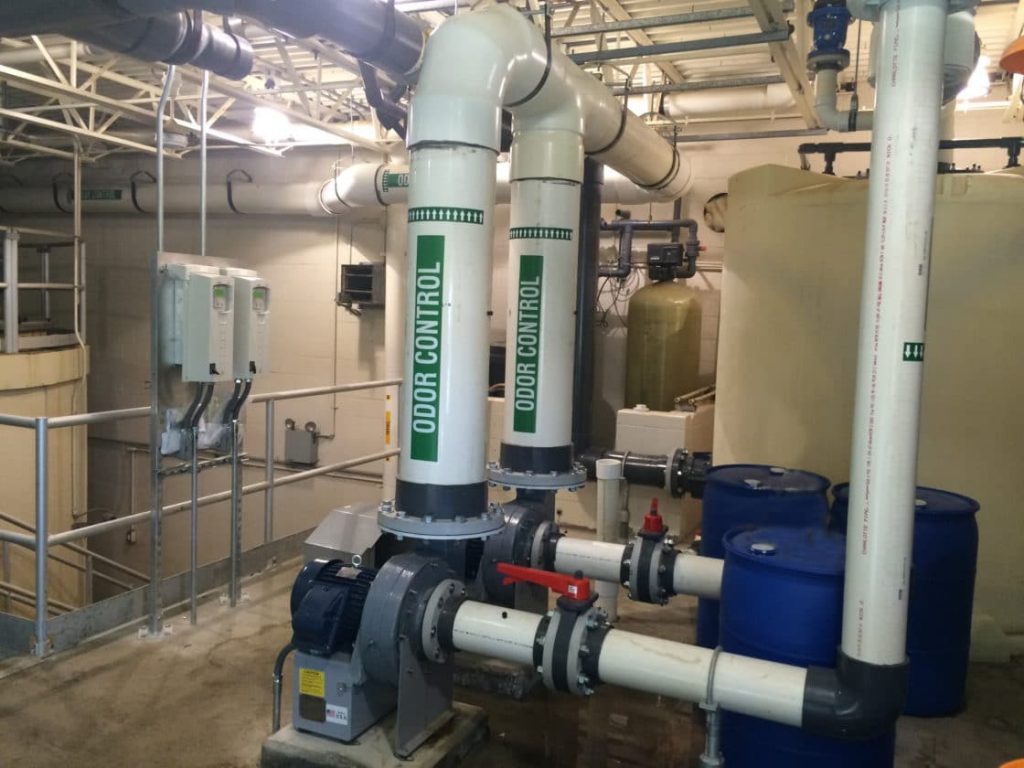
Tata & Howard provided engineering services for final design and construction documents associated with the design of a wastewater treatment facility utilizing membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology for the 50-acre Meadow Walk development at 526-528 Boston Post Road in Sudbury, Massachusetts. The site is a former Raytheon engineering and R&D facility.

Believing the site was well-suited for mixed-use residential and retail development, Sudbury selectmen and residents voted to approve zoning and development plans proposed by National Development and Avalon Bay. The site was in development for two years and is nearing completion. The project consists of several independent components, which collectively comprise a mixed-use development with new open space, retail, and restaurants as well as walkable access to adjacent retail, office, and other services along Boston Post Road. The project also included local roadway improvements, major upgrades to the streetscape and landscaping, wastewater treatment improvements, and improved water quality.
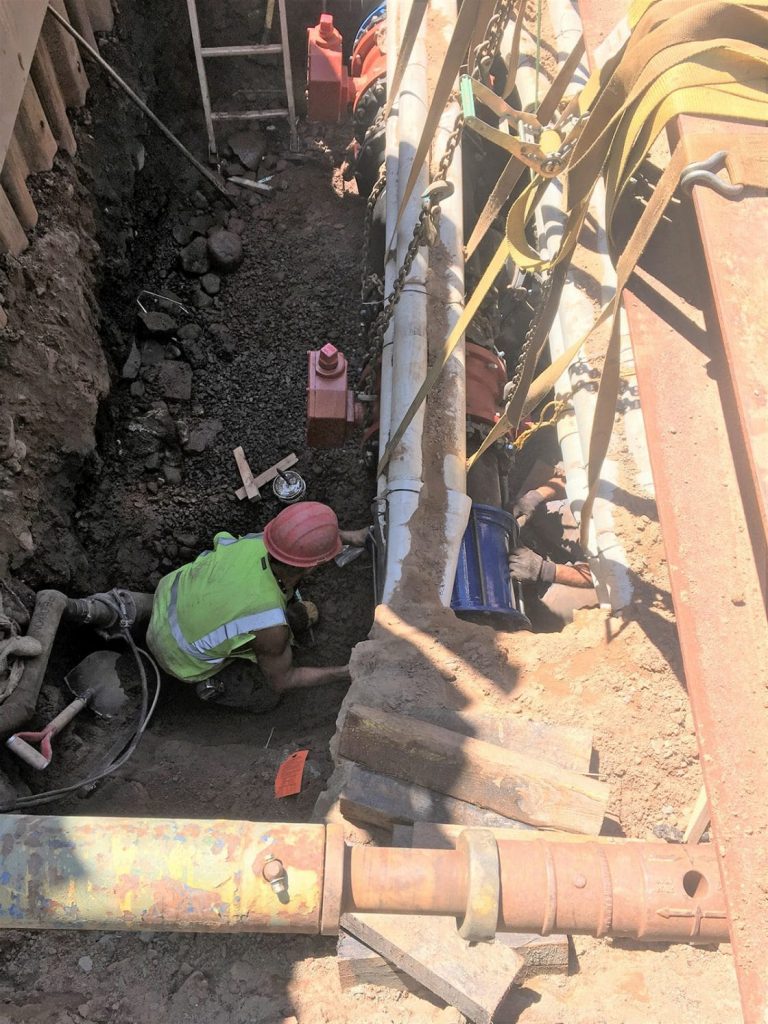
Tata & Howard was contacted initially to prepare studies of existing conditions and proposed modifications to enhance and then upgrade the wastewater facility and disposal area on the site. Additional out-of-scope changes included value engineered alternatives and additional design services. The existing wastewater treatment facility was over 25 years old and required increased discharge limits; conversion to an MBR system to achieve higher removal of BOD, TSS, TN, turbidity, and other wastewater constituents; additional treatment redundancy; upgrades to meet current Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) guidelines; increased groundwater recharge; odor control; replacement of old infrastructure with a new pump station, gravity lines, and force main; a change to mixed land/water use to result in wastewater generation that could be more efficiently treated at the new wastewater treatment facility; and a new leaching field.